Linux内核--网络协议栈深入分析(四)--套接字内核初始化和创建过程
本文分析基于Linux Kernel 3.2.1
原创作品,转载请标明http://blog.csdn.net/yming0221/article/details/7984238
更多请查看专栏http://blog.csdn.net/column/details/linux-kernel-net.html
作者:闫明
1、系统初始化过程中会调用sock_init函数进行套接字的初始化,主要是进行缓存的初始化
- static int __init sock_init(void)
- {
- int err;
- //初始化.sock缓存
- sk_init();
- //初始化sk_buff缓存
- skb_init();
- //初始化协议模块缓存
- init_inodecache();
- //注册文件系统类型
- err = register_filesystem(&sock_fs_type);
- if (err)
- goto out_fs;
- sock_mnt = kern_mount(&sock_fs_type);
- if (IS_ERR(sock_mnt)) {
- err = PTR_ERR(sock_mnt);
- goto out_mount;
- }
- .........................
- out:
- return err;
- out_mount:
- unregister_filesystem(&sock_fs_type);
- out_fs:
- goto out;
- }
- static int __init inet_init(void)
- {
- struct sk_buff *dummy_skb;
- struct inet_protosw *q;
- struct list_head *r;
- int rc = -EINVAL;
- BUILD_BUG_ON(sizeof(struct inet_skb_parm) > sizeof(dummy_skb->cb));
- sysctl_local_reserved_ports = kzalloc(65536 / 8, GFP_KERNEL);
- if (!sysctl_local_reserved_ports)
- goto out;
- //下面注册传输层协议操作集
- rc = proto_register(&tcp_prot, 1);
- if (rc)
- goto out_free_reserved_ports;
- rc = proto_register(&udp_prot, 1);
- if (rc)
- goto out_unregister_tcp_proto;
- rc = proto_register(&raw_prot, 1);
- if (rc)
- goto out_unregister_udp_proto;
- rc = proto_register(&ping_prot, 1);
- if (rc)
- goto out_unregister_raw_proto;
- //注册INET协议族的handler
- (void)sock_register(&inet_family_ops);
- .........................
- /*
- * Add all the base protocols.
- */
- //将INET协议族协议数据包接收函数添加到系统中
- if (inet_add_protocol(&icmp_protocol, IPPROTO_ICMP) < 0)
- printk(KERN_CRIT "inet_init: Cannot add ICMP protocol\n");
- if (inet_add_protocol(&udp_protocol, IPPROTO_UDP) < 0)
- printk(KERN_CRIT "inet_init: Cannot add UDP protocol\n");
- if (inet_add_protocol(&tcp_protocol, IPPROTO_TCP) < 0)
- printk(KERN_CRIT "inet_init: Cannot add TCP protocol\n");
- #ifdef CONFIG_IP_MULTICAST
- if (inet_add_protocol(&igmp_protocol, IPPROTO_IGMP) < 0)
- printk(KERN_CRIT "inet_init: Cannot add IGMP protocol\n");
- #endif
- /* Register the socket-side information for inet_create. */
- for (r = &inetsw[0]; r < &inetsw[SOCK_MAX]; ++r)
- INIT_LIST_HEAD(r);
- //将inetsw_array中的元素按套接字类型注册到inetsw链表数组中
- for (q = inetsw_array; q < &inetsw_array[INETSW_ARRAY_LEN]; ++q)
- inet_register_protosw(q);
- /*
- * Set the ARP module up
- */
- arp_init();
- /*
- * Set the IP module up
- */
- ip_init();
- tcp_v4_init();
- /* Setup TCP slab cache for open requests. */
- tcp_init();
- /* Setup UDP memory threshold */
- udp_init();
- /* Add UDP-Lite (RFC 3828) */
- udplite4_register();
- ping_init();
- /*
- * Set the ICMP layer up
- */
- if (icmp_init() < 0)
- panic("Failed to create the ICMP control socket.\n");
- .........................
