树和图详解
(1)二叉树的性质
1、在二叉树的第 i 层上至多有2^(i-1)个节点
2、深度为 k 的二叉树至多有2^(k)-1个节点
3、对于任何一个二叉树,若其叶子节点数为n1,度为2的节点数为n2,则n1=n2+1
树的节点树=所有节点度之和+1
4、具有n个节点的完全二叉树的深度为floor(log(2,n))+1
(2)图基本概念
1、图:一种表示“多对多”关系的复杂数据结构。
2、图的组成:图G由一个非空的有限顶点集合V(G)和一个有限边集合E(G)组成,定义为G=(V,E)。
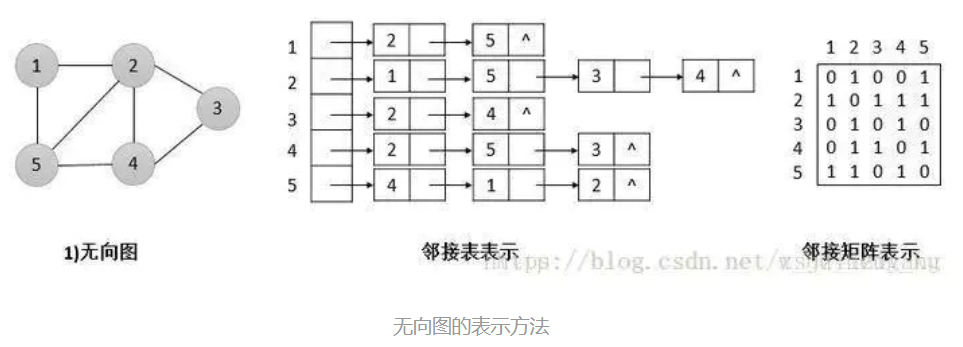
3、无向图:若图的每条边都没有方向,则称该图为无向图。
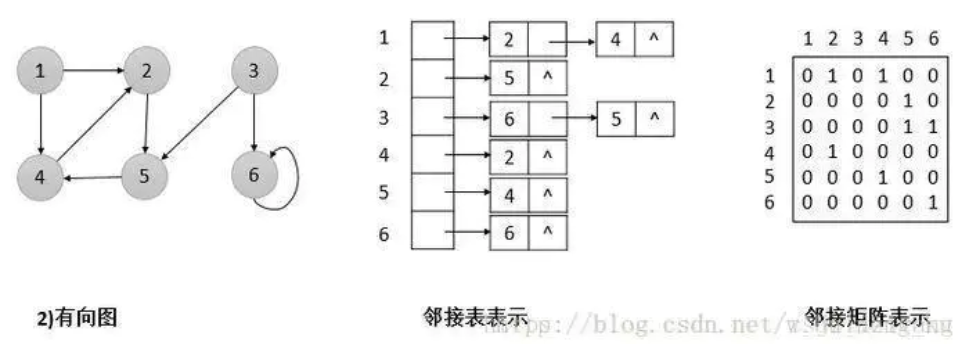
4、有向图:若图的每条边都有方向,则称该图为有向图。
5、对于无向图,顶点的度表示以该顶点作为一个端点的边的数目。
6、对于有向图,顶点的度分为入度和出度。入度是以该顶点为终点的入边数目,出度是以该顶点为起点的出边数目,该顶点的度等于其入度和出度之和。
7、路径:在图G中,存在一个顶点序列(Vp,Vi1,Vi2,Vi3…,Vin,Vq),使得(Vp,Vi1),(Vi1,Vi2),…,(Vim,Vq)均属于边集E(G),则称顶点Vp到Vq存在一条路径。
8、路径长度:一条路径上经过的边的数量。
9、环:某条路径包含相同的顶点两次或两次以上。
10、有向无环图:没有环的有向图,简称DAG。
11、带权有向图的最短路径长度:源点Vm到终点Vn的所有路径中,权值和最小的路径是最短路径,其长度是最短路径长度。
12、完全图:任意两个顶点都相连的图称为完全图,又分为无向完全图和有向完全图。
13、连通图:在无向图中,若任意两个顶点vivi与vjvj都有路径相通,则称该无向图为连通图。
14、强连通图:在有向图中,若任意两个顶点vivi与vjvj都有路径相通,则称该有向图为强连通图。
15、连通网:带权值的连通图叫做连通网。
16、生成树:将图中所有顶点以最少的边连通的子图。生成树包含全部n个顶点,有且仅有n-1条边,在添加边则必定成环。(因为每个结点(除根结点)都可以向上找到唯一的父节点,所有是树)。
17、最小生成树:在所有生成树中,权值和最小的生成树就是最小生成树。
18、树与图的关系:树的定义:有且只有一个结点的入度为0,其他节点的入度为1。树是一个无向连通图,其中任何两个顶点只通过一条路径连接。 换句话说,一个任何没有简单环路的连通图都是一棵树。
(2)图的表示
1、邻接矩阵:使用一个二维数组 G[N][N]存储图,如果顶点 Vi 和 顶点 Vj 之间有边,则 G[Vi][Vj] = 1 或 weight。邻接矩阵是对称的。
2、邻接表:图的一种链式存储结构:对于图 G 中每个顶点 Vi,把所有邻接于 Vi 的顶点 Vj 链成一个单链表,这个单链表称为顶点 Vi 的邻接表。
邻接表与邻接矩阵的区别:邻接表占用空间少,适合存储稀疏图;邻接矩阵适合存储稠密图。若判断任意两个结点之间是否有边连接,可用邻接矩阵。
(3)图的遍历
1、基于邻接矩阵
public class Graph { //顶点数量 private int vertexSize; //顶点数组 private int[] vertexs; private int[][] matrix; //设置不可到达的权值为1000 private static final int max=1000; private boolean[] isVisited; public Graph(int vertexSize){ this.vertexSize=vertexSize; matrix=new int[vertexSize][vertexSize]; vertexs=new int[vertexSize]; for(int i=0;i<vertexSize;i++){ vertexs[i]=i; } isVisited=new boolean[vertexSize]; } public int[] getVertexs() { return vertexs; } public void setVertexs(int[] vertexs) { this.vertexs = vertexs; } //获取某个顶点的出度 public int getOutDegree(int index){ int degree=0; for(int j=0;j<matrix[index].length;j++){ int weight=matrix[index][j]; if(weight!=0&&weight!=MAX_WEIGHT){ degree++; } } return degree; } //获取两个顶点之间的权值 public int getWeight(int v1,int v2){ return matrix[v1][v2]==0?0:(matrix[v1][v2]==MAX_WEIGHT?-1:matrix[v1][v2]); } // 获取某个顶点的第一个邻接点 public int getFirstNeigbour(int index){ for(int j=0;j<vertexSize;j++){ if(matrix[index][j]>0&&matrix[index][j]<MAX_WEIGHT){ return j; } } return -1; } // 图的深度优先遍历算法 private void depthFirstSearch(int i){ isVisited[i]=true; int w=getFirstNeigbour(i); while(w!