『源码阅读』Warp CTC 源码解读
推导简易版本知乎文章:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/43534801
完全版推导过程:https://blog.csdn.net/JackyTintin/article/details/79425866
源码地址:https://github.com/baidu-research/warp-ctc
便利的label稀疏化api讲解博客(官网没有讲解):tf.keras.backend.ctc_label_dense_to_sparse
百度实验室的高效CTC实现,对标tf远古版本1.4,不知道和新版tf实现是不是还有领先,之后会解读一下新版tf的CTC实现方案。
tensorflow_binding\src\warpctc_op.cc:
WarpCTCOpBase::Compute方法
get_workspace_size函数:获取工作区大小
compute_ctc_loss(activations_t.data(), // [max_time, batch_size, num_classes_raw]
grads_t.data(), // [max_time, batch_size, num_classes_raw]
flat_labels_t.data(), // [batch_size, max_time]
label_lengths_t.data(), // [batch_size]
input_lengths_t.data(), // [batch_size]
alphabet_size, batch_size, // int, int
costs_t.data(), // [batch_size]
workspace_t.data(), options); // 内存/显存申请尺寸
/** Compute the connectionist temporal classification loss between a sequence
* of probabilities and a ground truth labeling. Optionally compute the
* gradient with respect to the inputs.
* \param [in] activations pointer to the activations in either CPU or GPU
* addressable memory, depending on info. We assume a fixed
* memory layout for this 3 dimensional tensor, which has dimension
* (t, n, p), where t is the time index, n is the minibatch index,
* and p indexes over probabilities of each symbol in the alphabet.
* The memory layout is (t, n, p) in C order (slowest to fastest changing
* index, aka row-major), or (p, n, t) in Fortran order (fastest to slowest
* changing index, aka column-major). We also assume strides are equal to
* dimensions - there is no padding between dimensions.
* More precisely, element (t, n, p), for a problem with mini_batch examples
* in the mini batch, and alphabet_size symbols in the alphabet, is located at:
* activations[(t * mini_batch + n) * alphabet_size + p]
* \param [out] gradients if not NULL, then gradients are computed. Should be
* allocated in the same memory space as probs and memory
* ordering is identical.
* \param [in] flat_labels Always in CPU memory. A concatenation
* of all the labels for the minibatch.
* \param [in] label_lengths Always in CPU memory. The length of each label
* for each example in the minibatch.
* \param [in] input_lengths Always in CPU memory. The number of time steps
* for each sequence in the minibatch.
* \param [in] alphabet_size The number of possible output symbols. There
* should be this many probabilities for each time step.
* \param [in] mini_batch How many examples in a minibatch.
* \param [out] costs Always in CPU memory. The cost of each example in the
* minibatch.