- if (init_ipv4_mibs())
- printk(KERN_CRIT "inet_init: Cannot init ipv4 mibs\n");
- ipv4_proc_init();
- ipfrag_init();
- dev_add_pack(&ip_packet_type);
- rc = 0;
- out:
- return rc;
- out_unregister_raw_proto:
- proto_unregister(&raw_prot);
- out_unregister_udp_proto:
- proto_unregister(&udp_prot);
- out_unregister_tcp_proto:
- proto_unregister(&tcp_prot);
- out_free_reserved_ports:
- kfree(sysctl_local_reserved_ports);
- goto out;
- }
上面函数中的inetsw_array的定义中有四个元素:
- static struct inet_protosw inetsw_array[] =
- {
- {
- .type = SOCK_STREAM,
- .protocol = IPPROTO_TCP,
- .prot = &tcp_prot,
- .ops = &inet_stream_ops,
- .no_check = 0,
- .flags = INET_PROTOSW_PERMANENT |
- INET_PROTOSW_ICSK,
- },
- {
- .type = SOCK_DGRAM,
- .protocol = IPPROTO_UDP,
- .prot = &udp_prot,
- .ops = &inet_dgram_ops,
- .no_check = UDP_CSUM_DEFAULT,
- .flags = INET_PROTOSW_PERMANENT,
- },
- {
- .type = SOCK_DGRAM,
- .protocol = IPPROTO_ICMP,
- .prot = &ping_prot,
- .ops = &inet_dgram_ops,
- .no_check = UDP_CSUM_DEFAULT,
- .flags = INET_PROTOSW_REUSE,
- },
- {
- .type = SOCK_RAW,
- .protocol = IPPROTO_IP, /* wild card */
- .prot = &raw_prot,
- .ops = &inet_sockraw_ops,
- .no_check = UDP_CSUM_DEFAULT,
- .flags = INET_PROTOSW_REUSE,
- }
- };
上面的函数会将这个数组中的元素按照type为索引注册到inetsw指针数组中。
函数2中调用的sock_register函数就是想协议族数组net_families中添加inet协议族的net_proto_family的数据定义,主要是协议族的创建方法inet_create下面是它的实现
- int sock_register(const struct net_proto_family *ops)
- {
- int err;
- if (ops->family >= NPROTO) {
- printk(KERN_CRIT "protocol %d >= NPROTO(%d)\n", ops->family,
- NPROTO);
- return -ENOBUFS;
- }
- spin_lock(&net_family_lock);
- if (rcu_dereference_protected(net_families[ops->family],
- lockdep_is_held(&net_family_lock)))
- err = -EEXIST;
- else {
- RCU_INIT_POINTER(net_families[ops->family], ops);//这里就相当于将ops赋予net_families[ops->families]
- err = 0;
- }
- spin_unlock(&net_family_lock);
- printk(KERN_INFO "NET: Registered protocol family %d\n", ops->family);
- return err;
- }
3、套接字的创建
套接字分BSD socket的传输层的socket(struct sock结构,与具体的传输层协议有关)。
3.1、BSD socket的创建
应用程序使用函数socket会产生系统调用,调用sys_socket函数来创建BSD socket:
- SYSCALL_DEFINE3(socket, int, family, int, type, int, protocol)
- {
- int retval;
- struct socket *sock;
- int flags;
- /* Check the SOCK_* constants for consistency. */
- BUILD_BUG_ON(SOCK_CLOEXEC != O_CLOEXEC);
- BUILD_BUG_ON((SOCK_MAX | SOCK_TYPE_MASK) != SOCK_TYPE_MASK);
- BUILD_BUG_ON(SOCK_CLOEXEC & SOCK_TYPE_MASK);
- BUILD_BUG_ON(SOCK_NONBLOCK & SOCK_TYPE_MASK);
- flags = type & ~SOCK_TYPE_MASK;
- if (flags & ~(SOCK_CLOEXEC | SOCK_NONBLOCK))
- return -EINVAL;
- type &= SOCK_TYPE_MASK;
- if (SOCK_NONBLOCK != O_NONBLOCK && (flags & SOCK_NONBLOCK))
- flags = (flags & ~SOCK_NONBLOCK) | O_NONBLOCK;
- retval = sock_create(family, type, protocol, &sock);//调用sock_create创建套接字,参数分别是协议族号、套接字类型,使用的传输层协议、执行要创建的套接字的指针的地址。
- if (retval < 0)
- goto out;
- retval = sock_map_fd(sock, flags & (O_CLOEXEC | O_NONBLOCK));
- if (retval < 0)
- goto out_release;
- out:
- /* It may be already another descriptor 8) Not kernel problem. */
- return retval;
- out_release:
- sock_release(sock);
- return retval;
- }
- int __sock_create(struct net *net, int family, int type, int protocol,
- struct socket **res, int kern)
- {
- int err;
- struct socket *sock;
- const struct net_proto_family *pf;
- /*
- * 合法性检查
- */
- if (family < 0 || family >= NPROTO)
- return -EAFNOSUPPORT;
- if (type < 0 || type >= SOCK_MAX)
- return -EINVAL;
- /* Compatibility.
- This uglymoron is moved from INET layer to here to avoid
- deadlock in module load.
