spring源码解析之IOC容器(一)
学习优秀框架的源码,是提升个人技术水平必不可少的一个环节。如果只是停留在知道怎么用,但是不懂其中的来龙去脉,在技术的道路上注定走不长远。最近,学习了一段时间的spring源码,现在整理出来,以便日后温故知新。
IOC容器是spring最核心的模块之一,是整个spring体系的基石,spring其他模块中,都需要用到IOC容器的功能。spring框架为我们提供了多种IOC容器,DefaultableBeanFact
ory、FileSystemXmlApplicationContext、ClassPathXmlApplicationContext、XmlWebApplicationContext等。虽然我们平时很少在项目中使用这种硬编码的方式来获取IOC容器,继而获取IOC容器中的bean,但是研究这些IOC容器的源码,对我们理解IOC容器的原理还是很有必要的。BeanFactory这个接口是spring所有IOC容器最上层的接口,getBean()这个方法就是在这个接口中定义的,下面是其中定义的方法:
1 public interface BeanFactory { 2 Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException; 3 <T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException; 4 Object getBean(String name, Object... args) throws BeansException; 5 <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException; 6 <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType, Object... args) throws BeansException; 7 boolean containsBean(String name); 8 boolean isSingleton(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; 9 boolean isPrototype(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; 10 boolean isTypeMatch(String name, ResolvableType typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; 11 boolean isTypeMatch(String name, Class<?> typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; 12 Class<?> getType(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; 13 String[] getAliases(String name); 14 }
可以看到其中定义了获取bean的多种方式,和各种对bean的判断,以及获取bean的类型和别名的方法。这个接口是spring框架IOC容器的入口。下面以FileSystemXmlApplicatio
nContext为例,深入源码探究IOC容器的实现原理。IOC容器的初始化过程分为三个阶段:定位、载入和注册。接下来一一进行分析,先从XML的定位开始。
相信我们大家都使用以下代码获取过IOC容器,获取IOC容器之后,我们就可以得到想要的bean,然后进行操作了:
1 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext context = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
进入FileSystemXmlApplicationContext这个类,发现它定义了各种构造器,但最终都会调用下面这个构造器:
1 public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent) 2 throws BeansException { 3 4 super(parent); 5 setConfigLocations(configLocations); 6 if (refresh) { 7 refresh(); 8 } 9 }
在分析它的流程之前,有必要给一下它的UML图,上面标注了它的继承体系结构:
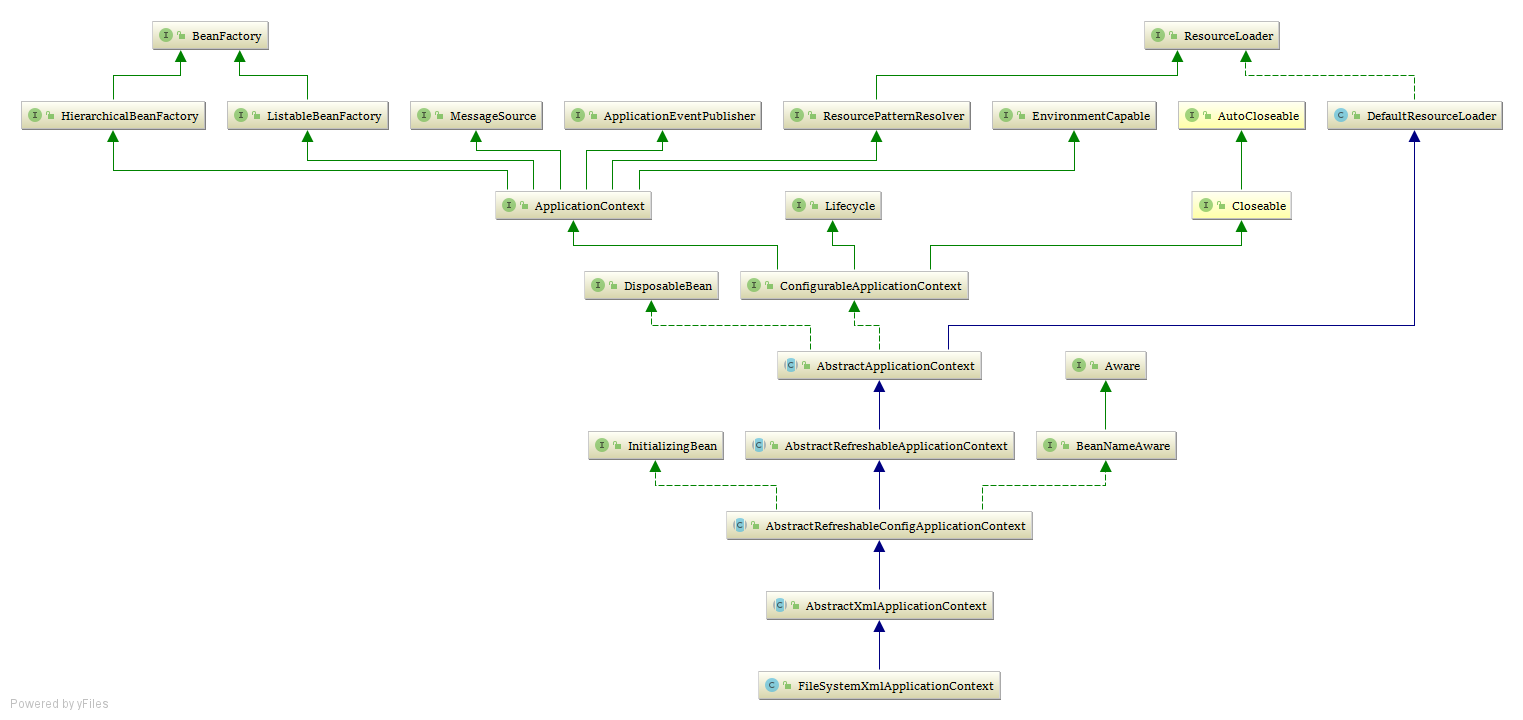
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的构造器中有个重要的方法refresh(),这是IOC容器的启动方法,在它的父类AbstractXmlApplicationContext中有实现,其代码如下:
1 @Override 2 public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { 3 synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { 4 // Prepare this context for refreshing. 5 //准备要进行刷新的上下文对象 6 //例如对系统环境进行准备和验证 7 prepareRefresh(); 8 9 // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. 10 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); 11 12 // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. 13 prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); 14 15 try { 16 // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. 17 postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); 18 19 // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. 20 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); 21 22 // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. 23 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); 24 25 // Initialize message source for this context. 26 initMessageSource(); 27 28 // Initialize event multicaster for this context. 29 initApplicationEventMulticaster(); 30 31 // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. 32 onRefresh(); 33 34 // Check for listener beans and register them. 35 registerListeners(); 36 37 // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. 38 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); 39 40 // Last step: publish corresponding event. 