* \param [in,out] workspace In same memory space as probs. Should be of
* size requested by get_workspace_size.
* \param [in] options see struct ctcOptions
*
* \return Status information
*
* */
API_REFERENCE ctcStatus_t compute_ctc_loss(const float* const activations,
float* gradients,
const int* const flat_labels,
const int* const label_lengths,
const int* const input_lengths,
int alphabet_size,
int minibatch,
float *costs,
void *workspace,
ctcOptions options);
注意:
element (t, n, p), for a problem with mini_batch examples in the mini batch, and alphabet_size symbols in the alphabet, is located at: activations[(t * mini_batch + n) * alphabet_size + p]
src\ctc_entrypoint.cpp:
get_workspace_size函数 compute_ctc_loss函数:此函数决定后面调用CPU实现还是调用GPU实现 cost_and_grad方法:计算梯度 参数:activations, gradients, costs, flat_labels, label_lengths, input_lengths score_forward方法:单纯forward
include\detail\cpu_ctc.h:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/23293860
CpuCTC<ProbT>::cost_and_grad方法 利用OpenMP并行循环batch // const int T = input_lengths[mb]; // const int L = label_lengths[mb]; // const int S = 2*L + 1; // Number of labels with blanks CpuCTC<ProbT>::cost_and_grad_kernel CpuCTC<ProbT>::CpuCTC_metadata CpuCTC<ProbT>::CpuCTC_metadata::setup_labels if (L + ctcm.repeats > T) return 0; // 标签+重复元素数目需要小于有效input长度,重复标签之间需要插入blank符号 CpuCTC<ProbT>::compute_alphas(probs, ctcm.repeats, S, T, ctcm.e_inc, ctcm.s_inc, ctcm.labels_w_blanks, ctcm.alphas); CpuCTC<ProbT>::compute_betas_and_grad
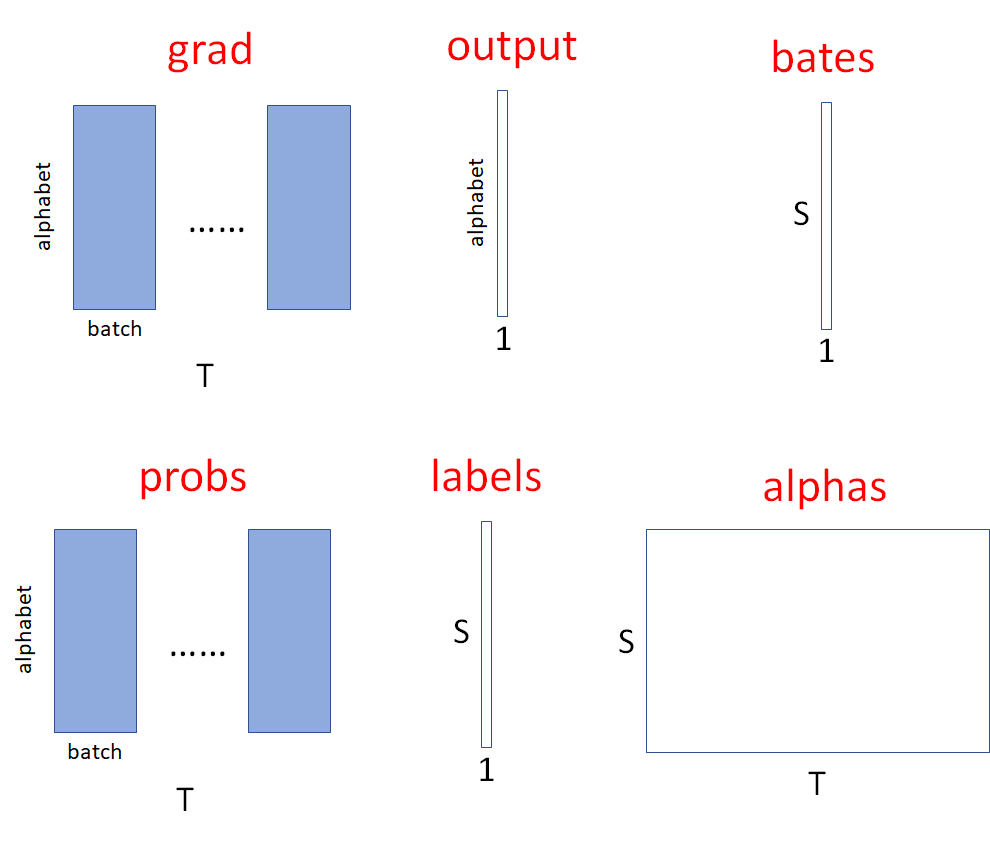
1、cpu下的前向传播
数据probs记录了网络输出的概率,labels用于将alphas中的位置索引到probs对应时刻的概率,这个程序就是在填充alphas,然后根据最后时刻的alpha计算出对数似然。三个主要数据其逻辑形式如下:

S=2*标签长度+1
T为句子长度,或者说timesteps长度
alphabet表示词表长度(实际上为+1,因为包含了blank)
// Computes forward probabilities
template<typename ProbT>
ProbT CpuCTC<ProbT>::compute_alphas(const ProbT* probs, int repeats, int S, int T,
const int* const e_inc,
const int* const s_inc,
const int* const labels,
ProbT* alphas) {
int start = (((S /2) + repeats - T) < 0) ? 0 : 1,
end = S > 1 ? 2 : 1;
for (int i = start; i < end; ++i) {
alphas[i] = std::log(probs[labels[i]]);
}
for(int t = 1; t < T; ++t) {
int remain = (S / 2) + repeats - (T - t);
if(remain >= 0)
start += s_inc[remain];
if(t <= (S / 2) + repeats)
end += e_inc[t - 1];
int startloop = start;
int idx1 = t * S, idx2 = (t - 1) * S, idx3 = t * (alphabet_size_ * minibatch_);
if (start == 0) {
alphas[idx1] = alphas[idx2] + std::log(probs[blank_label_ + idx3]);
startloop += 1;
}
for(int i = startloop; i < end; ++i) {
ProbT prev_sum = ctc_helper::log_plus<ProbT>()(alphas[i + idx2], alphas[(i-1) + idx2]);
// Skip two if not on blank and not on repeat.
