java se系列(三) 顺序语句、if...else、switch、While、do-while、for、break、continue
1 顺序语句
语句:使用分号分隔的代码称作为一个语句。

注意:没有写任何代码只是一个分号的时候,也是一条语句,称作空语句。

顺序语句就是按照从上往下的顺序执行的语句。
2 判断(if…else)
什么是判断语句:用于判断的语句叫判断语句。
1.格式一
if(判断条件){
如果符合条件执行的代码;
执行的代码块1;
执行的代码块2;
……………….;
执行的代码块n;
}
练习:提示用户输入一个整数。如果该整数是5的倍数,打印“5的倍数”,如果是2的倍数打印“2的倍数”
提示:为了便于让用户输入数据,我们使用Scanner这个类,固定用法Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); 该类需要导入包import java.util.Scanner;
int nextInt = sc.nextInt();获取用户输入的数字
1 import java.util.Scanner;
2
3 public class Demo9 {
4 public static void main(String[] args) {
5
6 Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
7 int nextInt = sc.nextInt();
8
9 if(nextInt%5==0){
10 System.out.println("是5的倍数");
11 }
12 if(nextInt%2==0){
13 System.out.println("是2的倍数");
14 }
15 }
16 }
2.格式二
if(判断条件){
执行的代码块1;
执行的代码块2;
……………….;
执行的代码块n;
}else{
执行的代码块1;
执行的代码块2;
……………….;
执行的代码块n;
}
案例:判断一个整数是奇数还是偶数
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2
3 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
4 System.out.println("请输入一个整数:");
5 int nextInt = sc.nextInt();
6
7 if (nextInt % 2 == 0) {
8 System.out.println("是偶数");
9 } else {
10 System.out.println("是奇数");
11 }
12
13 System.out.println("over");
14 }
同样道理,如果花括号中只有一条语句,那么花括号可以省略不写,初学者不推荐省略。
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2
3 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
4 System.out.println("请输入一个整数:");
5 int nextInt = sc.nextInt();
6
7 if (nextInt % 2 == 0)
8 System.out.println("是偶数");
9 else
10 System.out.println("是奇数");
11
12 System.out.println("over");
13 }
观察发现if else语句有点类似于三元运算符.其实三元运算符是if else 的一种简写格式.
1 Public static void main(String[] args) {
2
3 int x = 0, y = 1, b;
4
5 // if else 语句
6 if (x > y) {
7 b = x;
8 } else {
9 b = y;
10 }
11
12 System.out.println(b);// 1
13
14 // 3元运算
15 b = x > y ? x : y;
16 System.out.println(b); // 1
17 }
这两种格式是一样的。if else 结构 简写格式: 变量 = (条件表达式)?表达式1:表达式2;
三元运算符:
好处:可以简化if else代码。
弊端:因为是一个运算符,所以运算完必须要有一个结果。
3.格式三
if(判断条件1){
执行的代码块1;
}else if(判断条件2){
执行语句;
}else if(判断条件3){
执行语句;
}
需求: 根据用户定义的数值不同,打印对应的星期英文。if 只能进行一层判断,if else 只能进行两层判断,那么需要多层判断时呢?星期可是有7个数的。如何设计代码?使用if 语句
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2
3 int x = 8;
4
5 if (x == 1) {
6 System.out.println("星期一");
7 }
8 if (x == 2) {
9 System.out.println("星期二");
10 }
11 if (x == 3) {
12 System.out.println("星期三");
13 }
14 }
如果这样设计的话,第一个if语句执行完毕后,第二个语句仍会执行(去判断),是一个顺序结构.那么事实上当前定义的星期之后会有一个.假如,第一个已经符合条件,那么剩余的执行就没有意义了。属于逻辑错误。
用if else ,如果用户输入的是7以外的数据,那么怎么处理?就需要使用else 了
方案2:使用if else if语句
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 int x = 8;
3 if (x == 1) {
4 System.out.println("星期一");
5 } else if (x == 2) {
6 System.out.println("星期二");
7 } else if (x == 3) {
8 System.out.println("星期三");
9 } else if (x == 4) {
10 System.out.println("星期四");
11 } else if (x == 5) {
12 System.out.println("星期五");
13 } else if (x == 6) {
14 System.out.println("星期六");
15 } else if (x == 7) {
16 System.out.println("星期日");
17 } else {
18 System.out.println("请输入数字1-7");
19 }
20 }
注意:
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 int x = 5;
3 if (x == 1) {
4 System.out.println("1");
5 }
6 if (x == 2) {
7 System.out.println("2");
8 }
9 if (x == 3) {
10 System.out.println("3");
11 } else {
12 System.out.println("4"); // 4
13 }
14 }
该if 语句不是一个整体,第一个if 是一个语句,第二个又是一个语句,最后的if else 又是一个语句。
if语句特点
- 第二种格式与三元运算符的区别:三元运算符运算完要有值出现。好处是:可以写在其他表达式中。
- 条件表达式无论写成什么样子,只看最终的结构是否是true 或者 false。
练习1:根据用户输入的月份,打印出月份所属的季节.
