(一道面试题)关于线程
一.多线程的主要优点:提高效率 。但是存在线程安全,上代码:
现实多线程的方法:实现Runnable接口,继承Thread类
(一般是实现Runnable接口,主要原因是java不支持多重继承,一旦你继承了Thread类那么你就无法继承其他类,局限性太大了)
一.多线程的实现
1.这里我是实现Runnable接口来实现多线程
public class Producter implements Runnable {
public static List<String> nlist=new LinkedList<String>();//存放产品
private Integer number; //用来存放产品编号
private String productName; //用来存放产品名称
/*
* 实现Runnable接口,生产产品,并将其添加到容器中
*/
@Override
public void run() {
//定义产品编号,从1开始
number=nlist.size()+1;
//定义产品的名字
productName=number+"号产品";
//将生产好的产品存放到容器中
nlist.add(productName);
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}
2.测试类,定义100个线程来测试多线程时发生的问题
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//生产100个产品
for(int i=0;i<100;i++){
Thread thread=new Thread(new Producter());
thread.start();
}
//等待3s因为主线程跟线程是并行进行的.不等待返回的nlist的值不确定.
Thread.sleep(3000);
//遍历打印出的容器的产品
for(String s:Producter.nlist)
{
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
3.实验结果:

4.分析结果:
这是因为有多个线程同时访问了run()方法.造成了一个产品被多次制造。
二.多线程安全问题的解决:加锁(synchronized关键字)
给run()方法加锁.----目的: 当对象访问run()时只允许最多一个线程访问.这个就可以解决一个产品被多次制造的问题了.
1.修改Producter方法
public class Producter implements Runnable {
public static List<String> nlist=new LinkedList<String>();//存放产品
private Integer number; //用来存放产品编号
private String productName; //用来存放产品名称
/*
* 实现Runnable接口,生产产品,并将其添加到容器中
*/
@Override
public void run() {
//加锁最多允许一个线程进来
synchronized (this.getClass()) {
//定义产品编号,从1开始
number=nlist.size()+1;
//定义产品的名字
productName=number+"号产品";
//将生产好的产品存放到容器中
nlist.add(productName);
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}
}
2.为了容易观看修改了测试类代码(每打印10个换行):
public class TestDemo { private static int count=0; public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { //生产100个产品 for(int i=0;i<100;i++){ Thread thread=new Thread(new Producter()); thread.start(); } //等待3s因为主线程跟线程是并行进行的.不等待返回的nlist的值不确定. Thread.sleep(3000); //遍历打印出的容器的产品 for(String s:Producter.nlist) { //每10次换行 count++; System.out.print(s); if(count%10==0) { System.out.println(); } } } }
3.实验结果(没有一个重复的):
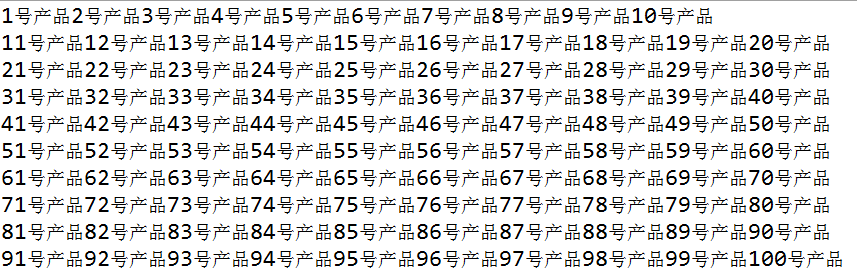
4.总结
在实现多线程时必须考虑到线程安全问题,不然会有许多的意外结果(BUG)~


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号