xxl-rpc源码阅读笔记之RpcProvider
一直对RPC这个名词非常好奇,xxl里面为RPC提供了一个实现--xxl-rpc。轻量级、分布式,阅读源码以后觉得收获非常大。整理最近看的过程,形成笔记记录下来。关于RPC的介绍可以参考这篇博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/twinhead/p/9900605.html
xxl-rpc可以分为服务提供者和服务消费者,这里咱们先讲RpcProvider。总的一个系统构成如下图所示:
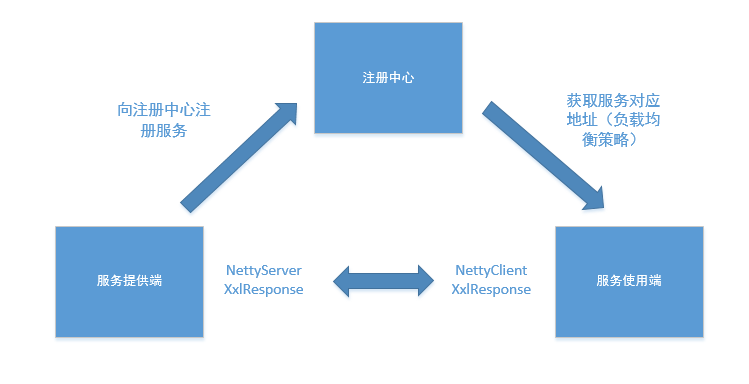
哈哈哈,画了一个很丑的图图。
从应用开始,官方提供了一个无框架版的RPC服务端模板,主要代码主要是初始化RPC服务提供端:
// init
XxlRpcProviderFactory providerFactory = new XxlRpcProviderFactory();
providerFactory.setServer(NettyServer.class);
providerFactory.setSerializer(HessianSerializer.class);
providerFactory.setCorePoolSize(-1);
providerFactory.setMaxPoolSize(-1);
providerFactory.setIp(null);
providerFactory.setPort(7080);
providerFactory.setAccessToken(null);
providerFactory.setServiceRegistry(null);
providerFactory.setServiceRegistryParam(null);
// add services
providerFactory.addService(DemoService.class.getName(), null, new DemoServiceImpl());
// start
providerFactory.start();
while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
TimeUnit.HOURS.sleep(1);
}
// stop
providerFactory.stop();
这里的DemoServiceImpl就是服务端提供的远端调用实现。里面只有一个方法就是返回一个UserDto对象。这里我们看到providerFactory的一些属性,包括底层的通信方案是使用的NettyServer、序列化方案是使用的Hessian。而设置的注册中心的方案是提供了三种方案的,包括本地注册、xxl-registry注册、Zookeeper三种。作者推荐的是xxl-registry方案,源码之前有看过,源码的笔记可以看我的另一篇博客。CorePoolSize、MaxPoolSize是NettyServer接收请求后处理请求的线程池。IP、Port是服务提供的地址。
这里咱们看看start()方法的代码,其实这里只实现了两个功能:向注册中心注册和启动NettyServer:
this.serializerInstance = serializer.newInstance();
// start server
serviceAddress = IpUtil.getIpPort(this.ip, port);
serverInstance = server.newInstance();
serverInstance.setStartedCallback(new BaseCallback() { // serviceRegistry started
@Override
public void run() throws Exception {
// start registry
if (serviceRegistry != null) {
serviceRegistryInstance = serviceRegistry.newInstance();
serviceRegistryInstance.start(serviceRegistryParam);
if (serviceData.size() > 0) {
serviceRegistryInstance.registry(serviceData.keySet(), serviceAddress);
}
}
}
});
serverInstance.setStopedCallback(new BaseCallback() { // serviceRegistry stoped
@Override
public void run() {
// stop registry
if (serviceRegistryInstance != null) {
if (serviceData.size() > 0) {
serviceRegistryInstance.remove(serviceData.keySet(), serviceAddress);
}
serviceRegistryInstance.stop();
serviceRegistryInstance = null;
}
}
});
serverInstance.start(this);
注册中心因此保留了键值对:服务名称(接口名)与提供该服务的地址链表。
NettyServer这里有两种实现方案,netty与netty_Http方案。Netty的配置可以去Netty的文档找,这里就不贴了。主要是xxl-rpc这里设置的序列化方案和Netty读取数据后的处理过程NettyServerHandler。
.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(0,0, Beat.BEAT_INTERVAL*3, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) // beat 3N, close if idle
.addLast(new NettyDecoder(XxlRpcRequest.class, xxlRpcProviderFactory.getSerializerInstance()))
.addLast(new NettyEncoder(XxlRpcResponse.class, xxlRpcProviderFactory.getSerializerInstance()))
.addLast(new NettyServerHandler(xxlRpcProviderFactory, serverHandlerPool));
IdleStateHandler是Netty的心跳。这里咱们需要重点看看Netty服务器接收到数据后是如何进行处理的:
@Override