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 int x = 1;
3 if (x == 3) {
4 System.out.println("spring");
5 } else if (x == 4) {
6 System.out.println("spring");
7 }
8 }
仔细观察:发现if和else if要执行的语句是一样的,可不可以合并呢。当然是可以的。怎么合并?使用逻辑运算符,那么使用哪个逻辑运算符呢, &肯定不行。需要全部为真才为真,月份是不可能同时满足的 那么使用|连接符号即可。意思只要其中一个为真,就为真。另外可以使用短路功能。
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 int x = 1;
3 if (x == 3 || x == 4 || x == 5) {
4 System.out.println("spring");
5 } else if (x == 6 || x == 7 || x == 8) {
6 System.out.println("Summer");
8 } else if (x == 9 || x == 10 || x == 11) {
9 System.out.println("autumn");
10 } else if(x == 12 || x == 1 || x == 2){
11 System.out.println("Winter");
12 } else {
13 System.out.println("月份不存在");
14 }
15 }
练习2:根据用户输入的成绩,进行评级,根据学生考试成绩划分ABCD
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
3 System.out.println("请输入考试分数:");
4 double score = sc.nextDouble();
5 char grade;
6 if (score >= 90.0)
7 grade = 'A';
8 else if (score >= 80.0)
9 grade = 'B';
10 else if (score >= 70.0)
11 grade = 'C';
12 else if (score >= 60.0)
13 grade = 'D';
14 else
15 grade = 'F';
16 System.out.println("你的成绩是:" + grade);
18 }
If语句常见的错误:
1.忘记必要的括号:如果代码块中只有一条语句的时候,可以省略花括号,但是当花括号将多条语句扩在一起时,花括号就不能在省略。
1 double radius = 4;
2 double area;
3 if (radius >= 0)
4 area = radius * radius * 3.14;//编译报错,area未初始化
5 System.out.println("The area " + " is " + area);
6
7 double radius = 4;
8 double area;
9 if (radius >= 0) {
10 area = radius * radius * 3.14;
11 System.out.println("The area " + " is " + area);
12 }
虽然代码一样多,但是第一个会编译报错(area没有出初始化),第二个正常运行。就是因为少了花括号。所以一定要仔细。
2.if语句后出现分号
1 double radius = 0;
2 double area;
3
4 if (radius > 0); {
5 area = radius * radius * 3.14;
6 System.out.println("The area " + " is " + area);
7 }
相当于判断符合条件后,执行一个空语句。
1 double radius = 0;
2 double area;
3
4 if (radius > 0){}{
5 area = radius * radius * 3.14;
6 System.out.println("The area " + " is " + area);
7 }
判断闰年
1:什么是闰年?可以被4整除不能被100整除,或者可以被400整除,那么这一年就是闰年(leap year)
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
3 System.out.println("请输入年份:");
4
5 int year = sc.nextInt();
6 // 判断年份能否被4整除
7 boolean isLeapYear = (year % 4 == 0);
8 // 年份能被4整除,并且不能被100整除并且使用&&(and)
9 isLeapYear = isLeapYear && (year % 100 != 0);
10 // 年份或者能够被400整除
11 isLeapYear = isLeapYear || (year % 400 == 0);
12 if (isLeapYear) {
13 System.out.println(year + "是闰年!");
14 }
15 // 简写格式;
16 if (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 || year % 400 == 0) {
17 System.out.println(year + "是闰年!");
18 }
19 }
3 选择判断语句(switch)
switch语句,格式:
1 switch(表达式) 2 { 3 case 取值1: 执行语句; break; 4 case 取值2: 执行语句; break; 5 …... 6 default: 执行语句; break; 7 }
switch语句特点:
1,switch语句选择的类型只有四种:byte,short,int , char。
2,case之间与default没有顺序。先判断所有的case,没有匹配的case执行default。
3,switch语句停止的条件是遇到了break关键字或者结束switch语句的大括号。
4,如果匹配的case或者default没有对应的break,那么程序会继续向下执行,运行可以执行的语句,直到遇到break或者switch结尾结束。
5,switch case中的值必须要与switch表达式的值具有相同的数据类型。而且case后跟的值必须是常量,不能跟变量。
案例:
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 int x = 3;
3 switch (x) {
4 case 1: System.out.println("1"); break;
5 case 2: System.out.println("2"); break;
6 case 3: System.out.println("3"); break;
7 default: System.out.println("ok");break;
8 }
9 }
case 就像选择题的答案之一。 break 就是如果该答案正确那么就可以跳出switch 了,意思就是说 已经找出了正确的答案了。那么这道题也就做完了。如果 case 没有匹配接着进行下一个case 匹配,直到匹配为止。 最后如果都没有匹配上,那么 switch 给提供了一个默认的答案,就是 default。
注意: ①case后跟的是冒号:
②每个case中的执行语句一定要加break;
练习:需求2:根据指定的月份,打印该月份所属的季节.
