10_How deploy a Django application using Nginx & Gunicorn in Production
地址:https://www.codewithharry.com/blogpost/django-deploy-nginx-gunicorn/
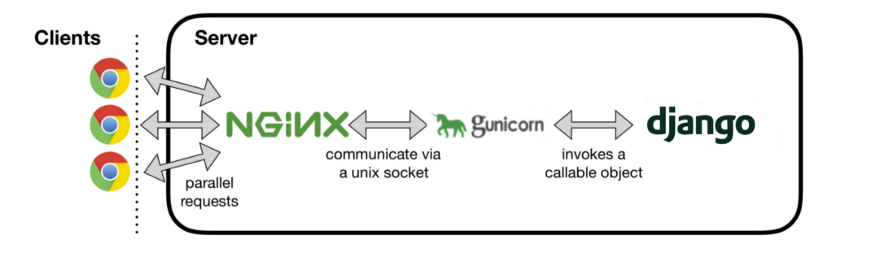
How to host Django Application using gunicorn & nginx in Production
In this post, we will see how to use nginx with gunicorn to serve django applications in production.
Django is a very powerful web framework and ships with a server which is able to facilitate development. This development server is not scalable and is not suited for production. Hence we need to configure gunicorn to get better scalability and nginx can be used as a reverse proxy and as a web server to serve static files. Let's get started
Before you follow the steps outlined below, I will assume that you have already configured your Ubuntu server with a non root user and firewall as outlined here.
Step 1 - Installing python and nginx
Let's update the server's package index using the command below:
This will install python, pip and nginx server
