Spring boot HibernateJPA CRUD
连接数据库和创建表
1.
pom安装
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
2. application.properties连接 (你的电脑本地要有mysql并且打开)
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test1 spring.datasource.username=test1 spring.datasource.password=123456 spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update spring.jpa.show-sql=true spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
3. 建立新的文件夹和类名
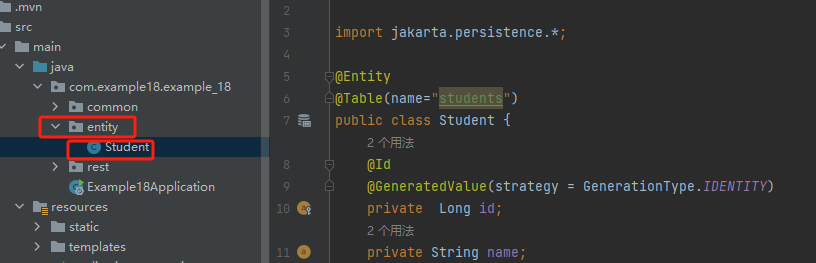
package com.example18.example_18.entity; import jakarta.persistence.*; @Entity @Table(name="students") public class Student { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Long id; private String name; private int age; public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }
增删改查
1.定义DOA接口
2.定义DOA实现
3.更新到主程序,注入DAO
这里我是实现一个最简单的查询功能,这一步的时候应该代表你一件完成上面的连接了
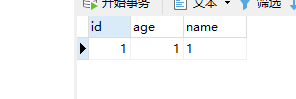
我的数据库内容
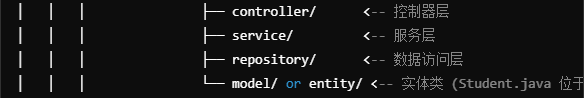
先说说目录结构
1.
model 或 enrity是生成数据表的
比如我的students表
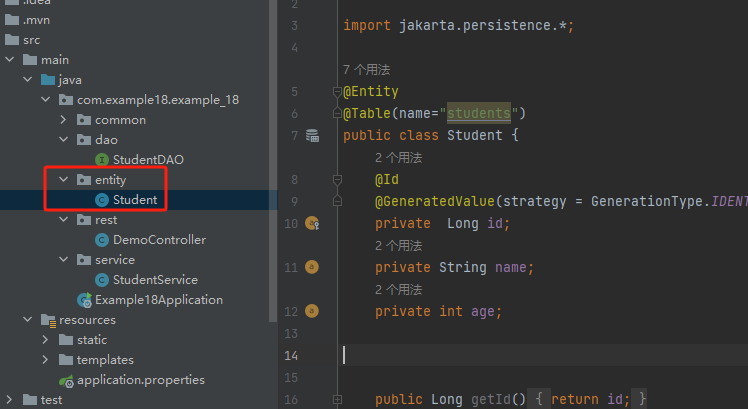
package com.example18.example_18.entity; import jakarta.persistence.*; @Entity @Table(name="students") public class Student { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Long id; private String name; private int age; public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }
2. repository目录,有些人写dao目录,其实一样用来数据访问的
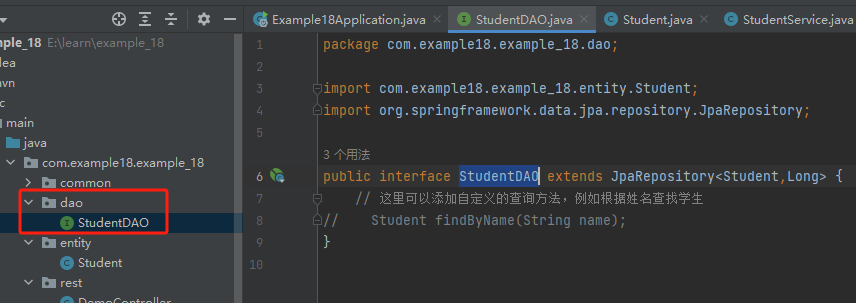
package com.example18.example_18.dao;
import com.example18.example_18.entity.Student;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public interface StudentDAO extends JpaRepository<Student,Long> { // 这里可以添加自定义的查询方法,例如根据姓名查找学生 // Student findByName(String name); }
3. service目录,就是用来实现repository目录的内容的
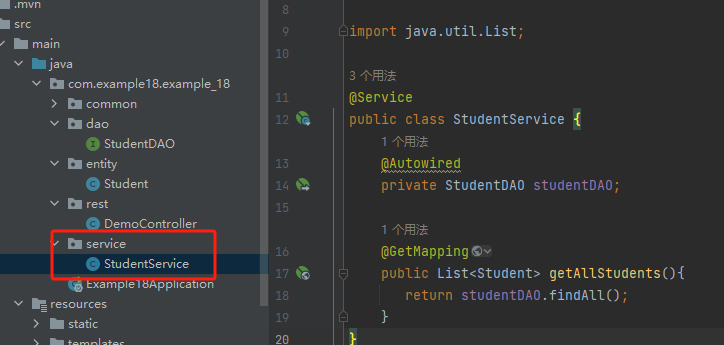
@Service xia不要@GetMapping的
package com.example18.example_18.service; import com.example18.example_18.dao.StudentDAO; import com.example18.example_18.entity.Student; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import java.util.List; @Service public class StudentService { @Autowired private StudentDAO studentDAO; public List<Student> getAllStudents(){ return studentDAO.findAll(); } }
4.controller控制器层,有些人写rest目录,就是http入口的地方
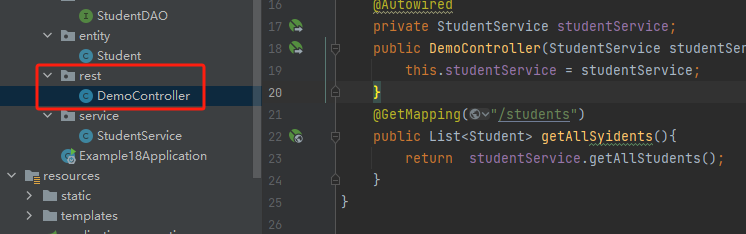
