Java异常2
Java异常2
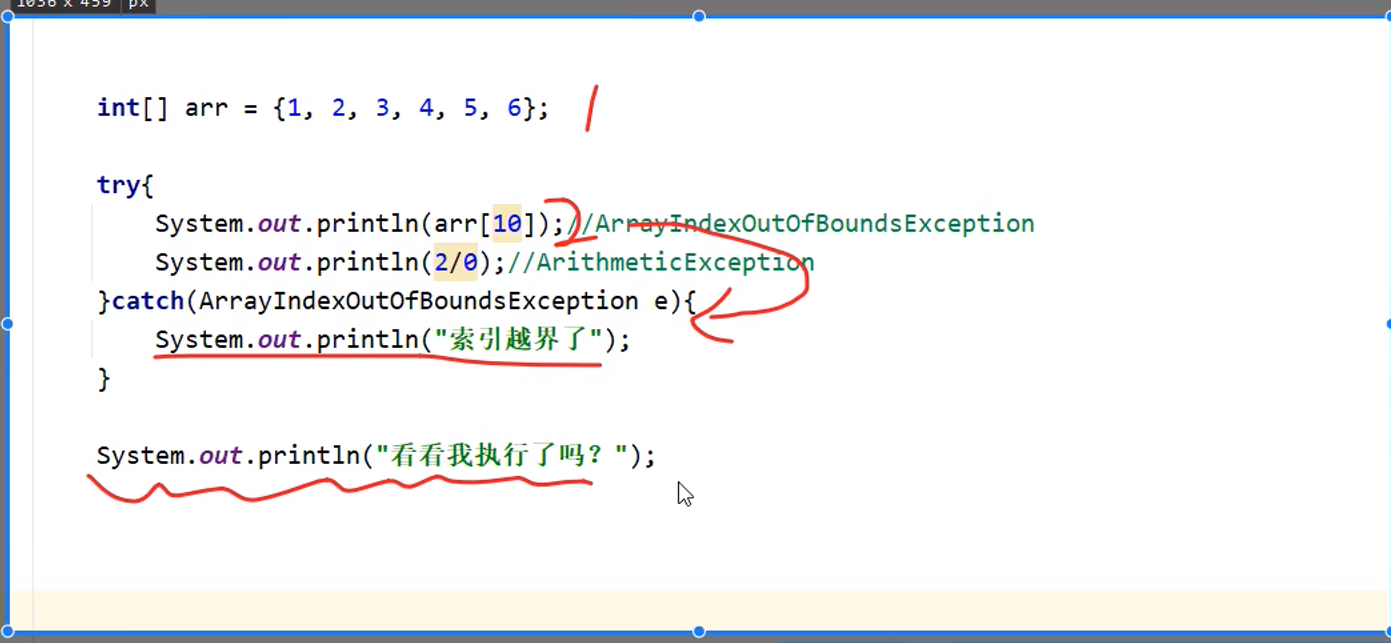
如果try没有遇到问题,怎么执行?
会把try里面所有代码执行完毕,不会执行catch()里面的内容.
public class Main7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
try {
System.out.println(arr[0]);
System.out.println(2 / 1);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("数组越界");
}
System.out.println("看看我执行了吗!!");
}
}
如果try遇到多个问题,怎么执行?
我们要写多个catch与其对应
也就是说在try里面如果发生异常,下面的代码就会被打断,然后执行对应的catch操作,(catch运行完这个语句就结束了)如果我们没有进行这个对应的catch操作,JDK就会自己默认处理.
import java.net.PortUnreachableException;
public class Main6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
try {
System.out.println(arr[100]);
System.out.println(2 / 0);
String s = null;
System.out.println(s.equals("abc"));
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("数组越界");
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("不能除以0");
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("空指针异常");
}
System.out.println("看看我执行了吗!!");
}
}
细节:
如果我们要捕获多个异常,这些异常存在父子关系的话,那么父类一定要写在下面.
在JDK7之后,我们可以在catch中捕获多个异常,中间使用|来进行隔开,表示如果出现了A异常或者B异常的话,采用同一种处理方案.
如果try中遇到的异常没有被捕获?
相当于try...catch代码没起作用,最后还是采用虚拟机默认进行处理.
public class Main7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
try {
System.out.println(2 / 0);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("数组越界");
}
System.out.println("看看我执行了吗!!");
}
}
如果try中遇到了问题,try下面的代码还会执行吗?
下面的代码就不会执行了,直接跳转到对应的catch当中,执行catch里面的语句体,但是如果没有对应的catch与其匹配,那么还是会交给虚拟机默认处理.
public class Main7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
try {
System.out.println(arr[100]);
System.out.println("你好,嘿嘿嘿,看看我执行了吗!!");
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("数组越界");
}
System.out.println("看看我执行了吗!!");
}
}
public class Main7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
try {
System.out.println(2/0);
System.out.println("你好,嘿嘿嘿,看看我执行了吗!!");
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("数组越界");
}
System.out.println("看看我执行了吗!!");
}
}
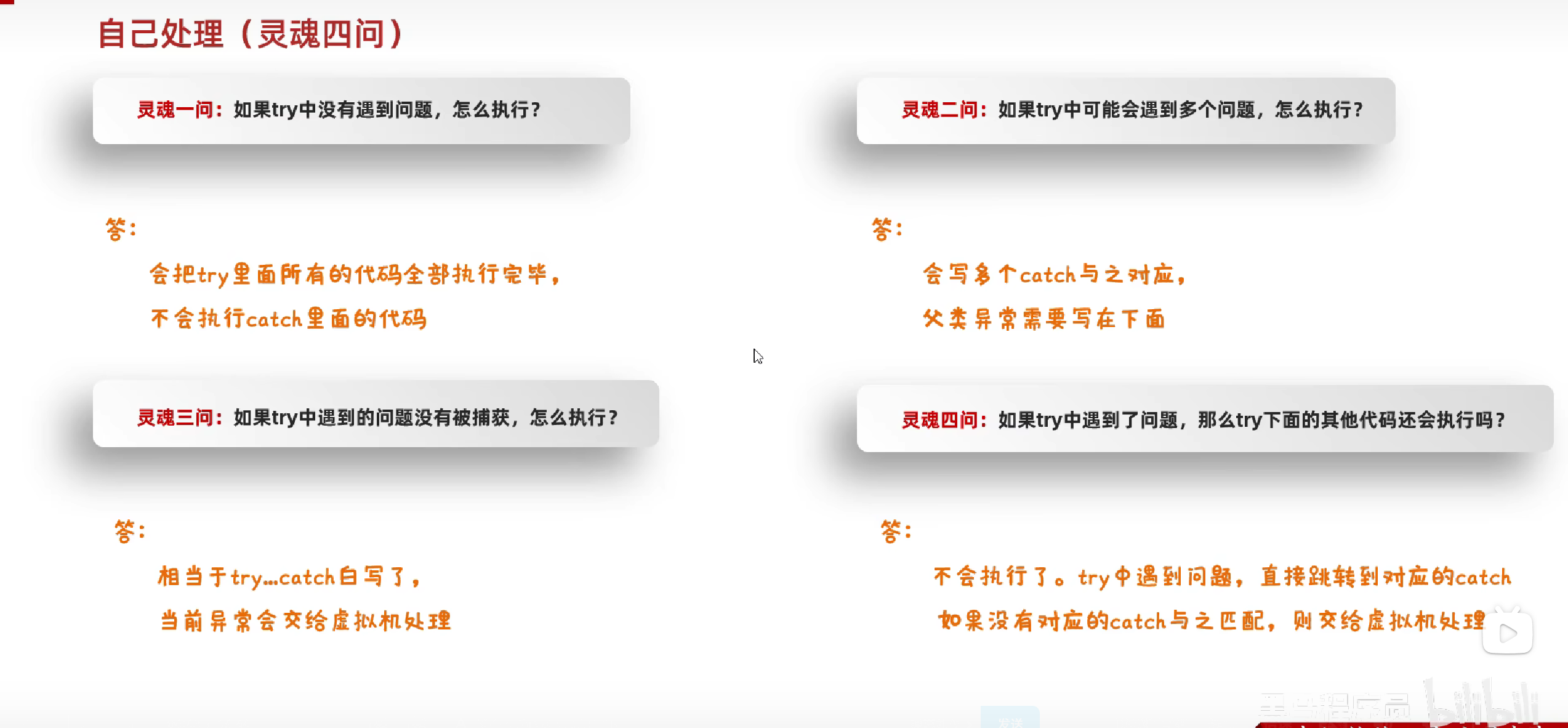
异常中的常见方法
Throwable 的成员方法
按CRTL+L+T可以快速生成异常处理
其中 public void printfStackTrace() 比较常用.细节:仅仅是打印信息,不会停止虚拟机.(以红色字体进行打印.包含的信息最多.)
public class Main7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
try {
System.out.println(arr[100]);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
String str = e.getMessage();//返回详细的字符串信息
System.out.println(str);
String s = e.toString();//返回简短的字符串信息
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("看看我执行了吗!!");
}
}
public class Main7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
try {
System.out.println(arr[100]);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
e.printStackTrace();//把错误信息输出到控制台
}
System.out.println("看看我执行了吗!!");
}
}

错误输出:信息为红色,可能不符合程序的从上向下运行.

抛出异常

手动创建一个异常对象,并且把这个异常交给方法的调用者处理
此时方法就会结束,下面的代码就不会执行了.
就是自己在方法内进行异常处理,并且抛出,并且返回到调用处.
import java.util.Random;
public class Main4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// int a[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
int a[] = null;
// int a[]={};
int ans = 0;
try {
ans = getmax(a);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("数组越界");
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("空指针异常");
}
System.out.println(ans);
//但是这个方法可能会出现异常.
}
public static int getmax(int[] arr)/* throws NullPointerException,ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException*/ {//运行时异常throws可以不写
if (arr == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if (arr.length == 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
int max = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] > max) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
return max;
}
}
小结

综合练习
抛出:写在方法里面
捕获:写在方法的调用处

Girlfriend类
public class Girlfriend {
private String name;
private int age;
public Girlfriend() {
}
public Girlfriend(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
/**
* 获取
*
* @return name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* 设置
*
* @param name
*/
public void setName(String name) throws RuntimeException {
if (name.length() < 3 || name.length() > 10) {
throw new RuntimeException();//名字长度不正确抛出运行时异常
}
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 获取
*
* @return age
*/
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
/**
* 设置
*
* @param age
*/
public void setAge(int age)throws RuntimeException{
if (age<18||age>40)
{
throw new RuntimeException();//年龄不正确抛出运行时异常
}
this.age = age;
}
public String toString() {
return "Girlfriend{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}";
}
}
Main方法
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Girlfriend one = new Girlfriend();
String name;
String ageStr;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
try {
System.out.println("请输入您女朋友的姓名:");
name = sc.nextLine();
one.setName(name);//可能出现姓名小于3个字符或者姓名大于10个字符的异常
System.out.println("请输入您女朋友的年龄");
ageStr = sc.nextLine();
int age = Integer.parseInt(ageStr);//可能出现String不是数字的异常
one.setAge(age);//可能出现age不在18-40数之间的异常
//运行的这里直接跳出循环
break;
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("年龄的输入有误,请输入数字!!");
//继续下一轮循环
continue;
