神经网络与深度学习(邱锡鹏)编程练习 2 实验3 基函数回归(最小二乘法优化)
通过基函数对元素数据进行交换,从而将变量间的线性回归模型转换为非线性回归模型。
- 最小二乘法 + 多项式基函数
- 最小二乘法 + 高斯基函数
def multinomial_basis(x, feature_num=10):
x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=1) # shape(N, 1)
feat = [x]
for i in range(2, feature_num+1):
feat.append(x**i)
ret = np.concatenate(feat, axis=1)
return ret
def gaussian_basis(x, feature_num=10):
centers = np.linspace(0, 25, feature_num)
width = 1.0 * (centers[1] - centers[0])
x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=1)
x = np.concatenate([x]*feature_num, axis=1)
out = (x-centers)/width
ret = np.exp(-0.5 * out ** 2)
return ret实验结果:
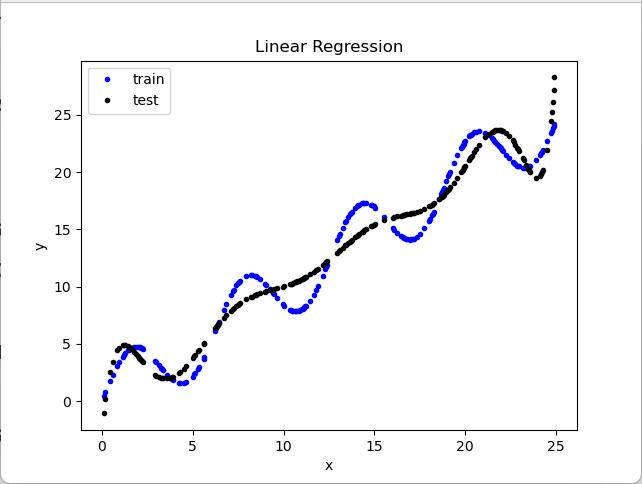
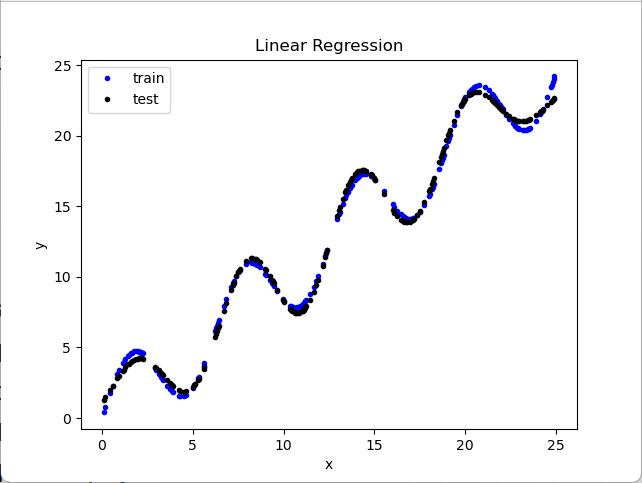
实验结果分析:
多项式回归(多项式基函数)比线性回归更好的拟合了数据
高斯基函数拟合效果比多项式基函数拟合效果更好
多项式基函数源代码:
查看代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def load_data(filename): # 载入数据
xys = []
with open(filename, 'r') as f:
for line in f:
xys.append(map(float, line.strip().split()))
xs, ys = zip(*xys)
return np.asarray(xs), np.asarray(ys)
def multinomial_basis(x, feature_num=10):
x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=1) # shape(N, 1)
feat = [x]
for i in range(2, feature_num + 1):
feat.append(x ** i)
ret = np.concatenate(feat, axis=1)
return ret
def main(x_train, y_train): # 训练模型,并返回从x到y的映射。
basis_func = multinomial_basis # shape(N, 1)的函数
phi0 = np.expand_dims(np.ones_like(x_train), axis=1) # shape(N,1)大小的全1 array
phi1 = basis_func(x_train) # 将x_train的shape转换为(N, 1)
phi = np.concatenate([phi0, phi1], axis=1) # phi.shape=(300,2) phi是增广特征向量的转置
print("phi shape = ", phi.shape)
# 使用最小二乘法优化w
w = np.dot(np.linalg.pinv(phi), y_train) # np.linalg.pinv(phi)求phi的伪逆矩阵(phi不是列满秩) w.shape=[2,1]
print("参数 w = ", w)
def f(x):
phi0 = np.expand_dims(np.ones_like(x), axis=1)
phi1 = basis_func(x)
phi = np.concatenate([phi0, phi1], axis=1)
y = np.dot(phi, w) # 矩阵乘法
return y
return f
def evaluate(ys, ys_pred): # 评估模型
std = np.sqrt(np.mean(np.abs(ys - ys_pred) ** 2))
return std
if __name__ == '__main__': # 程序主入口(建议不要改动以下函数的接口)
train_file = 'train.txt'
test_file = 'test.txt'
# 载入数据
x_train, y_train = load_data(train_file)
x_test, y_test = load_data(test_file)
print("x_train shape:", x_train.shape)
print("x_test shape:", x_test.shape)
# 训练模型,返回一个函数f()使得 y = f(x)
f = main(x_train, y_train)
y_train_pred = f(x_train) # 训练集 预测值
std = evaluate(y_train, y_train_pred) # 使用训练集评估模型
print('训练集 预测值与真实值的标准差:{:.1f}'.format(std))
y_test_pred = f(x_test) # 测试集 预测值