- */
- if (family == PF_INET && type == SOCK_PACKET) {
- static int warned;
- if (!warned) {
- warned = 1;
- printk(KERN_INFO "%s uses obsolete (PF_INET,SOCK_PACKET)\n",
- current->comm);
- }
- family = PF_PACKET;
- }
- err = security_socket_create(family, type, protocol, kern);
- if (err)
- return err;
- sock = sock_alloc();//分配inode结构并获得对应的socket结构
- if (!sock) {
- if (net_ratelimit())
- printk(KERN_WARNING "socket: no more sockets\n");
- return -ENFILE; /* Not exactly a match, but its the
- closest posix thing */
- }
- sock->type = type;
- rcu_read_lock();
- pf = rcu_dereference(net_families[family]);
- err = -EAFNOSUPPORT;
- if (!pf)
- goto out_release;
- /*
- * We will call the ->create function, that possibly is in a loadable
- * module, so we have to bump that loadable module refcnt first.
- */
- if (!try_module_get(pf->owner))//模块检测
- goto out_release;
- /* Now protected by module ref count */
- rcu_read_unlock();
- //这里调用inet_create函数对INET协议族进行创建
- err = pf->create(net, sock, protocol, kern);
- if (err < 0)
- goto out_module_put;
- /*
- * Now to bump the refcnt of the [loadable] module that owns this
- * socket at sock_release time we decrement its refcnt.
- */
- if (!try_module_get(sock->ops->owner))
- goto out_module_busy;
- /*
- * Now that we're done with the ->create function, the [loadable]
- * module can have its refcnt decremented
- */
- module_put(pf->owner);
- err = security_socket_post_create(sock, family, type, protocol, kern);
- if (err)
- goto out_sock_release;
- *res = sock;
- return 0;
- out_module_busy:
- err = -EAFNOSUPPORT;
- out_module_put:
- sock->ops = NULL;
- module_put(pf->owner);
- out_sock_release:
- sock_release(sock);
- return err;
- out_release:
- rcu_read_unlock();
- goto out_sock_release;
- }
- /* Standard well-defined IP protocols. */
- enum {
- IPPROTO_IP = 0, /* Dummy protocol for TCP */
- IPPROTO_ICMP = 1, /* Internet Control Message Protocol */
- IPPROTO_IGMP = 2, /* Internet Group Management Protocol */
- IPPROTO_IPIP = 4, /* IPIP tunnels (older KA9Q tunnels use 94) */
- IPPROTO_TCP = 6, /* Transmission Control Protocol */
- IPPROTO_EGP = 8, /* Exterior Gateway Protocol */
- IPPROTO_PUP = 12, /* PUP protocol */
- IPPROTO_UDP = 17, /* User Datagram Protocol */
- IPPROTO_IDP = 22, /* XNS IDP protocol */
- IPPROTO_DCCP = 33, /* Datagram Congestion Control Protocol */
- IPPROTO_RSVP = 46, /* RSVP protocol */
- IPPROTO_GRE = 47, /* Cisco GRE tunnels (rfc 1701,1702) */
- IPPROTO_IPV6 = 41, /* IPv6-in-IPv4 tunnelling */
- IPPROTO_ESP = 50, /* Encapsulation Security Payload protocol */
- IPPROTO_AH = 51, /* Authentication Header protocol */
- IPPROTO_BEETPH = 94, /* IP option pseudo header for BEET */
- IPPROTO_PIM = 103, /* Protocol Independent Multicast */
- IPPROTO_COMP = 108, /* Compression Header protocol */
- IPPROTO_SCTP = 132, /* Stream Control Transport Protocol */
- IPPROTO_UDPLITE = 136, /* UDP-Lite (RFC 3828) */
- IPPROTO_RAW = 255, /* Raw IP packets */
- IPPROTO_MAX
- };
3.2、INET层socket(inet_socket)和传输层socket(struct sock)创建
函数inet_create完成了上述功能,并初始化了sock的属性值,将socket的sk属性指向sock结构
- static int inet_create(struct net *net, struct socket *sock, int protocol,
- int kern)
- {
- struct sock *sk;