41 finishRefresh(); 42 } 43 44 catch (BeansException ex) { 45 if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { 46 logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + 47 "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); 48 } 49 50 // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. 51 destroyBeans(); 52 53 // Reset 'active' flag. 54 cancelRefresh(ex); 55 56 // Propagate exception to caller. 57 throw ex; 58 } 59 60 finally { 61 // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we 62 // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... 63 resetCommonCaches(); 64 } 65 } 66 }
进入obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法,其代码如下:
1 protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() { 2 refreshBeanFactory(); 3 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); 4 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 5 logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory); 6 } 7 return beanFactory; 8 }
继续跟,进入refreshBeanFactory()方法,在父类AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext中有实现,其代码如下:
1 @Override 2 protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException { 3 if (hasBeanFactory()) { 4 destroyBeans(); 5 closeBeanFactory(); 6 } 7 try { 8 //创建DefaultListableBeanFactory 9 DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory(); 10 //指定序列化的id,所以,如果需要反序列化这个BeanFactory,则可以直接根据这个id来进行反序列化 11 beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId()); 12 //定制化 13 customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory); 14 //初始化DocumentReader,读取XML 15 loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); 16 synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) { 17 this.beanFactory = beanFactory; 18 } 19 } 20 catch (IOException ex) { 21 throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex); 22 } 23 }
这段代码可以看到:
1、首先,创建了一个DefaultListableBeanFactory的IOC容器;
2、对容器进行了一些设置;
3、调用loadBeanDefinitions()方法对XML文件进行定位和加载。
所以,进入loadBeanDefinitions()方法继续探索,在类AbstractXmlApplicationContext中有实现,它是FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的父类,其代码如下:
1 protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException { 2 // Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory. 3 XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory); 4 5 // Configure the bean definition reader with this context's 6 // resource loading environment. 7 beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment()); 8 beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this); 9 beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this)); 10 11 // Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader, 12 // then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions. 13 initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader); 14 loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader); 15 }
这个方法中,使用XmlBeanDefinitionReader类来加载XML文件,最后经过一系列的设置,调用了loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader)这个方法,进入:
1 protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException { 2 Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources(); 3 if (configResources != null) { 4 reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources); 5 } 6 String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations(); 7 if (configLocations != null) { 8 reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations); 9 } 10 }