=-1){ if(!isVisited[w]){ //需要遍历该顶点 System.out.println("访问到了:"+w+"顶点"); depthFirstSearch(w); } w=getNextNeighbour(i, w); } } public void depthFirstSearch(){ isVisited=new boolean[vertexSize]; for(int i=0;i<vertexSize;i++){ if(!isVisited[i]){ System.out.println("访问到了:"+i+"顶点"); depthFirstSearch(i); } } isVisited=new boolean[vertexSize]; } public static void main(String[] args) { Graph graph=new Graph(9); int[] a1=new int[]{0,10,max,max,max,11,max,max,max}; int[] a2=new int[]{10,0,18,max,max,max,16,max,12}; int[] a3=new int[]{max,max,0,22,max,max,max,max,8}; int[] a4=new int[]{max,max,22,0,20,max,max,16,21}; int[] a5=new int[]{max,max,max,20,0,26,max,7,max}; int[] a6=new int[]{11,max,max,max,26,0,176,max,max}; int[] a7=new int[]{max,16,max,max,max,17,0,19,max}; int[] a8=new int[]{max,max,max,16,7,max,19,0,max}; int[] a9=new int[]{max,12,8,21,max,max,max,max,0}; graph.matrix[0]=a1; graph.matrix[1]=a2; graph.matrix[2]=a3; graph.matrix[3]=a4; graph.matrix[4]=a5; graph.matrix[5]=a6; graph.matrix[6]=a7; graph.matrix[7]=a8; graph.matrix[8]=a9; int degree=graph.getOutDegree(1); System.out.println("出度:"+degree); int weight=graph.getWeight(0, 4); System.out.println("权值:"+weight); graph.depthFirstSearch(); } }
2、基于邻接表
1)图的数据结构
package graph; import java.util.*; public class graphNode { public int val; public List<graphNode> neighbors; public boolean visited; public graphNode() { val = 0; neighbors = new ArrayList<graphNode>(); } public graphNode(int _val) { val = _val; neighbors = new ArrayList<graphNode>(); } public graphNode(int _val, ArrayList<graphNode> _neighbors) { val = _val; neighbors = _neighbors; } }
2)图的深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历
package graph; import java.util.*; public class create_And_Visited_Graph { //邻接表如下 /* 1->2-5 2->1-5-4 3->2-4 4->2-5-3 5->4-1-2 */ public static void main(String[] args) { //创建图节点 graphNode n1=new graphNode(1); graphNode n2=new graphNode(2); graphNode n3=new graphNode(3); graphNode n4=new graphNode(4); graphNode n5=new graphNode(5); //创建邻接表 n1.neighbors.add(n2); n1.neighbors.add(n5); n2.neighbors.add(n1); n2.neighbors.add(n5); n2.neighbors.add(n4); n3.neighbors.add(n2); n3.neighbors.add(n4); n4.neighbors.add(n2); n4.neighbors.add(n5); n4.neighbors.add(n3); n5.neighbors.add(n4); n5.neighbors.add(n1); n5.neighbors.add(n2); //深度优先遍历 DFS(n1); // System.out.println(); //广度优先遍历 // BFS(n1); } //深度优先遍历 public static void DFS(graphNode root){ if (root == null) { return; } root.visited=true; System.out.print(root.val+" "); for (graphNode node : root.neighbors) { if (!node.visited) { DFS(node); } } } //广度优先遍历 public static void BFS(graphNode root) { Queue<graphNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); root.visited=true; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { graphNode r = queue.poll(); System.out.print(r.val+" "); for (graphNode node : r.neighbors) { if (!node.visited) { queue.offer(node); node.visited=true; } } } } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号