proxy模式
参考资料
• 维基百科:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proxy_pattern
Proxy模式简介
GoF:Provide a surrogate or placeholder for another object to control access to it.
GoF:为其他对象提供一个代理来控制对其的访问。
Wikipedia:In computer programming, the proxy pattern is a software design pattern. A proxy, in its most general form, is a class functioning as an interface to something else. The proxy could interface to anything: a network connection, a large object in memory, a file, or some other resource that is expensive or impossible to duplicate. In short, a proxy is a wrapper or agent object that is being called by the client to access the real serving object behind the scenes.
Wikipedia:在计算机编程中,代理模式是一种软件设计模式。一个代理,其最普遍的形式,就是一个作为接口的类。代理可以为任何事物提供接口:网络连接、内存中的大对象、文件或其他资源。通常这些资源需要花费较大的代价来复制,或根本不可能被复制。简而言之,代理就是一个包装对象或中介对象,客户端调用代理来获取其背后的真正提供服务的对象。
百度百科:为其他对象提供一种代理以控制对这个对象的访问。在某些情况下,一个对象不适合或者不能直接引用另一个对象,而代理对象可以在客户端和目标对象之间起到中介的作用。
Proxy模式详解
• 设计意图
为其他对象提供一个代理对象来控制对其的访问。
• 代理种类
▶ Remote Proxy
远程代理为一个不同地址空间的对象提供一个本地表示。NEXTSTEP为此使用了一个NXProxy类。Coplien将这种类型的代理命名为Ambassador。
▶ Virtual Proxy
虚拟代理将创建用户需求的高开销对象。
▶ Protection Proxy
保护代理控制了对原始对象的访问操作。当对象需要不同的访问权限时,这种代理就十分有用。
• UML类图
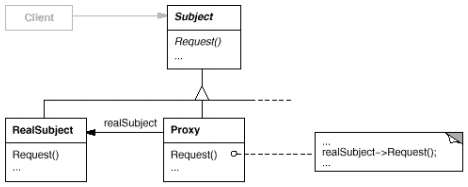
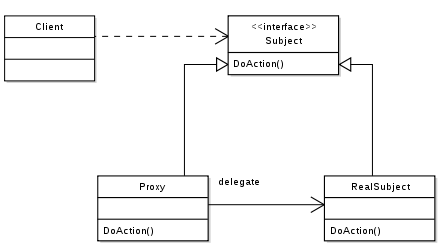
• 结构说明
▶ Proxy
代理角色。维护一个可以取得真实对象的引用。Proxy可以替代RealSubject,只要它们的接口定义是一致的。Proxy还负责控制访问RealSubject的操作,并且还可能负责创建和销毁该RealSubject。
▶ Subject
抽象主题角色。为RealSubject和Proxy定义通用接口,这样Proxy可以在RealSubject出现的任何一个地方替代使用。
▶ RealSubject
真实主题角色。定义了Proxy代理的真实对象内容。
Proxy模式举例
这个例子出自于Wikipedia:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proxy_pattern,例子的原型出自于GOF。
#include <string> #include <iostream> using namespace std; // Subject class Image { public: Image() {} virtual ~Image() {} public: virtual void DisplayImage() = 0; }; // RealSubject class RealImage : public Image { private: string m_strFileName; public: RealImage(const string &strFileName = "") : m_strFileName(strFileName) { LoadImageFromDisk(); } virtual ~RealImage() {} public: virtual void DisplayImage() { cout << "Displaying " << m_strFileName << endl; } private: void LoadImageFromDisk() { cout << "Loading " << m_strFileName << endl; } }; // Proxy class ProxyImage : public Image { private: string m_strFileName; RealImage *m_pRealImage; public: ProxyImage(const string &strFileName = "") : m_strFileName(strFileName), m_pRealImage(NULL) {} virtual ~ProxyImage() { if (m_pRealImage) { delete m_pRealImage; } } public: virtual void DisplayImage() { if (NULL == m_pRealImage) { m_pRealImage = ::new RealImage(m_strFileName); } m_pRealImage->DisplayImage(); } }; int main() { Image *pImage1 = ::new ProxyImage("HiRes_10MB_Photo1"); Image *pImage2 = ::new ProxyImage("HiRes_10MB_Photo2"); pImage1->DisplayImage(); // loading necessary pImage1->DisplayImage(); // loading unnecessary pImage2->DisplayImage(); // loading necessary pImage2->DisplayImage(); // loading unnecessary pImage1->DisplayImage(); // loading unnecessary delete pImage1; delete pImage2; return 1; }