- struct inet_protosw *answer;
- struct inet_sock *inet;
- struct proto *answer_prot;
- unsigned char answer_flags;
- char answer_no_check;
- int try_loading_module = 0;
- int err;
- if (unlikely(!inet_ehash_secret))
- if (sock->type != SOCK_RAW && sock->type != SOCK_DGRAM)
- build_ehash_secret();
- sock->state = SS_UNCONNECTED;
- /* Look for the requested type/protocol pair. */
- lookup_protocol:
- err = -ESOCKTNOSUPPORT;
- rcu_read_lock();
- //根据传输层协议的类型创建sock结构
- //遍历inetsw链表
- list_for_each_entry_rcu(answer, &inetsw[sock->type], list) {
- err = 0;
- /* Check the non-wild match. */
- if (protocol == answer->protocol) {
- if (protocol != IPPROTO_IP)
- break;//找到了适配的inetsw[]元素
- } else {
- /* Check for the two wild cases. */
- if (IPPROTO_IP == protocol) {
- protocol = answer->protocol;
- break;
- }
- if (IPPROTO_IP == answer->protocol)
- break;
- }
- err = -EPROTONOSUPPORT;
- }
- //到这里answer指向了合适的inetsw结构,若是TCP协议,answer指向内容如下
- /*
- * .type = SOCK_STREAM,
- * .protocol = IPPROTO_TCP,
- * .prot = &tcp_prot,
- * .ops = &inet_stream_ops,
- * .no_check = 0,
- * .flags = INET_PROTOSW_PERMANENT |
- * INET_PROTOSW_ICSK,
- */
- if (unlikely(err)) {
- if (try_loading_module < 2) {
- rcu_read_unlock();
- /*
- * Be more specific, e.g. net-pf-2-proto-132-type-1
- * (net-pf-PF_INET-proto-IPPROTO_SCTP-type-SOCK_STREAM)
- */
- if (++try_loading_module == 1)
- request_module("net-pf-%d-proto-%d-type-%d",
- PF_INET, protocol, sock->type);
- /*
- * Fall back to generic, e.g. net-pf-2-proto-132
- * (net-pf-PF_INET-proto-IPPROTO_SCTP)
- */
- else
- request_module("net-pf-%d-proto-%d",
- PF_INET, protocol);
- goto lookup_protocol;
- } else
- goto out_rcu_unlock;
- }
- err = -EPERM;
- if (sock->type == SOCK_RAW && !kern && !capable(CAP_NET_RAW))
- goto out_rcu_unlock;
- err = -EAFNOSUPPORT;
- if (!inet_netns_ok(net, protocol))
- goto out_rcu_unlock;
- sock->ops = answer->ops;
- answer_prot = answer->prot;
- answer_no_check = answer->no_check;
- answer_flags = answer->flags;
- rcu_read_unlock();
- WARN_ON(answer_prot->slab == NULL);
- err = -ENOBUFS;
- //分配sock结构体内存,这里在inet_init函数初始化好的高速缓冲区中分配内存,然后做一些初始化工作。后面有进一步分析。
- sk = sk_alloc(net, PF_INET, GFP_KERNEL, answer_prot);
- if (sk == NULL)
- goto out;
- err = 0;
- sk->sk_no_check = answer_no_check;
- if (INET_PROTOSW_REUSE & answer_flags)
- sk->sk_reuse = 1;
- inet = inet_sk(sk);//后面有进一步分析,为何可以强制转换?!!
- inet->is_icsk = (INET_PROTOSW_ICSK & answer_flags) != 0;
- inet->nodefrag = 0;
- if (SOCK_RAW == sock->type) {
- inet->inet_num = protocol;
- if (IPPROTO_RAW == protocol)
- inet->hdrincl = 1;
- }
- if (ipv4_config.no_pmtu_disc)
- inet->pmtudisc = IP_PMTUDISC_DONT;
- else
- inet->pmtudisc = IP_PMTUDISC_WANT;
- inet->inet_id = 0;
- //对sk进行初始化设置并将sock中的sk指针指向sk结构
- sock_init_data(sock, sk);
- //进一步设置sk的其他属性信息
- sk->sk_destruct = inet_sock_destruct;
- sk->sk_protocol = protocol;
- sk->sk_backlog_rcv = sk->sk_prot->backlog_rcv;
- inet->uc_ttl = -1;
- inet->mc_loop = 1;
- inet->mc_ttl = 1;
- inet->mc_all = 1;
- inet->mc_index = 0;
- inet->mc_list = NULL;
- sk_refcnt_debug_inc(sk);
- if (inet->inet_num) {
- /* It assumes that any protocol which allows
- * the user to assign a number at socket
- * creation time automatically
- * shares.