一旦case匹配,就会顺序执行后面的程序代码,而不管后面的case是否匹配,直到遇见break,利用这一特性可以让好几个case执行统一语句.
345 spring 678 sunmer 9 10 11 autumn 12 1 2 winter
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 int x = 3;
3 switch (x) {
4 case 3:
5 case 4:
6 case 5: System.out.println("spring"); break;
7 case 6:
8 case 7:
9 case 8: System.out.println("sunmer"); break;
10 case 9:
11 case 10:
12 case 11: System.out.println("autumn"); break;
13 case 12:
14 case 0:
15 case 1: System.out.println("winter");
16 default: System.out.println("ok"); break;
17 }
18 }
练习:char 类型在switch 中的使用.
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 int x = 1, y = 2;
3 char ch = '*';
4 switch (ch) {
5 case '+': System.out.println("x*y=" + (x + y)); break;
6 case '-': System.out.println("x-y="+(x-y)); break;
7 case '*': System.out.println("x*y="+(x*y)); break;
8 case '/': System.out.println("x/y="+(x/y)); break;
9 default: System.out.println("不靠谱");
10 }
11 }
if 和switch 语句很像,具体什么场景下,应用哪个语句呢?
如果判断的具体数值不多,而是符号byte,short int char 四种类型。虽然2个语句都可以使用,建议使用switch语句.因为效率稍高.
其他情况:对区间判断,对结果为boolean 类型判断,使用if,if的使用范围更广。
if 除了能判断具体数值还能判断区间。switch 判断区间会很费劲的。要写好多case 对于运算结果是boolean型的 if 能判断 switch 是不能实现的。例如:根据学生考试成绩划分ABCD A90-100 B80-89 C70-79 D60-69 E0-59。
实际开发怎么选择呢?
如果要对具体数值进行判断,并且数值不多,那么 就用switch 来完成。switch的case条件都是编译期整数常量,编译器可以做到表格跳转查询,查找速度快。但是switch 的局限性比较大,必须是4种类型,并且值不多。一般都是使用if。 最后在jdk 7中对switch 进行了增强 还可以判断字符串。5.0 增加了对枚举的判断。
备注:JDK7.0开始可以使用switch可以使用字符串类型的数据了.