package com.example18.example_18.rest; import com.example18.example_18.common.Coach; import com.example18.example_18.dao.StudentDAO; import com.example18.example_18.entity.Student; import com.example18.example_18.service.StudentService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import java.util.List; @RestController public class DemoController { @Autowired private StudentService studentService; public DemoController(StudentService studentService) { this.studentService = studentService; } @GetMapping("/students") public List<Student> getAllSyidents(){ return studentService.getAllStudents(); } }
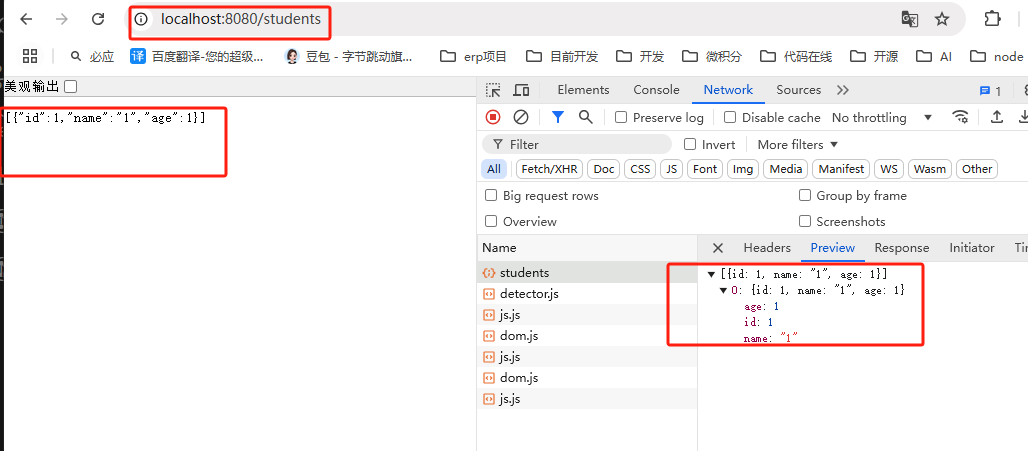
最后,我运行跑起来
也可以使用
import jakarta.persistence.EntityManager;
import jakarta.persistence.TypedQuery;
TypedQuery一类的查询
例子
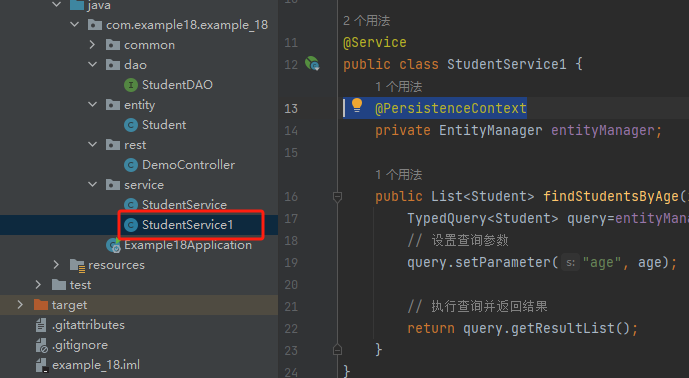
package com.example18.example_18.service; import com.example18.example_18.entity.Student; import jakarta.persistence.EntityManager; import jakarta.persistence.PersistenceContext; import jakarta.persistence.TypedQuery; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.util.List; @Service public class StudentService1 { @PersistenceContext private EntityManager entityManager; public List<Student> findStudentsByAge(int age){ TypedQuery<Student> query=entityManager.createQuery("SELECT s FROM Student s WHERE s.age > :age ",Student.class); // 设置查询参数 query.setParameter("age", age); // 执行查询并返回结果 return query.getResultList(); } }
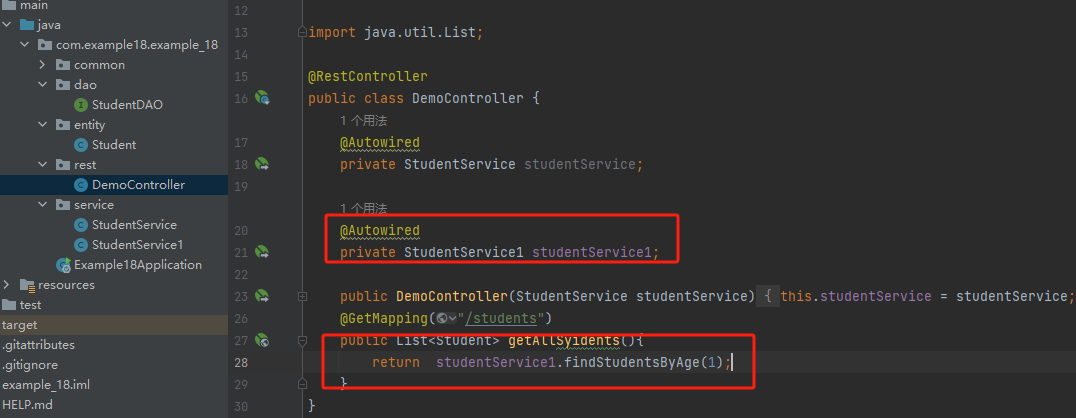
package com.example18.example_18.rest; import com.example18.example_18.common.Coach; import com.example18.example_18.dao.StudentDAO; import com.example18.example_18.entity.Student; import com.example18.example_18.service.StudentService; import com.example18.example_18.service.StudentService1; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import java.util.List; @RestController public class DemoController { @Autowired private StudentService studentService; @Autowired private StudentService1 studentService1; public DemoController(StudentService studentService) { this.studentService = studentService; } @GetMapping("/students") public List<Student> getAllSyidents(){ return studentService1.findStudentsByAge(1); } }
完成
下面是GPT的例子:仅仅参考作用
1.创建实体类
使用 @Entity 注解定义数据库表的实体类,例如 Student:
import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.GenerationType; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.Table; @Entity @Table(name = "students") public class Student { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Long id; private String name; private int age; // Getters and Setters public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }
2.创建 Repository 接口
Spring Data JPA 提供了 JpaRepository 接口,继承它可以快速实现基本的 CRUD 操作:
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; public interface StudentRepository extends JpaRepository<Student, Long> { // 这里可以添加自定义的查询方法,例如根据姓名查找学生 Student findByName(String name); }
3.创建 Service 类
在 Service 类中使用 StudentRepository 来管理 Student 数据:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import javax.transaction.Transactional; import java.util.List; @Service public class StudentService { @Autowired private StudentRepository studentRepository; public List<Student> getAllStudents() { return studentRepository.findAll(); } public Student getStudentById(Long id) { return studentRepository.findById(id).orElse(null); } @Transactional public Student createStudent(Student student) { return studentRepository.save(student); } @Transactional public Student updateStudent(Long id, Student studentDetails) { Student student = getStudentById(id); if (student != null) { student.setName(studentDetails.getName()); student.setAge(studentDetails.getAge()); return studentRepository.save(student); } return null; } @Transactional public void deleteStudent(Long id) { studentRepository.deleteById(id); } }
4.创建 Controller 类
通过 REST API 暴露 CRUD 操作,以便外部调用:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; import java.util.List; @RestController @RequestMapping("/students") public class StudentController { @Autowired private StudentService studentService; @GetMapping public List<Student> getAllStudents() { return studentService.getAllStudents(); } @GetMapping("/{id}") public Student getStudentById(@PathVariable Long id) { return studentService.getStudentById(id); } @PostMapping public Student createStudent(@RequestBody Student student) { return studentService.createStudent(student); } @PutMapping("/{id}") public Student updateStudent(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestBody Student studentDetails) { return studentService.updateStudent(id, studentDetails); } @DeleteMapping("/{id}") public void deleteStudent(@PathVariable Long id) { studentService.deleteStudent(id); } }






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 25岁的心里话
· 按钮权限的设计及实现