12_How to deploy Flask apps on Ubuntu VPS Using gunicorn and Ngnix
地址:https://www.codewithharry.com/blogpost/flask-app-deploy-using-gunicorn-nginx/
How to deploy flask app on Ubuntu VPS using Nginx and gunicorn
In this post, we will see how to deploy flask applications using gunicorn WSGI server and nginx as a reverse proxy and static files server.
Follow the steps below:
Step 1 - Install required packages
Now let's install python3, python3-pip, and Nginx using the commands below:

Step 2 - Creating a directory (for our flask app) and virtual environment
Let's install virtualenv
Lets now create a directory to host our flask application
run the following command to create a virtual environment named env
Finally activate the virtual environment
Lets now install flask and gunicorn using pip
Step 3 - Creating a sample project and wsgi entry point
Let us now create a sample project by entering the command below:
Paste the contents below to app.py file
Next, we’ll create a file that will serve as the entry point for our application. This will tell our Gunicorn server how to interact with the application.
copy the contents below to wsgi.py
We can test gunicorn's ability to serve our project by running the command below:
Folder structure so far:
Lets deactivate our virtual environment now:
Step 4 - Creating a systemd service
Lets now create a systemd service using the following commands:
Now paste the contents below to this file:
Activate this service by typing:
A file named app.sock will be automatically created. Folder structure so far:
Step 5 - Configuring Nginx
Create a file named app inside /etc/nginx/sites-available
Now copy the below contents to this file:
Important: I have used my server IP, you should use yours!
Activate this configuration by executing this:
Restart nginx and your website should work fine!
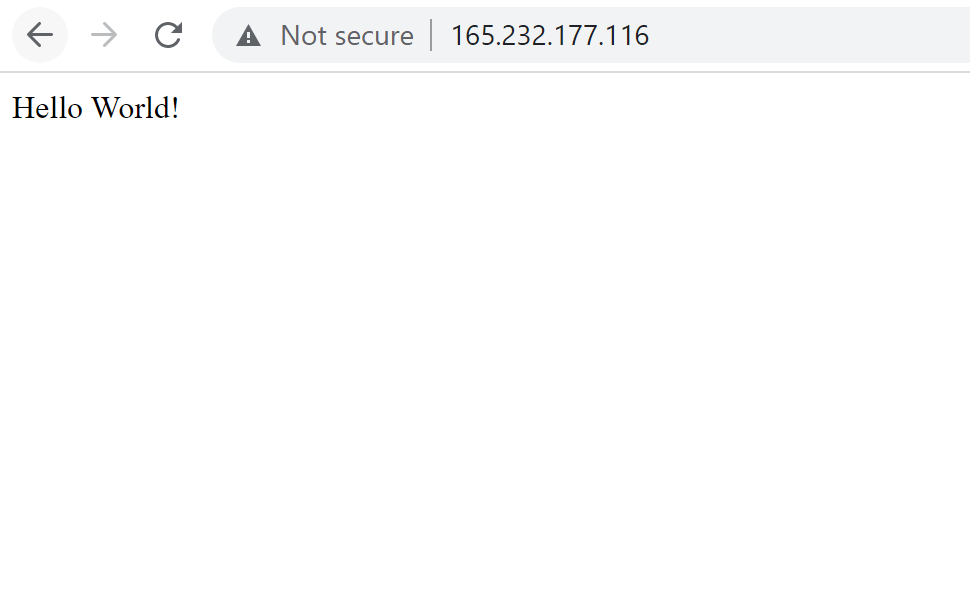
Visiting http://165.232.177.116/ on browser shows a page like this
If you are using a firewall (for eg. ufw), don't forget to allow nginx to receive incoming traffic on port 80
Happy coding!