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
System.out.println("姓名的长度或者年龄的范围有误请检查!!!");
continue;
}
}
System.out.println(one);
}
}
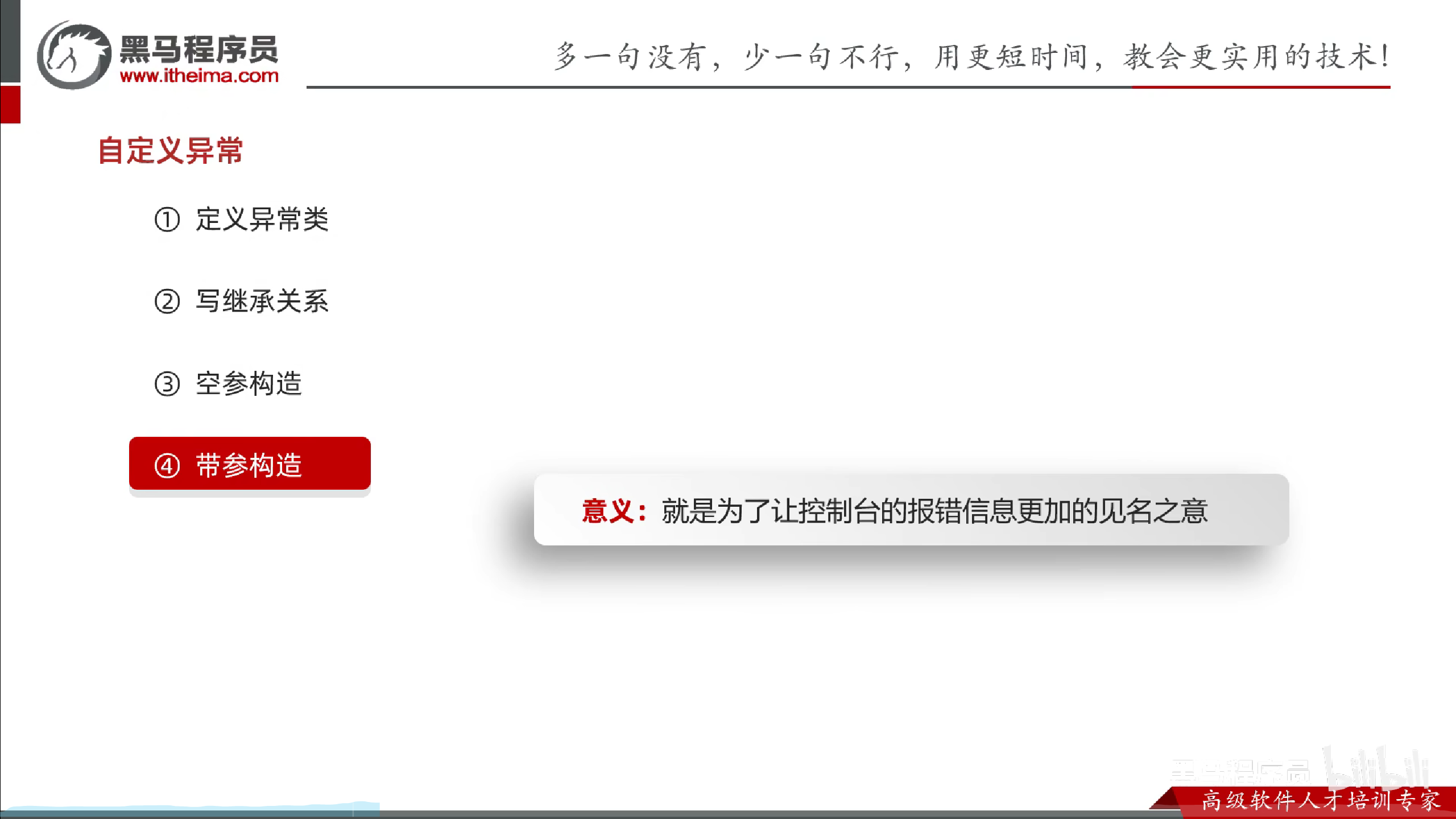
自定义异常
意义:就是为了让控制台的报错信息更加的见名之意.
- 定义异常类
- 写继承关系
- 空参构造
- 带参构造

AgeOutOfBoundsException
package demo01;
public class AgeOutOfBoundsException extends RuntimeException{
public AgeOutOfBoundsException() {
}
public AgeOutOfBoundsException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
NameFormatExcepton
package demo01;
public class NameFormatExcepton extends RuntimeException{
public NameFormatExcepton() {
}
public NameFormatExcepton(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
女朋友类
package demo01;
public class Girlfriend {
private String name;
private int age;
public Girlfriend() {
}
public Girlfriend(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
/**
* 获取
*
* @return name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* 设置
*
* @param name
*/
public void setName(String name){
if (name.length() < 3 || name.length() > 10) {
throw new NameFormatExcepton(name+"姓名长度有误请输入长度为3-10的名字");//名字长度不正确抛出相应的异常
}
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 获取
*
* @return age
*/
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
/**
* 设置
*
* @param age
*/
public void setAge(int age){
if (age<18||age>40)
{
throw new AgeOutOfBoundsException(age+"年龄超出范围");//年龄不正确抛出运行时异常
}
this.age = age;
}
public String toString() {
return "Girlfriend{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}";
}
}
测试类
package demo01;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Girlfriend one = new Girlfriend();
String name;
String ageStr;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
try {
System.out.println("请输入您女朋友的姓名:");
name = sc.nextLine();
one.setName(name);//可能出现姓名小于3个字符或者姓名大于10个字符的异常
System.out.println("请输入您女朋友的年龄");
ageStr = sc.nextLine();
int age = Integer.parseInt(ageStr);//可能出现String不是数字的异常
one.setAge(age);//可能出现age不在18-40数之间的异常
//运行的这里直接跳出循环
break;
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
//继续下一轮循环
continue;
} catch (AgeOutOfBoundsException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
continue;
}
catch (NameFormatExcepton e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
continue;
}
}
System.out.println(one);
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号