2020软件工程作业03
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | 2018级软件工程 - 中南林业科技大学涉外学院 |
|---|---|
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | |
| 这个作业的目标 | 通过习题熟悉PSP流程 |
| 其他参考 |
【1】数独~编程作业 |
PSP表格
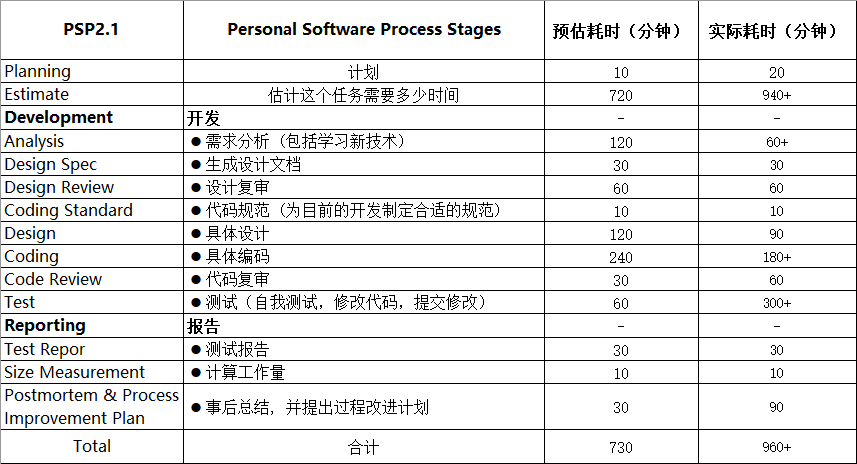
注:加号代表在实际操作时未准确计时,只是一个保守的估计。
解题思路
作为一个算法菜鸡,看完题目的第一感觉就是.....没看懂。反复阅读后才冒出一个暴力扫描的想法。正当准备开始编码的时候,我突然看到题目描述中提到 “输入保证有且仅有一个解” ,我才意识到,数独宫格是拥有唯一解的(或者只有少数几个数字不同)。这意味着若是开始的几个格子未能填入正确答案,则后面的格子会出现无数可填的情况(又暴露了没玩过数独的事实😱)。若是出现了无数可填的情况则说明之前有答案是错误的,则需要回溯。可以用DFS来逐个试探答案。最终走到最后一个格子时。意味着所有的格子都已填入了正确答案,此时就可以把输出了。
设计实现
Sudoku.java
1 import java.io.*; 2 3 public class Sudoku { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 String inputPath = ""; 6 String outputPath = ""; 7 Integer numOfBoard = null; 8 Integer size = null; 9 for(int i=0;i<args.length;i++){ 10 if(args[i].equals("-i")){ 11 inputPath = args[i+1]; 12 } 13 if(args[i].equals("-o")){ 14 outputPath = args[i+1]; 15 } 16 if(args[i].equals("-m")){ 17 size = Integer.valueOf(args[i+1]); 18 } 19 if(args[i].equals("-n")){ 20 numOfBoard = Integer.valueOf(args[i+1]); 21 } 22 } 23 24 if(inputPath.equals("") && outputPath.equals("") && numOfBoard == null && size == null){ 25 System.out.println("Parameter Error."); 26 return; 27 } 28 29 try { 30 SudokuUtil sudokuUtil = new SudokuUtil(size, numOfBoard, outputPath, inputPath); 31 sudokuUtil.run(); 32 }catch (Exception e){ 33 System.out.println("Parameter Error,Please Check Your Format."); 34 } 35 36 } 37 }
首先是主函数入口类,这里主要包括的是输入参数验证以及错误处理。
SudokuUtil.java
1 package New.Learn; 2 3 import java.io.*; 4 import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; 5 import java.util.ArrayList; 6 7 public class SudokuUtil { 8 9 Integer size; 10 Integer numOfBoard; 11 String outputPath; 12 String inputPath; 13 ArrayList<Integer[][]> arrayNumList = new ArrayList<Integer[][]>(); 14 //ArrayList用于容纳多个数独盘的结果 15 16 public Integer getSize() { 17 return size; 18 } 19 20 public Integer getNumOfBoard() { 21 return numOfBoard; 22 } 23 24 public String getOutputPath() { 25 return outputPath; 