4 While循环
需求:需要打印一行字符串"hello world",100次
需要将该语句打印100遍System.out.println("hello world");那么如何解决该问题?Java提供个一个称之为循环的结构,用来控制一个操作的重复执行。
1 int count = 0;
2 while (count < 100) {
3 System.out.println("hello world");
4 count++;
5 }
6 System.out.println("over");
变量count初始化值为0,循环检查count<100 是否为true,如果为true执行循环体(while后{}之间的语句),输出"hello world"语句,然后count自增一,重复循环,直到count是100时,也就是count<100为false时,循环停止。执行循环之后的下一条语句。
Java提供了三种类型的循环语句:while循环,do-while循环和for循环。
1 //while语句格式:
2 while(条件表达式)
3 {
4 执行语句;
5 }
定义需求: 想要打印5次helloworld
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 System.out.println("hello world");
3 System.out.println("hello world");
4 System.out.println("hello world");
5 System.out.println("hello world");
6 System.out.println("hello world");
7 }
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 int x = 0;
3 while (x < 5) {
4 System.out.println("hello java ");
5 }
6 }
如果是在dos里编译和运行,是不会停止,除非系统死机。需要ctrl+c来结束。这就是真循环或者死循环。因为x<5 永远为真。
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 int x = 0;
3 while (x < 5) {
4 System.out.println("hello java ");
5 x++;
6 }
7 }
让x自增,那么就会有不满足条件的时候。循环就会结束。
练习:想要打印出1-100之间的奇数
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 int x = 1;
3 while (x < 100) {
4 System.out.println(x);
5 x = x + 2;
6 }
7 }
1 public static void main(String[] args){
2 int x=1;
3 while(x<100){
4
5 if(x%2!=0){
6 System.out.print(x);
7 }
8 x++;
9 }
10 System.out.println();
11 }
练习2:计算1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9 的值
1 int sum = 0;
2 int i = 1;
3
4 while (i < 10) {
5 sum = sum + i;
6 i++;
7 }
8
9 System.out.println(sum);
注意:要精确控制循环的次数。
常犯错误是是循环多执行一次或者少执行一次。例如会执行101次,想要执行100次,要么是count初始值为1,然后count<=100,要么是count初始值为0,coung<100
1 int count = 0;
2
3 while (count <=100) {
4 System.out.println("hello gzitcast");
5 count++;
6 }
7
8 System.out.println("over");
猜数字游戏:
编写程序随即生成一个0-100之间的随机数。程序提示用户输入一个数字,不停猜测,直到猜对为止。最后输出猜测的数字,和猜测的次数。并且如果没有猜中要提示用户输入的值是大了还是小了。
思考:如何生成1-100之间随机数?
(int)(Math.random()*100)+1;
如何提示用户输入数字,
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int guessNum = sc.nextInt();
需要将随机数和用户输入的数字进行比较。
猜一次:
1 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
2 int num = (int)(Math.random()*100)+1;// 随机数
3 System.out.println("请输入0-100之间整数");
4 int guessNum = sc.nextInt();
5
6 if (guessNum == num) {
7 System.out.println("中啦");
8 } else if (guessNum < num) {
9 System.out.println("小啦");
10 } else {
11 System.out.println("大了");
12 }
这个程序只能才一次,如何让用户重复输入直到猜对?,可以使用while循环
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 int num = (int)(Math.random()*100)+1;//随机数
3 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
4 while (true) {
5 System.out.println("请输入1-100之间整数");
6 int guessNum = sc.nextInt();
7 if (guessNum == num) {
8 System.out.println("中啦");
9 } else if (guessNum < num) {
10 System.out.println("小啦");
11 } else {
12 System.out.println("大了");
13 }
14 }
15 }
该方案发现了问题,虽然实现了让用户不停的输入,但是即使猜中了程序也不会停止。那么就需要控制循环次数了。也就是while() 括号中的条件表达式。当用户猜测的数和系统生成的数字不相等时,就需要继续循环。
1 int num = (int)(Math.random()*100)+1;
2 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
3
4 int guessNum = -1;
5 while (guessNum != num) {
6 System.out.println("请输入1-100之间整数");
7 guessNum = sc.nextInt();
8 if (guessNum == num) {
9 System.out.println("中啦");
10 } else if (guessNum < num) {
11 System.out.println("小啦");
12 } else {
13 System.out.println("大了");
14 }
15 }
为什么将guessNum初始化值为-1?因为如果初始化为0到100之间程序会出错,因为可能是要猜的数。