std = evaluate(y_test, y_test_pred) # 使用测试集评估模型
print('测试集 预测值与真实值的标准差:{:.1f}'.format(std))
# 显示结果
# plt.plot(x_train, y_train, 'r.') # 训练集
plt.plot(x_test, y_test, 'b.') # 测试集
plt.plot(x_test, y_test_pred, 'k.') # 测试集 的 预测值
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.title('Linear Regression')
plt.legend(['train', 'test', 'pred'])
plt.show()高斯基函数源代码:
查看代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def load_data(filename): # 载入数据
xys = []
with open(filename, 'r') as f:
for line in f:
xys.append(map(float, line.strip().split()))
xs, ys = zip(*xys)
return np.asarray(xs), np.asarray(ys)
def gaussian_basis(x, feature_num=10):
centers = np.linspace(0, 25, feature_num)
width = 1.0 * (centers[1] - centers[0])
x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=1)
x = np.concatenate([x] * feature_num, axis=1)
out = (x - centers) / width
ret = np.exp(-0.5 * out ** 2)
return ret
def main(x_train, y_train): # 训练模型,并返回从x到y的映射。
basis_func = gaussian_basis # shape(N, 1)的函数
phi0 = np.expand_dims(np.ones_like(x_train), axis=1) # shape(N,1)大小的全1 array
phi1 = basis_func(x_train) # 将x_train的shape转换为(N, 1)
phi = np.concatenate([phi0, phi1], axis=1) # phi.shape=(300,2) phi是增广特征向量的转置
print("phi shape = ", phi.shape)
# 使用最小二乘法优化w
w = np.dot(np.linalg.pinv(phi), y_train) # np.linalg.pinv(phi)求phi的伪逆矩阵(phi不是列满秩) w.shape=[2,1]
print("参数 w = ", w)
def f(x):
phi0 = np.expand_dims(np.ones_like(x), axis=1)
phi1 = basis_func(x)
phi = np.concatenate([phi0, phi1], axis=1)
y = np.dot(phi, w) # 矩阵乘法
return y
return f
def evaluate(ys, ys_pred): # 评估模型
std = np.sqrt(np.mean(np.abs(ys - ys_pred) ** 2))
return std
if __name__ == '__main__': # 程序主入口(建议不要改动以下函数的接口)
train_file = 'train.txt'
test_file = 'test.txt'
# 载入数据
x_train, y_train = load_data(train_file)
x_test, y_test = load_data(test_file)
print("x_train shape:", x_train.shape)
print("x_test shape:", x_test.shape)
# 训练模型,返回一个函数f()使得 y = f(x)
f = main(x_train, y_train)
y_train_pred = f(x_train) # 训练集 预测值
std = evaluate(y_train, y_train_pred) # 使用训练集评估模型
print('训练集 预测值与真实值的标准差:{:.1f}'.format(std))
y_test_pred = f(x_test) # 测试集 预测值
std = evaluate(y_test, y_test_pred) # 使用测试集评估模型
print('测试集 预测值与真实值的标准差:{:.1f}'.format(std))
# 显示结果
# plt.plot(x_train, y_train, 'r.') # 训练集
plt.plot(x_test, y_test, 'b.') # 测试集
plt.plot(x_test, y_test_pred, 'k.') # 测试集 的 预测值
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.title('Linear Regression')
plt.legend(['train', 'test', 'pred'])
plt.show()