public void channelRead0(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx, final XxlRpcRequest xxlRpcRequest) throws Exception {
// filter beat
if (Beat.BEAT_ID.equalsIgnoreCase(xxlRpcRequest.getRequestId())){
logger.debug(">>>>>>>>>>> xxl-rpc provider netty server read beat-ping.");
return;
}
// do invoke
try {
serverHandlerPool.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// invoke + response
XxlRpcResponse xxlRpcResponse = xxlRpcProviderFactory.invokeService(xxlRpcRequest);
ctx.writeAndFlush(xxlRpcResponse);
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
// catch error
XxlRpcResponse xxlRpcResponse = new XxlRpcResponse();
xxlRpcResponse.setRequestId(xxlRpcRequest.getRequestId());
xxlRpcResponse.setErrorMsg(ThrowableUtil.toString(e));
ctx.writeAndFlush(xxlRpcResponse);
}
}
注意到这么一行
XxlRpcResponse xxlRpcResponse = xxlRpcProviderFactory.invokeService(xxlRpcRequest);
xxlRpcRequest是服务端发送的请求,大体里面填充了要请求那个接口、具体哪个方法,其中会包含一个ID值,依据ID进行请求的返回。而xxlRpcResponse则是返回到客户端的内容,主要包括请求ID、执行结果,通过Netty回传到客户端。invokeService方法根据请求的接口、方法,从serviceData中取出对应的实现(如开头的new DemoServiceImpl()),通过反射得到运行结果,并将结果回传。
public XxlRpcResponse invokeService(XxlRpcRequest xxlRpcRequest) {
// make response
XxlRpcResponse xxlRpcResponse = new XxlRpcResponse();
xxlRpcResponse.setRequestId(xxlRpcRequest.getRequestId());
// match service bean
String serviceKey = makeServiceKey(xxlRpcRequest.getClassName(), xxlRpcRequest.getVersion());
Object serviceBean = serviceData.get(serviceKey);
// valid
if (serviceBean == null) {
xxlRpcResponse.setErrorMsg("The serviceKey["+ serviceKey +"] not found.");
return xxlRpcResponse;
}
if (System.currentTimeMillis() - xxlRpcRequest.getCreateMillisTime() > 3*60*1000) {
xxlRpcResponse.setErrorMsg("The timestamp difference between admin and executor exceeds the limit.");
return xxlRpcResponse;
}
if (accessToken!=null && accessToken.trim().length()>0 && !accessToken.trim().equals(xxlRpcRequest.getAccessToken())) {
xxlRpcResponse.setErrorMsg("The access token[" + xxlRpcRequest.getAccessToken() + "] is wrong.");
return xxlRpcResponse;
}
try {
// invoke
Class<?> serviceClass = serviceBean.getClass();
String methodName = xxlRpcRequest.getMethodName();
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = xxlRpcRequest.getParameterTypes();
Object[] parameters = xxlRpcRequest.getParameters();
Method method = serviceClass.getMethod(methodName, parameterTypes);
method.setAccessible(true);
Object result = method.invoke(serviceBean, parameters);
/*FastClass serviceFastClass = FastClass.create(serviceClass);
FastMethod serviceFastMethod = serviceFastClass.getMethod(methodName, parameterTypes);
Object result = serviceFastMethod.invoke(serviceBean, parameters);*/
xxlRpcResponse.setResult(result);
} catch (Throwable t) {
// catch error
logger.error("xxl-rpc provider invokeService error.", t);
xxlRpcResponse.setErrorMsg(ThrowableUtil.toString(t));
}
return xxlRpcResponse;
}
至此服务端生成客户端请求的内容,并将内容封装在XxlRpcResponse中通过Netty回传。
= =发现一个比我写的好很多的博客。。。地址是:https://www.jianshu.com/p/081a84641806
看我这个云里雾里的可以去看这个博客哈。