if (labels[i] != blank_label_ && i != 1 && labels[i] != labels[i-2])
prev_sum = ctc_helper::log_plus<ProbT>()(prev_sum, alphas[(i-2) + idx2]);
alphas[i + idx1] = prev_sum + std::log(probs[labels[i] + idx3]);
}
}
ProbT loglike = ctc_helper::neg_inf<ProbT>();
for(int i = start; i < end; ++i) {
loglike = ctc_helper::log_plus<ProbT>()(loglike, alphas[i + (T - 1) * S]);
}
return loglike;
}
函数返回最后一个step的结果之和(对数,实际上是相乘),为整个任务的对数似然(loglike)。
其他参量中:remain表示在当前t时刻,至少要到达的有效标签数目(位置索引),start表示当前时刻最慢路径位置,end表示最快路径位置,两者组成的窗表示当前时刻的全部可能位置。
// remain=标签长度+必要的blank分隔符-剩余时间步
int remain = (S / 2) + repeats - (T - t);
if(remain >= 0) start += s_inc[remain]; // s_inc的索引表示本步骤已经完成remain个有效字符
if(t <= (S / 2) + repeats) end += e_inc[t - 1]; // e_inc在0时刻已经完成一个字符,所以t-1时刻已经完成t个有效字符,本时刻将到达t+1个字符
s_inc、e_inc表示每完成当前位置较下一个必要字符(必须要输出的,不是可选的,包含有效字符和重复字符间的blank)需要的步长。start起始位置为第一个空格,s_inc[0]表示从第一个空格到第一个字符的距离1,s_inc[2]表示第一个字符到第二个字符的必要距离2;end起始位置为第一个字符,e_inc[0]表示第一个字符到第二个字符的必要距离2。出现重复字符时(假设重复一次),两者会+2到达第一个位置,然后+1到达空格,再+1到达第二个位置。据此可以构建出s_inc、e_inc两个步长对未扩充标签的函数。start的终点是最后一个有效字符,end终点是最后一个空格。
| 索引 | s[0] | e[0] | s[-1] | e[-1] | |||||||
| label | - | s | - | a | - | t | - | t | - | e | - |
| s_inc | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||
| e_inc | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
由于start是最慢的路径,当前最慢路径到达remain计算出的必要的字符即可;end是最快路径,当前时刻的最快路径是上一时刻最快路径位置的下一有效字符,每一个时刻都要向前到下一个有效字符。
2、cpu下反向传播
包含步骤如下:
计算bate
将alpha*beta更新在alpha矩阵中
对每一时刻计算output(将每一时刻同一字符的概率进行叠加,入satte中每一时刻有2个t)
更新grad矩阵
// Starting from T, we sweep backward over the alpha array computing one column
// of betas as we go. At each position we can update product alpha * beta and then
// sum into the gradient associated with each label.
// NOTE computes gradient w.r.t UNNORMALIZED final layer activations.
// Assumed passed in grads are already zeroed!
template<typename ProbT>
ProbT CpuCTC<ProbT>::compute_betas_and_grad(ProbT* grad, const ProbT* const probs,
ProbT log_partition, int repeats,
int S, int T, const int* const e_inc,
const int* const s_inc,
const int* const labels,
ProbT* alphas,
ProbT* betas,
ProbT* output) {
int start = S > 1 ? (S - 2) : 0,
end = (T > (S / 2) + repeats) ? S : S-1;
std::fill(output, output + alphabet_size_, ctc_helper::neg_inf<ProbT>());
//set the starting values in the beta column at the very right edge
for (int i = start; i < end; ++i) {
betas[i] = std::log(probs[labels[i] + (T - 1) * (alphabet_size_ * minibatch_)]);
//compute alpha * beta in log space at this position in (S, T) space
alphas[i + (T - 1) * S] += betas[i];
//update the gradient associated with this label
//essentially performing a reduce-by-key in a sequential manner
output[labels[i]] =
ctc_helper::log_plus<ProbT>()(alphas[i + (T - 1) * S], output[labels[i]]);
}
//update the gradient wrt to each unique label
for (int i = 0; i < alphabet_size_; ++i) {
int idx3 = (T - 1) * alphabet_size_ * minibatch_ + i;
if (output[i] == 0.0 || output[i] == ctc_helper::neg_inf<ProbT>() ||
probs[idx3] == 0.0) {
grad[idx3] = probs[idx3];
} else {
grad[idx3] = probs[idx3] - std::exp(output[i] -
std::log(probs[idx3]) - log_partition);
}
}
//loop from the second to last column all the way to the left
for(int t = T - 2; t >= 0; --t) {
int remain = (S / 2) + repeats - (T - t);
if(remain >= -1)
start -= s_inc[remain + 1];
if(t < (S / 2) + repeats)
end -= e_inc[t];
int endloop = end == S ? end - 1 : end;
int idx1 = t * S, idx3 = t * (alphabet_size_ * minibatch_);
std::fill(output, output + alphabet_size_, ctc_helper::neg_inf<ProbT>());
for(int i = start; i < endloop; ++i) {
ProbT next_sum = ctc_helper::log_plus<ProbT>()(betas[i], betas[(i+1)]);
// Skip two if not on blank and not on repeat.