1:首先程序生成了一个随机数
2:用户输入一个数字
3:循环检查用户数字和随机数是否相同,知道相同位置,循环结束
5 do while 语句
do while语句格式:
1 do
2 {
3 执行语句;
4 }while(条件表达式);
5
6 //do while特点是条件无论是否满足,循环体至少被执行一次。
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 int x = 0, y = 0;
3 do {
4 System.out.println(x);
5 x++;
6 } while (x < 0);
7 // do while do会先执行一次,不管是否满足循环条件。
8 while (y < 0) {
9 System.out.println(y);
10 y++;
11 }
12 }
while:先判断条件,只有条件满足才执行循环体。
do while: 先执行循环体,再判断条件,条件满足,再继续执行循环体,至少会执行一次。
简单一句话:
do while:无论条件是否满足,循环体至少执行一次。
注意一个细节:do while 后面有分号“;”
案例:改写猜数字游戏
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 // 记录用户输入的数字
3 int guess = -1;
4 // 记录用户输入次数
5 int count = 0;
6 // 生成1-100之间随机数
7 int num = (int)(Math.random()*100)+1;
8 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
9
10 // 循环猜数字
11 do {
12 System.out.println("请输入1-100之间的数字");
13 guess = sc.nextInt();
14 if (guess > num) {
16 System.out.println("太大了");
17 } else if (guess < num) {
19 System.out.println("太小了");
20 } else {
22 System.out.println("中啦");
23 }
24 count++;
26 } while (num != guess);
27 System.out.println("你猜测的数字是:" + num + "猜测了" + count + "次");
28 }
案例:计算器,系统自动生成2个随机数用于参与运算。
系统生成0-4之间的随机数,表示加减乘除取模运算。使用switch 进行匹配
1 class Couter {
2 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
3 // 生成随机数Math.random()生成0-1值,不包含0和1,
4 //乘以10得到0和10之间的数(double类型),不包含0和10
5 //强转为int,并加1得到1和10之间的数,包含1和10
6 int x = (int)(Math.random()*10)+1;
7 int y = (int)(Math.random()*10)+1;
8 System.out.println(x);
9 System.out.println(y);
10 // 创建0-4随机数 0 1 2 3 4 各表示加减乘除取模
11 int z = (int)(Math.random()*5);
12 System.out.println(z);
13
14 switch (z) {
15 case 0:
16 System.out.println(x + "+" + y + "=?");
17 System.out.println("哥们快猜。。。。");
18 Thread.sleep(2000);
19 System.out.println(x + "+" + y + "=" + (x + y));
20 break;
21 case 1:
22 System.out.println(x + "-" + y + "=?");
23 System.out.println("哥们快猜。。。。");
24 Thread.sleep(2000);
25 System.out.println(x + "-" + y + "=" + (x - y));
26 break;
27 case 2:
28 System.out.println(x + "*" + y + "=?");
29 System.out.println("哥们快猜。。。。");
30 Thread.sleep(2000);
31 System.out.println(x + "*" + y + "=" + (x * y));
32 break;
33 case 3:
34 System.out.println(x + "/" + y + "=?");
35 System.out.println("哥们快猜。。。。");
36 Thread.sleep(2000);
37 System.out.println(x + "/" + y + "=" + (x / y));
38 break;
39 case 4:
40 System.out.println(x + "%" + y + "=?");
41 System.out.println("哥们快猜。。。。");
42 Thread.sleep(2000);
43 System.out.println(x + "%" + y + "=" + (x % y));
44 break;
45 }
46
47 }
48 }
int x = (int)(Math.random()*10)+1;
Math.random() 生成0-1之间的数字,double类型
Math.random()*10 就是0-9之间的数,是double类型
(int)(Math.random()*10)将double类型强转成int类型,去掉小数点,便于计算。
(int)(Math.random()*10)+1,生成了1到10之间随机数。
int z = (int)(Math.random()*5);
生成0-4之间的数字,可以用0表示加,1表示减,2表示乘,3表示除,4表示取模
为了减慢程序,使用了Thread.sleep(2000); 让程序等待一会。
6 for 循环
格式:
for(初始化表达式;循环条件表达式;循环后的操作表达式)
{
执行语句;
}
需求: 想要打印5次hello world
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 for (int x = 0; x < 5; x++) { 3 System.out.println("hello world"); 4 } 5 }
3.for的执行流程
for 知道要进行循环,读到x=0 的时候,在内存中开辟了空间,定义变量x 赋值为0。接着进行条件判断 x<5,为真,这个时候对满足条件后执行了循环体的内容System.out.println("hello java");当循环体执行完毕之后,执行x < 5;后的表达式即 x++ 。x自增后变为了1 ,再次进行判断 x<5 (int x=0 只执行一次),如果为真就再次运行System.out.println("hello java");如果为假,for循环结束。
for 和while的区别
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 for (int x = 0; x < 5; x++) {
3 System.out.println("hello java");
4 }
5 System.out.println(x); //编译报错
6 //x cannot be resolved to a variable
7
8 int y = 0;
9 while (y < 5) {
10 System.out.println("hello world");
11 y++;
12 }
13 System.out.println(y);
14 }
编译报错
解释 x 为什么会找不到,注意了变量的作用域,也就是变量的作用范围。x 只在 for 循环的大括号内有效,出了这个区域,就无效了.在内存中就消失了。x消失后,仍要访问它,肯定会报错的。
y 就不一样了,y 是定义在while 外的。while循环完毕仍有效 while的初始化动作在外边,循环结束后y 仍然存在。当定义的y只作为循环增量存在的话的,循环完毕后y就没有用了,但是y还是占着一块内存。所以,如果定义的变量只作为循环增量存在的话,就用for 循环可以节约内存。
其实for 和while 是可以互换的。
最后总结:
1、for里面的两个表达式运行的顺序,初始化表达式只读一次,判断循环条件,为真就执行循环体,然后再执行循环后的操作表达式,接着继续判断循环条件,重复找个过程,直到条件不满足为止。
2、while与for可以互换,区别在于for为了循环而定义的变量在for循环结束时就在内存中释放。而while循环使用的变量在循环结束后还可以继续使用。
3、最简单无限循环格式:while(true) , for(;;),无限循环存在的原因是并不知道循环多少次,而是根据某些条件,来控制循环。推荐使用while(true)
1 while(true){ }
4 for(;;){ }
7 for(;true;){ }
for 练习:
- 获取1-10的和,并打印。
- 1-100之间 7的倍数的个数,并打印。
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 // 获取1到10的和1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9+10
3 int sum = 0;
4 for (int x = 1; x <= 10; x++) {
5 System.out.println((sum + x) + "=" + sum + "+" + x);
6 sum = sum + x;
7 }
8 System.out.println(sum);// 55
9 }
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 // 1-100之间 7的倍数的个数,并打印。
3 int count = 0;
4 for (int x = 0; x <= 100; x++) {
5 if (x % 7 == 0) {
6 System.out.println(x);
7 count++;
8 }
9 }
10 System.out.println(count);
11 }
累加思想:通过变量记录住循环操作后的结果;通过循环的形式.进行累加的动作。
计数器思想:通过一个变量记录住数据的状态变化,也是通过循环完成。
循环常见错误:
多加分号:在for括号后和循环体之间加分号是常见错误。
错误:程序编译运行都可以通过,只是不是我们想要的结果。
1 for(int i=0;i<100;i++);{
2 System.out.println("hello ");
3 }
正确:
1 for(int i=0;i<100;i++){
2 System.out.println("hello ");
3 }
错误;是一个死循环
1 int i=0;
2 while(i<100);{
3 System.out.println("hello");
4 i++;
5 }
正确:
1 int i=0;
2 while(i<100){
3 System.out.println("hello");
4 i++;
5 }
语句的嵌套应用
什么是嵌套形式,其实就是语句中还有语句。
想要打印出矩形:

1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 for (int x = 0; x < 5; x++) {
3 System.out.println("*");
4 }
5 }

1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 for (int x = 0; x < 5; x++) { 3 System.out.print("*"); 4 } 5 }

这里用“*”表示矩形的边。
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 for (int x = 0; x < 5; x++) { 3 for(int y=0;y<6;y++){ 4 System.out.print("*"); 5 } 6 System.out.println(); 7 } 8 }

forfor 嵌套for循环练习2
打印此种格式的图案
*****
****
***
**
*
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 for (int x = 5; x > 0; x--) {
3 for(int y=x;y>0;y--){
4 System.out.print("*");
5 }
6 System.out.println("");
7 }
8 }
练习:
*
**
***
****
*****
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 for (int x = 0; x < 5; x++) {
3 for (int y = 0; y <= x; y++) {
4 System.out.print("*");
5 }
6 System.out.println("");
7 }
8
9 }
练习:99乘法表
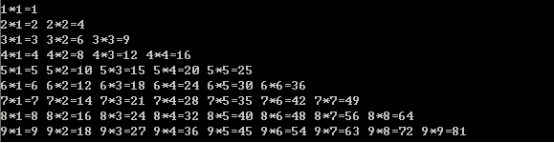
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 for (int x = 1; x <= 9; x++) {
3 for (int y = 1; y <= x; y++) {
4 System.out.print(y + "*" + x + "=" + x * y + '\t');
5 }
6 System.out.println(" ");
7 }
8 }
7 break、continue关键字
break关键字:break 语句用于终止最近的封闭循环或它所在的 switch 语句。控制传递给终止语句后面的语句(如果有的话)。
适用:for循环 、 switch两种循环语句。
break的用法:
- 单独使用。
- 与标签一起使用。(标签:即一个名字,满足标识符的条件即可)。
使用细节: 不要再break语句之后,编写其他语句,永远都执行不到,编译报错。

continue关键字:语句将控制权传递给它所在的封闭迭代语句的下一次迭代。(跳出本循环,执行下一次循环)。
适用于:while 、 do while 、 for循环语句
使用细节:
1. 如果continue出现在循环的末尾(最后一条语句),那么可以省略。
2. 如果continue出现在循环的第一条语句,那么后面的语句都无法执行,所以编译报错。
3. 可以结合标记使用。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号