- */
- inet->inet_sport = htons(inet->inet_num);
- /* Add to protocol hash chains. */
- sk->sk_prot->hash(sk);//调用inet_hash函数
- }
- if (sk->sk_prot->init) {
- err = sk->sk_prot->init(sk);//调用tcp_v4_init_sock函数进行进一步的初始化,由于在函数sk_alloc中一些属性被设置成0了,所以在此调用进行初始化
- if (err)
- sk_common_release(sk);
- }
- out:
- return err;
- out_rcu_unlock:
- rcu_read_unlock();
- goto out;
- }
关于套接字struct sock与struct inet_sock、struct tcp_sock、struct inet_connection_sock等结构之间的关系有待进一步了解。
上篇中已经写过,内核中套接字struct socket、struct sock、struct inet_sock、struct tcp_sock、struct raw_sock、struct udp_sock、struct inet_connection_sock、struct inet_timewait_sock和struct tcp_timewait_sock的关系是:
*struct socket这个是BSD层的socket,应用程序会用过系统调用首先创建该类型套接字,它和具体协议无关。
*struct inet_sock是INET协议族使用的socket结构,可以看成位于INET层,是struct sock的一个扩展。它的第一个属性就是struct sock结构。
*struct sock是与具体传输层协议相关的套接字,所有内核的操作都基于这个套接字。
*struct tcp_sock是TCP协议的套接字表示,它是对struct inet_connection_sock的扩展,其第一个属性就是struct inet_connection_sock inet_conn。
*struct raw_sock是原始类型的套接字表示,ICMP协议就使用这种套接字,其是对struct sock的扩展。
*struct udp_sock是UDP协议套接字表示,其是对struct inet_sock套接字的扩展。
*struct inet_connetction_sock是所有面向连接协议的套接字,是对struct inet_sock套接字扩展。
后面两个是用于控制超时的套接字。
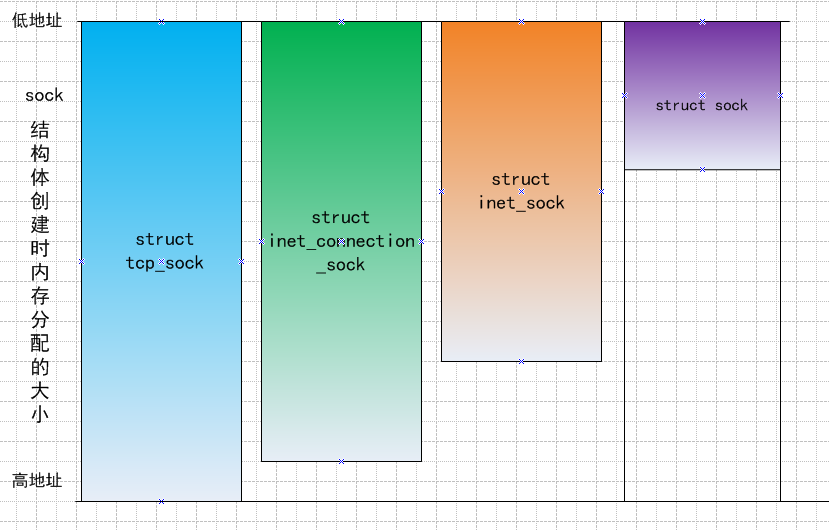
就拿struct inet_sock和struct sock为例来说明,为什么内核中可以直接将sock结构体首地址强制转换成inet_sock的首地址?并且inet_sock的大小要大于sock,直接进行如下强制转换
- inet = inet_sk(sk);
- static inline struct inet_sock *inet_sk(const struct sock *sk)
- {
- return (struct inet_sock *)sk;
- }
不会发生内存非法访问吗?!那就是在分配的时候并不只是分配的struct sock结构体大小的存储空间!
可以细看sock结构体分配的代码:
- struct sock *sk_alloc(struct net *net, int family, gfp_t priority,
- struct proto *prot)
- {
- struct sock *sk;
- sk = sk_prot_alloc(prot, priority | __GFP_ZERO, family);
- if (sk) {
- sk->sk_family = family;
- sk->sk_prot = sk->sk_prot_creator = prot;
- sock_lock_init(sk);
- sock_net_set(sk, get_net(net));
- atomic_set(&sk->sk_wmem_alloc, 1);
- sock_update_classid(sk);
- }
- return sk;
- }
- static struct sock *sk_prot_alloc(struct proto *prot, gfp_t priority,
- int family)
- {
- struct sock *sk;
- struct kmem_cache *slab;
- slab = prot->slab;
- if (slab != NULL) {
- sk = kmem_cache_alloc(slab, priority & ~__GFP_ZERO);
- ..............................
- } else
- sk = kmalloc(prot->obj_size, priority);
- .....................
- return sk;
- ......................
- }
如果是TCP协议中的tcp_prot中指明该属性的大小为.obj_size = sizeof(struct tcp_sock)。
所以,程序中给struct sock指针分配的不是该结构体的实际大小,而是大于其实际大小,以便其扩展套接字的属性占用。
以图例说明tcp_sock是如何从sock强制转换来的:
下篇将分析套接字的绑定、连接等一系列操作的实现。