if (labels[i] != blank_label_ && i != (S-2) && labels[i] != labels[i+2]){
next_sum = ctc_helper::log_plus<ProbT>()(next_sum, betas[(i+2)]);
}
betas[i] = next_sum + std::log(probs[labels[i] + idx3]);
//compute alpha * beta in log space
alphas[i + idx1] += betas[i];
//update the gradient associated with this label
output[labels[i]] =
ctc_helper::log_plus<ProbT>()(alphas[i + idx1], output[labels[i]]);
}
if (end == S) {
betas[(S-1)] = betas[(S-1)] + std::log(probs[blank_label_ + idx3]);
alphas[(S-1) + idx1] += betas[(S-1)];
output[labels[S-1]] =
ctc_helper::log_plus<ProbT>()(alphas[S-1 + idx1], output[labels[S-1]]);
}
//go over the unique labels and compute the final grad
// wrt to each one at this time step
for (int i = 0; i < alphabet_size_; ++i) {
if (output[i] == 0.0 || output[i] == ctc_helper::neg_inf<ProbT>() ||
probs[idx3] == 0.0) {
grad[idx3] = probs[idx3];
} else {
grad[idx3] = probs[idx3] - std::exp(output[i] -
std::log(probs[idx3]) - log_partition);
}
++idx3;
}
}
ProbT loglike = ctc_helper::neg_inf<ProbT>();
for(int i = start; i < end; ++i) {
loglike = ctc_helper::log_plus<ProbT>()(loglike, betas[i]);
}
return loglike;
}
include\detail\gpu_ctc.h
GpuCTC<ProbT>::cost_and_grad(const ProbT* const activations,
ProbT* grads,
ProbT* costs,
const int* const flat_labels,
const int* const label_lengths,
const int* const input_lengths)
GpuCTC<ProbT>::compute_cost_and_score(const ProbT* const activations,
ProbT* grads,
ProbT* costs,
const int* const flat_labels,
const int* const label_lengths,
const int* const input_lengths,
bool compute_alpha,
bool compute_betas_and_grad)
GpuCTC<ProbT>::create_metadata_and_choose_config(const int* const flat_labels,
const int* const label_lengths,
const int* const input_lengths,
size_t& best_config)
GpuCTC<ProbT>::setup_gpu_metadata(const int* const flat_labels,
const int* const label_lengths,
const int* const input_lengths)
// 计算辅助参数,并将其注册到gpu上
// 主要信息为batch的input_lengths、label_lengths、flat_labels,以及labels的索引用偏移个每个label的repeat信息
// activation_cols_ = minibatch_ * Tmax;
// 依据S_(batch中最长有效标签长度)在几个预定义config中找到最小的有效config
GpuCTC<ProbT>::compute_probs(const ProbT* const activations)
// 将probs(网络输出)存入gpu,每行为词表长度(实际上是一维向量,这里取义)
reduce_max 计算每行最大值
prepare_stable_SM_kernel 将probs更新为和对应行最大值的差值
reduce_exp 获取每行的指数和(即softmax分母,前面的做差是为了数值稳定)
compute_probs_kernel 各个位置除以分母
truncate_probs_kernel 最小值截断,防止数值问题
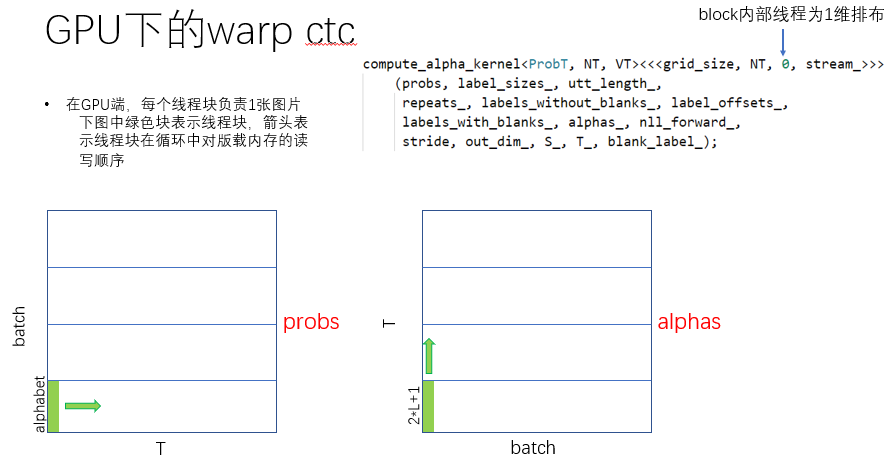
1、GPU下的前向传播:compute_alphas
相关参数说明:






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号