跟到这里,到底是走哪个方法呢?我们再回过头看一下,FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的那个构造器,其中有个setConfigLocations(configLocations)方法,通过这个方法将我们配置的XML文件的路径设置进来了,跟代码,发现它调用的是父类的方法,并将路径赋给了AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext类中的configLocations成员变量,而getConfigLocations()方法也是AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext类中的,它正好获取了configLocations的值,所以configLocations一定不为null,上面方法应该走下面的loadBeanDefinitions()方法。跟进,其代码如下:
1 public int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 2 Assert.notNull(locations, "Location array must not be null"); 3 int counter = 0; 4 for (String location : locations) { 5 counter += loadBeanDefinitions(location); 6 } 7 return counter; 8 }
1 public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 2 return loadBeanDefinitions(location, null); 3 }
1 public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, Set<Resource> actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 2 ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader(); 3 if (resourceLoader == null) { 4 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( 5 "Cannot import bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available"); 6 } 7 8 if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) { 9 // Resource pattern matching available. 10 try { 11 Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location); 12 int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resources); 13 if (actualResources != null) { 14 for (Resource resource : resources) { 15 actualResources.add(resource); 16 } 17 } 18 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 19 logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]"); 20 } 21 return loadCount; 22 } 23 catch (IOException ex) { 24 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( 25 "Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", ex); 26 } 27 } 28 else { 29 // Can only load single resources by absolute URL. 30 Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location); 31 int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resource); 32 if (actualResources != null) { 33 actualResources.add(resource); 34 } 35 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 36 logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location [" + location + "]"); 37 } 38 return loadCount; 39 } 40 }
这里先得到一个ResourceLoader对象。在类AbstractXmlApplicationContext中的loadBeanDefinitions()方法中有beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this)这段代码,而
DefaultListableBeanFactory又是继承了DefaultResourceLoader的,所以,这里的resourceLoader对象是DefaultResourceLoader类型的,所以走下面的逻辑。首先,获取一个resource
对象,getResource方法在DefaultResourceLoader中有实现,其代码如下:
1 public Resource getResource(String location) { 2 Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null"); 3 4 for (ProtocolResolver protocolResolver : this.protocolResolvers) { 5 Resource resource = protocolResolver.resolve(location, this); 6 if (resource != null) { 7 return resource; 8 } 9 } 10 11 if (location.startsWith("/")) { 12 return getResourceByPath(location); 13 } 14 else if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) { 15 return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader()); 16 } 17 else { 18 try { 19 // Try to parse the location as a URL... 20 URL url = new URL(location); 21 return new UrlResource(url); 22 } 23 catch (MalformedURLException ex) { 24 // No URL -> resolve as resource path. 25 //如果都不是,则使用子类重写的方法,例如子类FileSystemXMLApplicationContext中就重写了这个方法 26 return getResourceByPath(location); 27 } 28 } 29 }
根据不同的情况,生成一个ResourceLoader对象,这样就完成了对配置的xml文件的定位。
经过这么一长条的跟踪,终于完成了XML资源的定位工作。spring的继承体系特别深,刚开始的时候感觉特别绕,但是多跟着代码跟几遍,基本就清晰了,关键是要有耐心。在上面的分析中,我们发现,spring使用了很多的模板方法,比如getResource方法,还有就是单一职责原则,每个类很清晰,每个方法中都是一个一个方法的调用,而不是代码的堆砌,这点是值得我们平时好好学习和运用的。



