ASP.NET Web API编程——向客户端返回执行结果
向客户端返回执行结果中包含着两类信息,一类是请求的数据资源,另一类是操作执行的结果。第一类信息一般在响应的消息体中即可获得。只有按照框架提供的编程模式,正确设置操作(Action)的返回值即可,对于如何返回第二类信息以及应包含什么信息,值得探讨。
为了便于客户端调试,同时又不能暴露服务端对事物具体的处理逻辑和服务端异常的详细信息,那么应该精心设计返回信息。常用的表达操作(Action)执行状态的方式是用状态码来表示,状态码是一串数字、字母、或数字和字母的组合。然后定义每一个状态码所代表的含义。
一般有两种方式将状态码包含到响应中:传统的RPC模式,将状态码放入响应的消息体中;另一种方式利用类型为HttpStatusCode的HttpResponseMessage.StatusCode属性,这是一种非常优雅的属性,将请求获得的实体数据与其他信息分离,Web API框架在设计之初已经想到了这一点。
下面是HttpStatusCode的定义

框架不仅提供了状态码,还提供了和状态码相关的原因短语。使用HttpResponseException类并设置错误码。服务端抛出HttpResponseException类型的异常并不会被服务端异常过滤器捕获,可利用此类向客户端抛出异常相关的信息。可以使用HttpResponseException的构造函数设置响应的状态码。
HttpResponseException的定义如下所示:

例:使用系统定义的状态码
客户端:
string url = "http://localhost/webApi_test/api/testapi"; using (HttpClient client = new HttpClient()) { Task<HttpResponseMessage> taskResult = client.GetAsync(url); HttpResponseMessage responseMessage = taskResult.Result; Console.WriteLine("状态码:{0},原因短语:{1}", (int)responseMessage.StatusCode,responseMessage.ReasonPhrase); if(responseMessage.StatusCode==HttpStatusCode.OK) { Task<string> contentStr = responseMessage.Content.ReadAsStringAsync(); contentStr.Wait(); Console.WriteLine(contentStr.Result); } } Console.ReadLine();
服务端:
public IHttpActionResult Get(DataModel model) { if (!ModelState.IsValid || model==null) { throw new HttpResponseException(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest); } return Ok(model); }
在服务端,当模型绑定失败或操作参数值为null时向客户端抛出HttpResponseException类型的异常,状态码设置为HttpStatusCode.BadRequest,表示服务器未识别该请求,当我们不知道准确的错误、已定义的错误代码不能表达这种错误时使用HttpStatusCode.BadRequest
执行结果:

自定义状态码
虽然Web API框架定义了一些状态码,但在实际项目中使用自定状态码结合Web API框架预定义状态码更有优势。
自定义状态码,同时还要指定相应的消息短语。最好遵循以下原则:
1)必须是整数
2)必须小于999
3)600以内的码最好别用
4)消息短语使用英文。消息短语只支持英文字符,中文或其他语言文字显示乱码。
此外消息短语不应很长,如果想更加详细的表达消息,那么也可以使用代码代替消息短语,但要注意代码不能是三位数字,否则客户端无法正常获得消息内容。
例如:
客户端
public IHttpActionResult Get(DataModel model) { if (!ModelState.IsValid || model==null) { throw new HttpResponseException(new HttpResponseMessage { StatusCode = (HttpStatusCode)701, ReasonPhrase = "ModelState is not valid or model is null" }); } return Ok(model); }
运行结果:

若果自定义状态码非常多,那么应该使用配置文件来管理状态码。
例:使用配置文件管理状态码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <root> <StatusCode code ="701"> <ReasonPhrase>ModelState is not valid or model is null</ReasonPhrase> </StatusCode> <StatusCode code ="702"> <ReasonPhrase>login session has expired</ReasonPhrase> </StatusCode> </root>
如果完成一个操作要调用一系列的模块,那么一个状态码就无法定位到具体的模块。为了解决这个问题可以使用另一个状态码。这个状态码指定产生异常的具体模块。当然不指定具体模块也是可以的,但使用这样一个状态码更便于客户端调试,我称之为辅助状态码。
例:
<root>
<MainStatus>
<StatusCode code ="701">
<ReasonPhrase>The parameter is null</ReasonPhrase>
</StatusCode>
<StatusCode code ="702">
<ReasonPhrase>login session has expired</ReasonPhrase>
</StatusCode>
</MainStatus>
<HelpStatus>
<StatusCode code ="A001">
<ReasonPhrase>login model methord longin</ReasonPhrase>
</StatusCode>
</HelpStatus>
</root>
可以将辅助状态码放在响应的消息短语中,辅助状态码不能是三位数字,否则无法正常显示信息,最好使用字母和数字的组合。
例:使用辅助状态码
服务端:
public IHttpActionResult Get(DataModel model) { if (!ModelState.IsValid || model==null) { throw new HttpResponseException(new HttpResponseMessage { StatusCode = (HttpStatusCode)701, ReasonPhrase = "A701,model is null" }); } return Ok(model); }
客户端如上例所示,执行结果为:

