数据分析常用分类算法
常见分类模型与算法
线性判别法
距离判别法
贝叶斯分类器
决策树
支持向量机(SVM)
神经网络
1.线性判别法
原理:用一条直线来划分学习集(这条直线不一定存在吗?),然后根据待测点在直线的哪一边决定它的分类

R语言实现:library(MASS)
ld=lda(G~x1+x2)
ld
2.距离判别法
原理:计算待测点与各类的距离,取最短者为其所属分类
常用距离:
绝对值距离
欧氏距离
闵可夫斯基距离
切比雪夫距离
马氏距离
Lance和Williams距离
离散变量的距离计算
各种类与类之间距离计算的方法
最短距离法
最长距离法
中间距离法
类平均法
重心法
离差平方和法
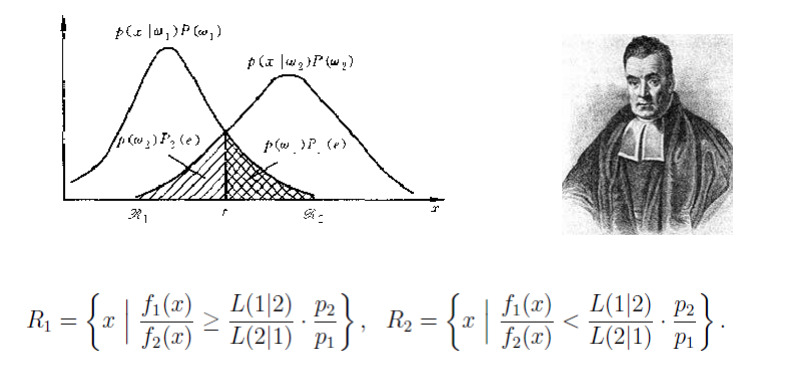
3.贝叶斯分类器
原理:
4.决策树 decision tree
输入:学习集
输出:分类规则(决策树)
R语言实现决策树:rpart扩展包
以鸢尾花数据集作为算例说明:
iris.rp = rpart(Species~., data=iris, method="class")
plot(iris.rp, uniform=T, branch=0, margin=0.1, main=“ Classification Tree\nIris Species by Petal and Sepal Length")
text(iris.rp, use.n=T, fancy=T, col="blue")
Rule 1: if Petal.Length>=2.45&Petal.Width<1.75, then it is versicolor(0/49/5)
Rule 2: if Petal.Length>=2.45&Petal.Width>=1.75, then it is virginica (0/1/45)
Rule 3: if Petal.Length<2.45, then it is setosa (50/0/0)
结果:

5. Knn算法(k近邻算法)
算法主要思想:
1 选取k个和待分类点距离最近的样本点
2 看1中的样本点的分类情况,投票决定待分类点所属的类
6. 人工神经网络(ANN=Artificial Neural Networks)

使用R语言实现人工神经网络:
library(AMORE)
# P is the input vector
P <- matrix(sample(seq(-1,1,length=1000), 1000, replace=FALSE), ncol=1)
# The network will try to approximate the target P^2 target <- P^2
# We create a feedforward network, with two hidden layers.
# The first hidden layer has three neurons and the second has two neurons.
# The hidden layers have got Tansig activation functions and the output layer is Purelin. net <- newff(n.neurons=c(1,3,2,1), learning.rate.global=1e-2, momentum
.global=0.5, error.criterium="LMS", Stao=NA, hidden.layer="tansig", output.layer="purelin", method="ADAPTgdwm")
result <- train(net, P, target, error.criterium="LMS", report=TRUE, show.step=100, n.shows=5 )
y <- sim(result$net, P)
plot(P,y, col="blue", pch="+")
points(P,target, col="red", pch="x")
影响精度的因素:
训练样本数量
隐含层数与每层节点数。层数和节点太少,不能建立复杂的映射关系,预测误差较大 。但层数和节点数过多,学习时间增加,还会产生“过度拟合”的可能。预测误差随 节点数呈现先减少后增加的趋势。
激活函数的影响
神经网络方法的优缺点
可以用统一的模式去处理高度复杂问题
便于元器件化,形成物理机器
中间过程无法从业务角度进行解释
容易出现过度拟合问题
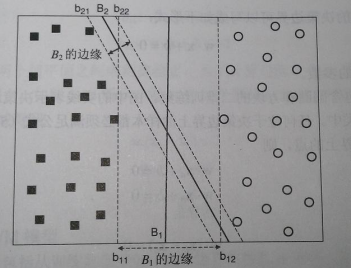
7.支持向量机 SVM
支持向量机,英文为Support Vector Machine,简称SV机。它是一种监督式学习的方法,它广泛的应用于统计分类以及回归分析中。支持向量机将向量映射到一个更高维的空间里,在这个空间里建立有一个最大间隔超平面。在分开数据的超平面的两边建有两个互相平行的超平面,分隔超平面使两个平行超平面的距离最大化。
优化目标:决策边界边缘距离最远


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号