26 } 27 28 public String getInputPath() { 29 return inputPath; 30 } 31 32 SudokuUtil(Integer size, Integer numOfBoard, String outputPath, String inputPath) { 33 this.size = size; 34 this.numOfBoard = numOfBoard; 35 this.outputPath = outputPath; 36 this.inputPath = inputPath; 37 } 38 39 public String inputFile(String filePath) throws IOException { 40 File file = new File(filePath); 41 if (file.isFile() && file.exists()) { 42 InputStreamReader read = 43 new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file), StandardCharsets.UTF_8); 44 BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(read); 45 String lineTxt = null; 46 StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(); 47 while ((lineTxt = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) { 48 result.append(lineTxt); 49 result.append("\n"); 50 } 51 read.close(); 52 return result.toString(); 53 } else { 54 System.out.println("No such file or directory"); 55 System.exit(0); 56 } 57 return null; 58 } 59 60 public void outputFile(Integer size, ArrayList<Integer[][]> arrayNum, String filePath) throws IOException { 61 BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(filePath)); 62 for (Integer[][] num : arrayNum) { 63 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { 64 for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) { 65 bufferedWriter.write(num[i][j].toString()); 66 bufferedWriter.write(" "); 67 } 68 bufferedWriter.newLine(); 69 } 70 bufferedWriter.newLine(); 71 } 72 bufferedWriter.close(); 73 } 74 75 public ArrayList<Integer[][]> inData(Integer numOfBoard, Integer size, String input) { 76 //分割多个数独盘 77 String[] board = input.split("\n\n"); 78 ArrayList<Integer[][]> inputArrayNum = new ArrayList<Integer[][]>(); 79 80 for (int k = 0; k < numOfBoard; k++) { 81 Integer[][] num = new Integer[size][size]; 82 83 String[] line = board[k].split("\n"); 84 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { 85 String[] single = line[i].split(" "); 86 for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) { 87 num[i][j] = Integer.valueOf(single[j]); 88 } 89 } 90 inputArrayNum.add(num); 91 } 92 return inputArrayNum; 93 } 94 95 public void pr(Integer size, Integer[][] num) { 96 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { 97 for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) { 98 System.out.print(num[i][j]); 99 System.out.print(" "); 100 } 101 System.out.print("\n"); 102 } 103 System.out.println("-----------------------"); 104 } 105 106 public boolean check(Integer size, Integer[][] num, Integer tar, Integer col, Integer line) { 107 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { 108 if (num[i][line].equals(tar) || num[col][i].equals(tar)) { 109 return false; 110 } 111 } 112 if (size == 4) { 113 //可以把宫格看做是一个大的块 114 int cellx = line / 2; 115 int celly = col / 2; 116 117 for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) { 118 for (int k = 0; k < 2; k++) { 119 if (num[celly * 2 + j][cellx * 2 + k].equals(tar)) { 120 return false; 121 } 122 } 123 } 124 } else if (size == 6) { 125 int cellx = line / 3; 126 int celly = col / 2; 127 128 for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) { 129 for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++) { 130 if (num[celly * 2 + j][cellx * 3 + k].equals(tar)) { 131 return false; 132 } 133 } 134 } 135 } else if (size == 8) { 136 int cellx = line / 2; 137 int celly = col / 4; 138 139 for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) { 140 for (int k = 0; k < 2; k++) { 141 if (num[celly * 4 + j][cellx * 2 + k].equals(tar)) { 142 return false; 143 } 144 } 145 } 146 } else if (size == 9) { 147 int cellx = line / 3; 148 int celly = col / 3; 149 150 for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) { 151 for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++) { 152 if (num[celly * 3 + j][cellx * 3 + k].equals(tar)) { 153 return false; 154 } 155 } 156 } 157 } 158 return true; 159 } 160 161 public void write(Integer size, Integer[][] num, Integer wy, Integer wx) { 162 Integer nextx = wx + 1; 163 Integer nexty = wy; 164 165 if (nextx >= size) { 166 nextx = 0; 167 nexty++; 168 } 169 170 if (wy.equals(size) && wx.equals(0)) { 171 pr(size, num); 172 Integer[][] tempArray = new Integer[size][size]; 173 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { 174 for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) { 175 tempArray[i][j] = num[i][j]; 176 } 177 } 178 //若直接传递num,则该num为递归栈顶值,因为只是传递了num地址 179 //因而需要进行一次深拷贝 180 arrayNumList.add(tempArray); 181 return; 182 } 183 if (!num[wy][wx].equals(0)) { 184 //若该项不为0,则递归走下一步 185 write(size, num, nexty, nextx); 186 } else { 187 for (int x = 1; x <= size; x++) { 188 if (check(size, num, x, wy, wx)) { 189 num[wy][wx] = x; 190 //DFS递归走下一步 191 write(size, num, nexty, nextx); 192 num[wy][wx] = 0; 193 } 194 } 195 196 } 197 198 } 199 200 public void run() throws IOException { 201 String in = inputFile(inputPath); 202 ArrayList<Integer[][]> inArrayNum = inData(numOfBoard, size, in); 203 for (Integer[][] num : inArrayNum) { 204 write(size, num, 0, 0); 205 } 206 outputFile(size, arrayNumList, outputPath); 207 } 208 }
SudokuUtil类是真正的计算数独的部分。方法调用关系如下。
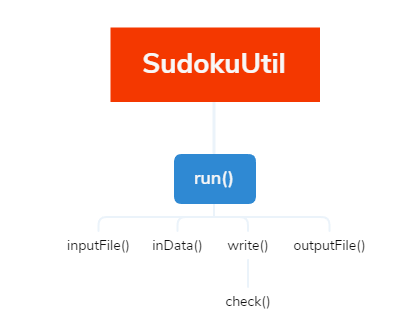
- inputFile 方法是文件读取方法。
- inData 方法是将读取的字符串处理成为数组列表。
- write 方法就是核心算法DFS部分,通过递归回溯生成最终答案。
- check 方法则是用于检测该数字是否能在当前宫格内填入。
- inputFile 方法是文件输出方法。
程序测试
九宫格
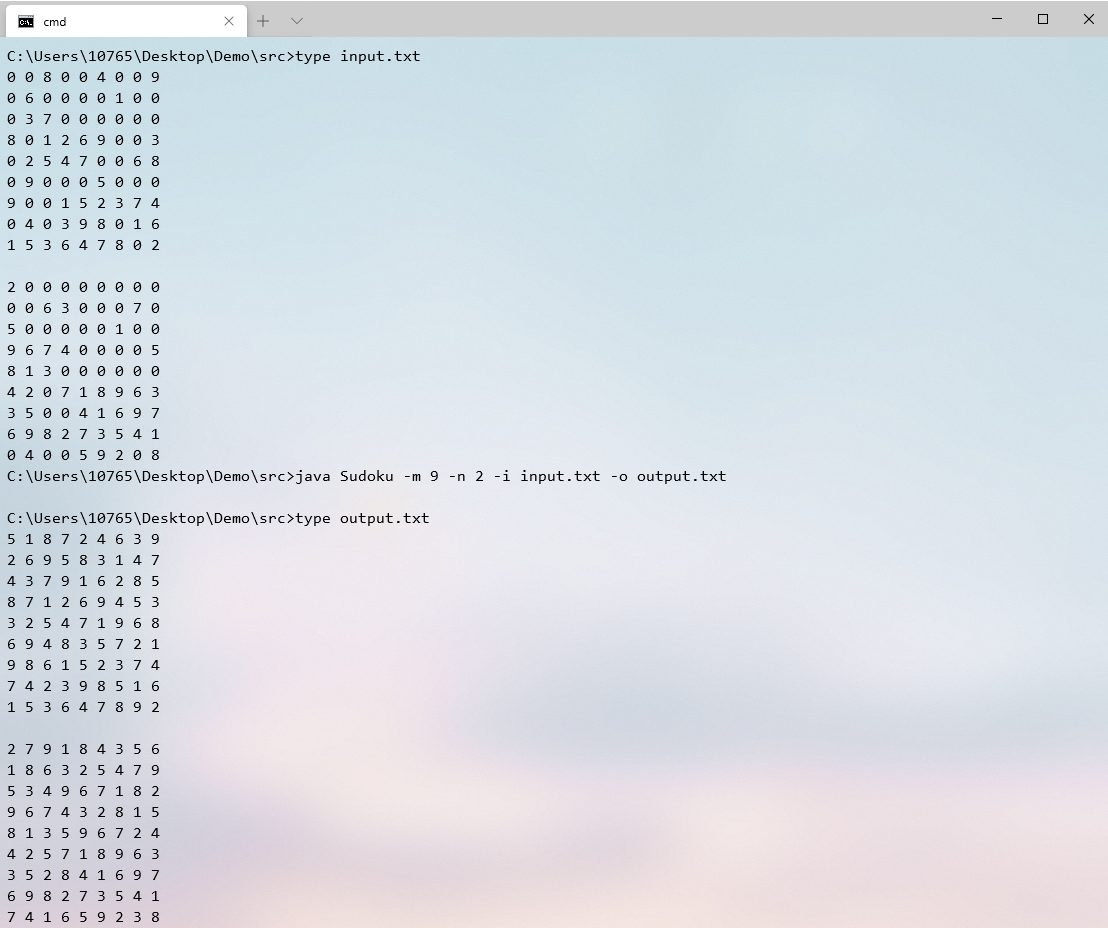
八宫格

七宫格

六宫格
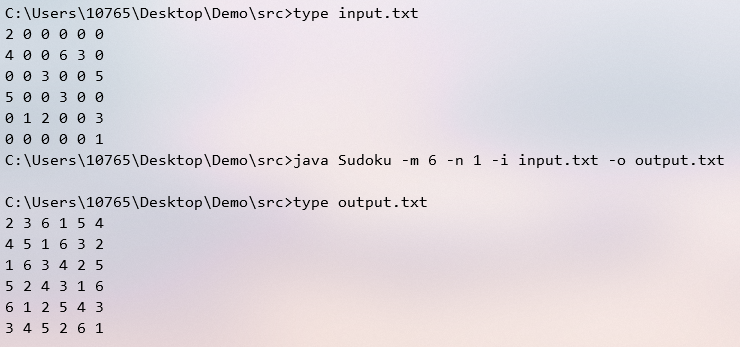
五宫格

四宫格

三宫格

程序性能分析与优化
JProfiler分析结果
关于优化
使用回溯过深的递归调用必然会使用大量的栈空间,这样的算法效率显然是不高的。
根据某个师傅的博客,还是有不少方法可以优过回溯的。可惜的是这位师傅没有自己造线性规划轮子而是调用的库函数。

除此之外,暂时未找到其他更优解
心路历程与收获
这个作业最大的感受就是有点杀鸡用牛刀的感觉。我非常能理解PSP表格中各个项目对应软件开发的各个流程。但我认为PSP更适合做需要长期维护的项目,而不是像这次作业的算法练习题。例如算法题不需要非常详细的设计文档,往往三言两语就能将核心思想交代清楚、算法题不需要反复的review,因为算法题往往目标是更高效的计算某个东西而不是更好的代码可读性(当然这也是非常重要的,但许多算法高手写出来的代码通常可读性较差)和更好的可维护性等等。
回到这道题上,这道题的编码时间其实是非常短的。但是因为递归不太好调试的原因(这也是我不喜欢递归的原因之一),我一步步调试了很久才调出来一些细节问题。期间参考了【2】数独(Sudoku)游戏之我见 判断方法,比我的妙多了🤣,虽然最后没用。而后在做文件IO和核心整合的时候遇到了一个递归后无法传最终值的问题。直到参考了【1】数独~编程作业 这篇文章使用的方法,瞬间明白了,相当于深拷贝之后再传递出来,再递归栈中传递的对象都是传递地址但递归栈再最后弹出时传递的值会回到栈底即初始状态。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号