例:使用XML管理状态码
解析XML。下面的代码在真实环境中有待改进,第一次运行应将XML加载到内存在,而不应每次都解析一次。
public class CustomStatus { public HttpStatusCode Code { set; get; } public string ReasonPhrase { set; get; } } public class HelpStatus { public string Code { set; get; } public string ReasonPhrase { set; get; } } public CustomStatus GetMainCustomStatus(int code) { Dictionary<int, CustomStatus> dict = new Dictionary<int, CustomStatus>(); XmlDocument xmlDoc = new XmlDocument(); xmlDoc.Load(@"E:\projgxz_myself\WebApi_Test\App_Data\CustomStatus.xml"); var root = xmlDoc.SelectSingleNode("./root"); var mainNode = root.SelectSingleNode("./MainStatus"); XmlNodeList codeLsit = mainNode.SelectNodes("./StatusCode"); foreach (XmlNode codeNode in codeLsit) { int httpCode = Int32.Parse(codeNode.Attributes["code"].Value); string reasonPhrase = codeNode.SelectSingleNode("./ReasonPhrase").InnerText; dict.Add(httpCode, new CustomStatus { Code = (HttpStatusCode)httpCode, ReasonPhrase = reasonPhrase }); } return dict[code]; } public HelpStatus GetHelpStatus(string code) { Dictionary<string, HelpStatus> dict = new Dictionary<string, HelpStatus>(); XmlDocument xmlDoc = new XmlDocument(); xmlDoc.Load(@"E:\projgxz_myself\WebApi_Test\App_Data\CustomStatus.xml"); var root = xmlDoc.SelectSingleNode("./root"); var mainNode = root.SelectSingleNode("./HelpStatus"); XmlNodeList codeLsit = mainNode.SelectNodes("./StatusCode"); foreach (XmlNode codeNode in codeLsit) { string httpCode = codeNode.Attributes["code"].Value; string reasonPhrase = codeNode.SelectSingleNode("./ReasonPhrase").InnerText; dict.Add(httpCode, new HelpStatus { Code = httpCode, ReasonPhrase = reasonPhrase }); } return dict[code]; }
服务端:
public IHttpActionResult Post(Model1 model) { if (!ModelState.IsValid || model == null) { throw new HttpResponseException(new HttpResponseMessage { StatusCode = GetMainCustomStatus(701).Code, ReasonPhrase = "A001"+":"+GetHelpStatus("A001").ReasonPhrase+";"+GetMainCustomStatus(701).ReasonPhrase }); } return Ok(model); }
客户端
public static void TestClient() { string url = "http://localhost/webApi_test/api/testapi"; List<Model2> model2List = new List<Model2> { new Model2 { Field21 = "f1", Field22 = "f2" }, new Model2 { Field21 = "f21", Field22 = "f22" } }; Model1 model = null; using (HttpClient client = new HttpClient()) { Task<HttpResponseMessage> taskResult = client.PostAsync(url, model, new BsonMediaTypeFormatter()); HttpResponseMessage responseMessage = taskResult.Result; Console.WriteLine("状态码:{0},原因短语:{1}", (int)responseMessage.StatusCode, responseMessage.ReasonPhrase); Task<Model1> models = responseMessage.Content.ReadAsAsync<Model1>(new List<BsonMediaTypeFormatter> { new BsonMediaTypeFormatter() }); models.Wait(); if (responseMessage.StatusCode==HttpStatusCode.OK) { Console.WriteLine(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(models.Result, Formatting.Indented)); } } Console.ReadLine(); }
运行结果:
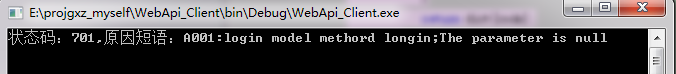
例:强制客户端抛出异常
当服务端抛出HttpResponseException异常后,客户端不会捕获这种异常,为在响应状态码不为200时,强制客户端抛出异常,可以使用HttpResponseMessage.EnsureSuccessStatusCode()方法。
客户端:
public static void TestClient() { string url = "http://localhost/webApi_test/api/testapi"; List<Model2> model2List = new List<Model2> { new Model2 { Field21 = "f1", Field22 = "f2" }, new Model2 { Field21 = "f21", Field22 = "f22" } }; Model1 model = null;// new Model1 { Name = "集合", List1 = model2List }; using (HttpClient client = new HttpClient()) { Task<HttpResponseMessage> taskResult = client.PostAsync(url, model, new BsonMediaTypeFormatter()); HttpResponseMessage responseMessage = taskResult.Result; responseMessage.EnsureSuccessStatusCode(); Console.WriteLine("状态码:{0},原因短语:{1}", (int)responseMessage.StatusCode, responseMessage.ReasonPhrase); Task<Model1> models = responseMessage.Content.ReadAsAsync<Model1>(new List<BsonMediaTypeFormatter> { new BsonMediaTypeFormatter() }); models.Wait(); if (responseMessage.StatusCode==HttpStatusCode.OK) { Console.WriteLine(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(models.Result, Formatting.Indented)); } } Console.ReadLine(); }
运行客户端,成功抛出异常:
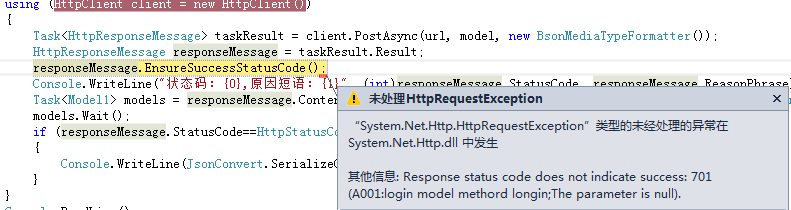
--------------------------------------------------------------------
转载与引用请注明出处。
时间仓促,水平有限,如有不当之处,欢迎指正。