Step 2 - Creating a python virtual environment
This will install a virtual environment package in python. Let's create a project directory to host our Django application and create a virtual environment inside that directory.
A virtual environment named env will be created. Let's activate this virtual environment:
Step 3 - Installing Django and gunicorn
This installs Django and gunicorn in our virtual environment
Step 4 - Setting up our Django project
At this point you can either copy your existing Django project into the projectdir folder or create a fresh one as shown below:
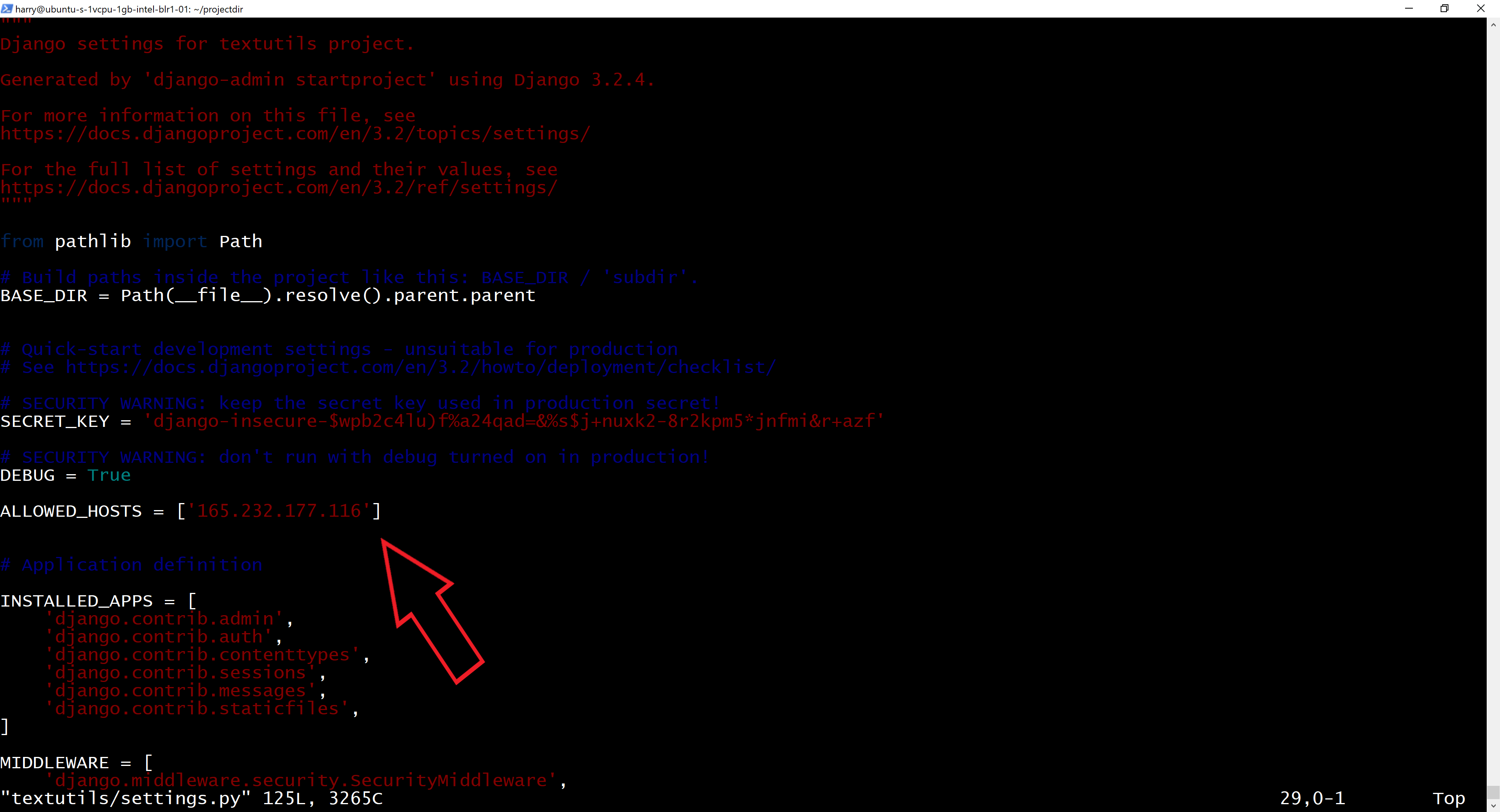
Add your IP address or domain to the ALLOWED_HOSTS variable in settings.py.
If you have any migrations to run, perform that action:
Let's test this sample project by running the following commands:
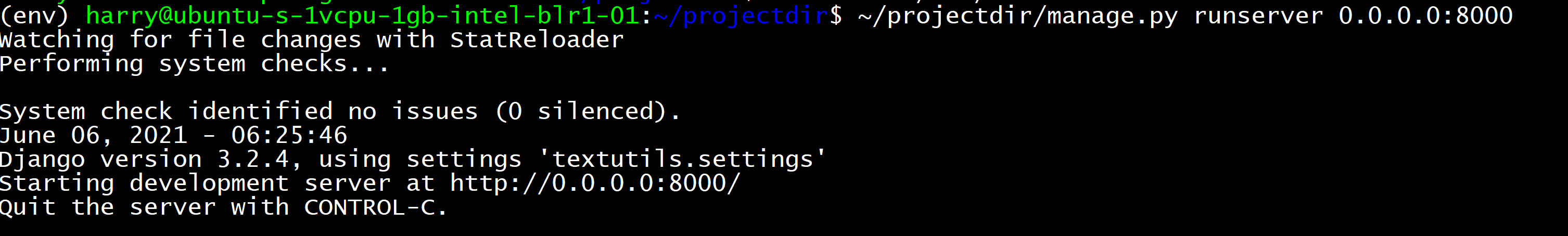
This opens port 8000 by allowing it over the firewall. Let's start our Django development server to test the setup so far:
Step 5 - Configuring gunicorn
Lets test gunicorn's ability to serve our application by firing the following commands:

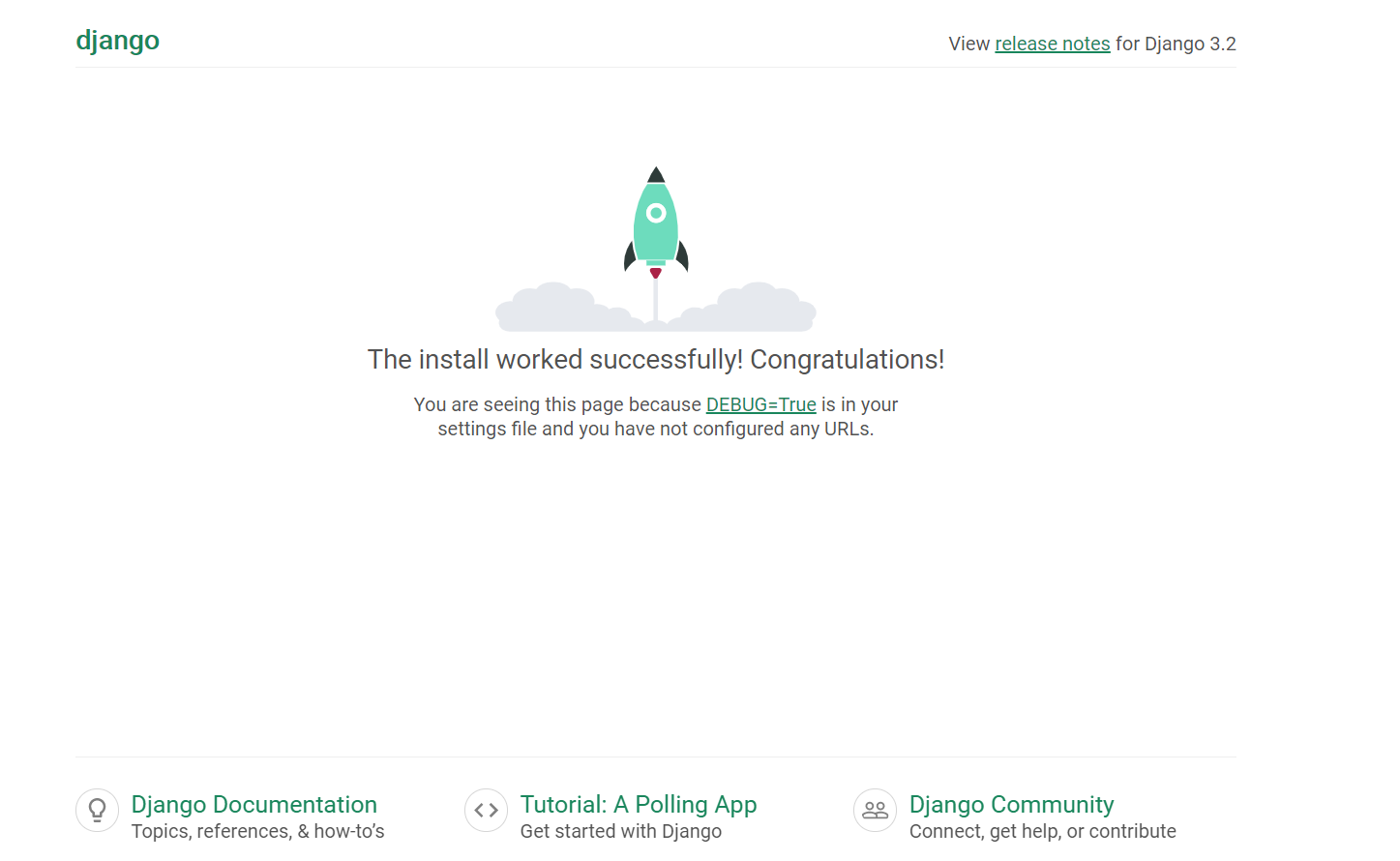
This should start gunicorn on port 8000. We can go back to the browser to test our application. Visiting http://<ip-address>:8000 shows a page like this:
Deactivate the virtualenvironment by executing the command below:
Let's create a system socket file for gunicorn now:
Paste the contents below and save the file
Next, we will create a service file for gunicorn
Paste the contents below inside this file:
Lets now start and enable the gunicorn socket
Step 6 - Configuring Nginx as a reverse proxy
Create a configuration file for Nginx using the following command
Paste the below contents inside the file created
Activate the configuration using the following command:
Restart nginx and allow the changes to take place.
Your Django website should now work fine! Happy Coding





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 25岁的心里话
· 按钮权限的设计及实现