大端模式和小端模式
参考资料
维基百科:http://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%AD%97%E8%8A%82%E5%BA%8F
术语定义
Byte Endian :字节序,是指字节在内存中的组织顺序,所以也称为Byte Ordering或Byte Order。
Big Endian :大端模式,是指数据的高字节保存在内存的低地址中,而数据的低字节保存在内存的高地址中的存储模式。
Little Endian:小端模式,是指数据的高字节保存在内存的高地址中,而数据的低字节保存在内存的低地址中的存储模式。
MSB :Most Significant Byte,最高有效字节,指多字节序列中最大权重的字节。
LSB :Least Significant Byte,最低有效字节,指多字节序列中最小权重的字节。
16位数0x1234在大端模式下的存放方式为(假设从地址0x4000开始存放):

16位数0x1234在小端模式下的存放方式为(假设从地址0x4000开始存放):

32位数0x12345678在大端模式下的存放方式为(假设从地址0x4000开始存放):

32位数0x12345678在小端模式下的存放方式为(假设从地址0x4000开始存放):

判断大小端
• 代码一
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char **argv) { short x = 0x1122; char x0 = ((char *)&x)[0]; char x1 = ((char *)&x)[1]; if (0x11 == x0) { cout << "Big Endian" << endl; } else { cout << "Little Endian" << endl; } return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
• 代码二
#include <iostream> using namespace std; static union { char c[4]; unsigned long e; } EndianTestUnion = { { 'l', '?', '?', 'b' } }; #define ENDIANNESS ((char)EndianTestUnion.e) int main(int argc, char **argv) { cout << ENDIANNESS << endl; return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
• 代码三
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char **argv) { short x = 1; if (*(char *)&x) { cout << "Little Endian" << endl; } else { cout << "Big Endian" << endl; } return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
一些面试题
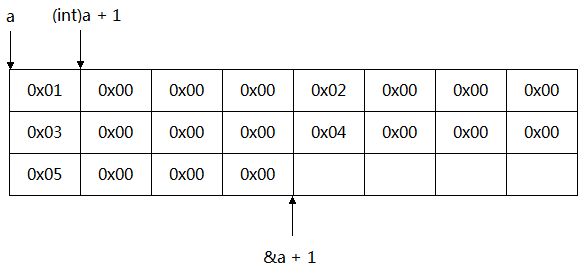
1. 对于32位x86系统,以下程序的输出是:5,2000000
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main(int argc, char ** argv) { int a[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; int *p1 = (int *)(&a + 1); int *p2 = (int *)((int)a + 1); printf("%x,%x", p1[-1], *p2); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
此题内存布局如下图: