Java--异常
Java--异常
异常

异常的分类
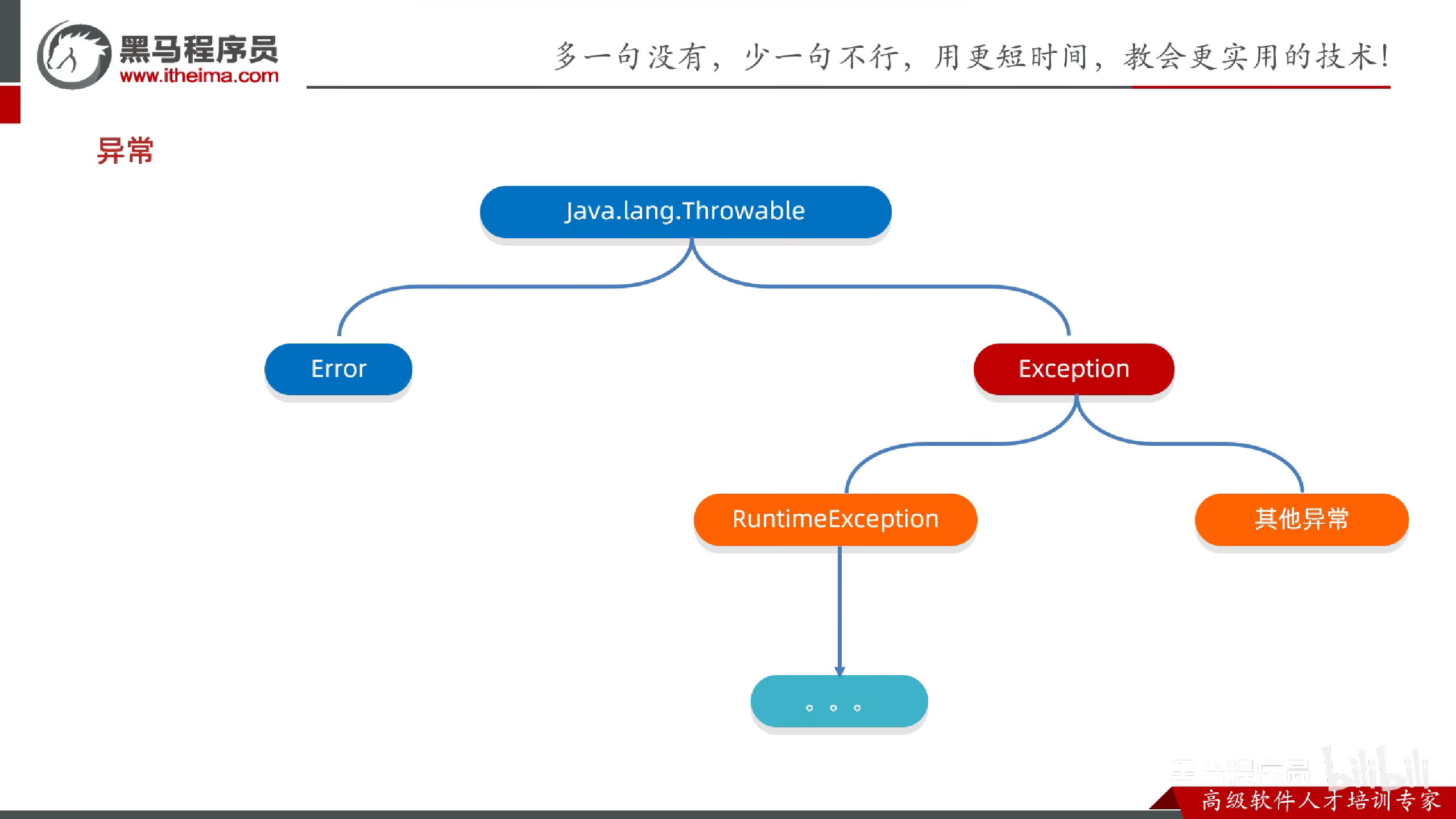
Error

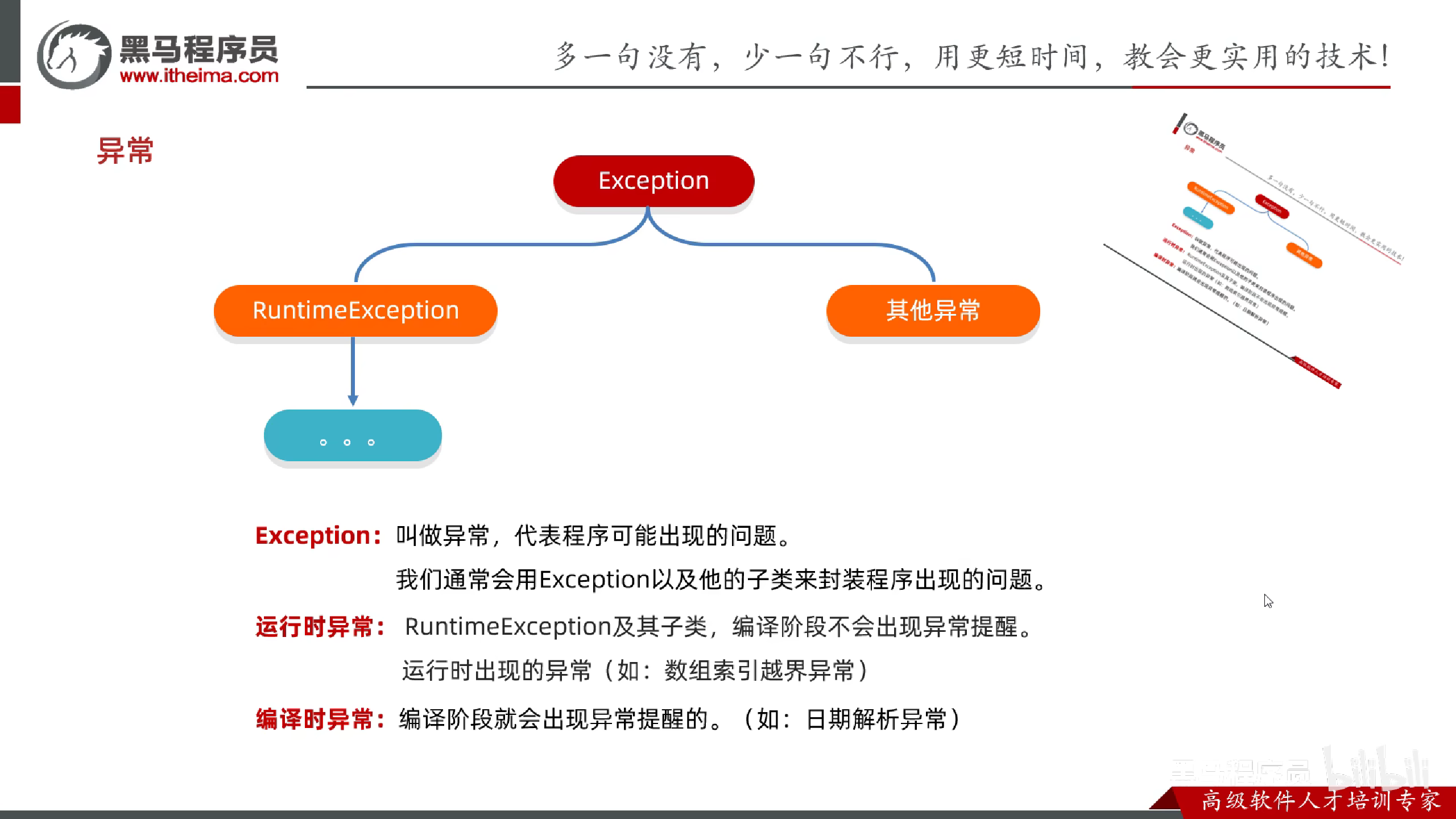
Exception
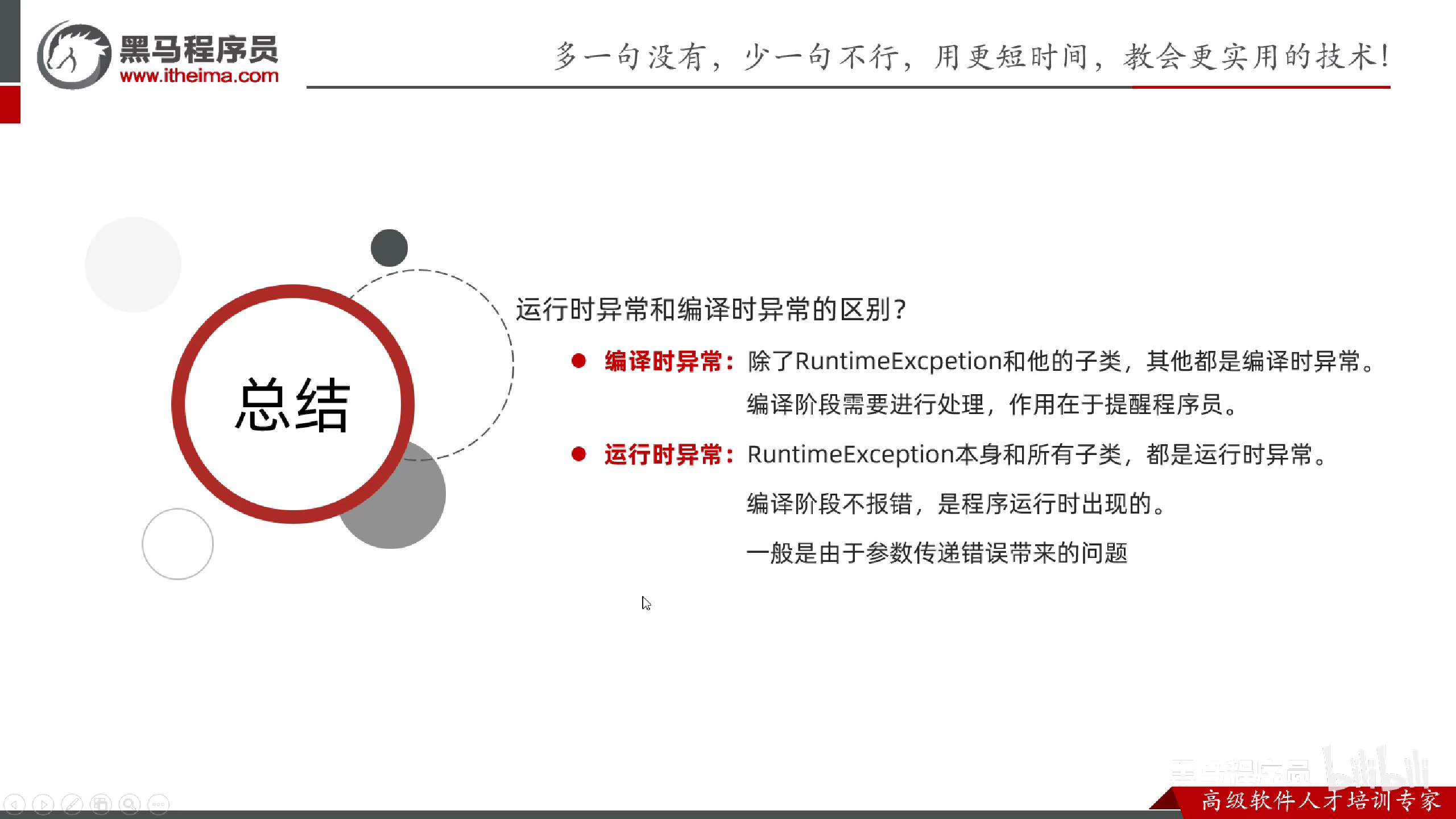
总结
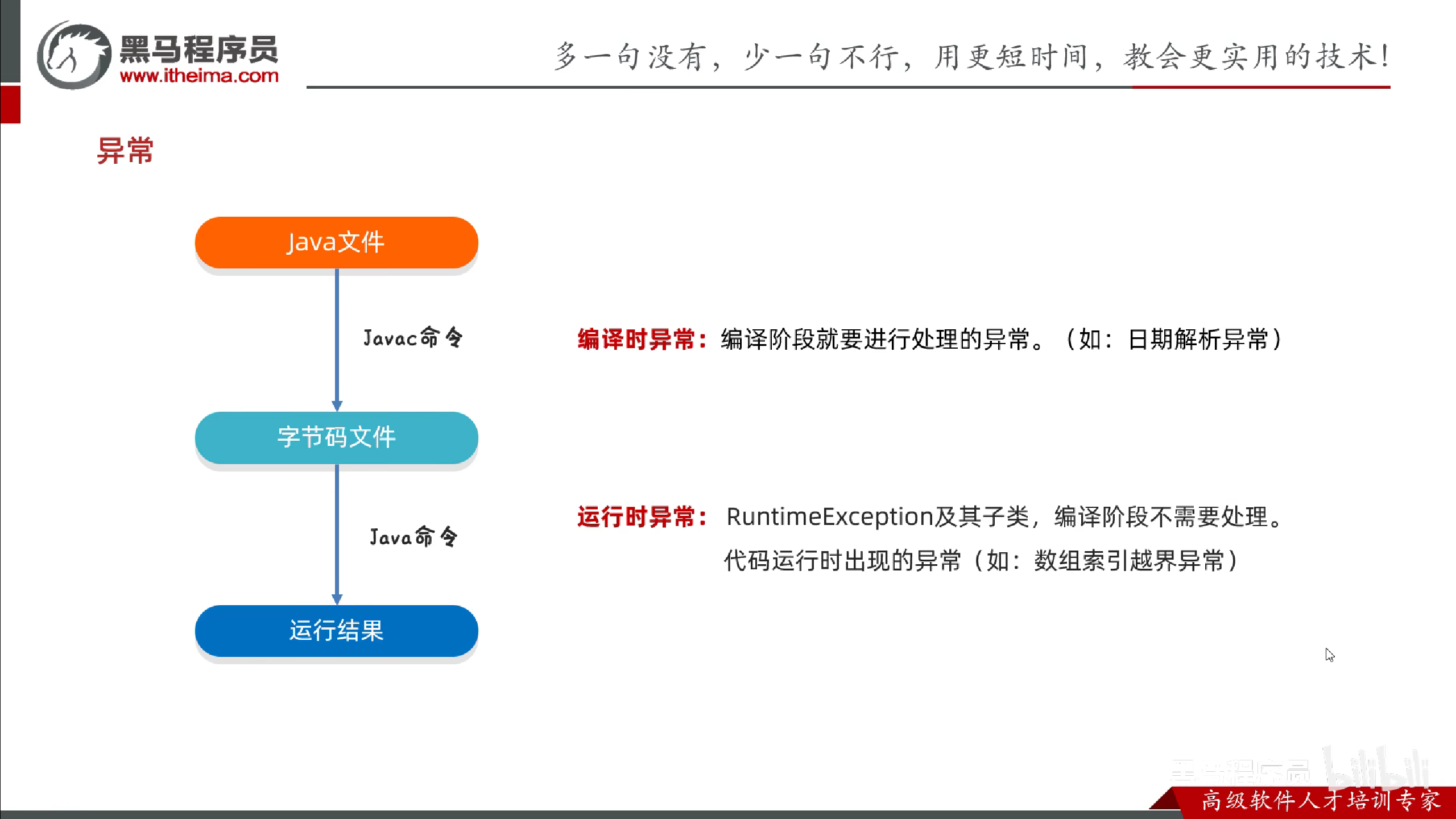
编译时期异常和运行时期异常
编译时期异常
在编译阶段,必须要手动处理,否则代码报错.
运行时期异常
在编译时期不需要处理,是代码运行时出现的异常.
区别
异常的作用
异常作用1:异常是用来查询bug的关键信息.
异常作用2:异常作为方法内部的一种特殊返回值,以便得知调用者底层的执行情况.

异常可以返回调用处这样就可以让调用处自己处理,或者打印在控制台上面.
代码示例
Student类
public class Student {
private int age;
public Student(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Student() {
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
if (age < 18 || age > 40) {
throw new RuntimeException();//抛出一个运行时异常
} else {
this.age = age;
}
}
}
Main类
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student one = new Student();
one.setAge(50);
}
}
异常的处理方式
- JVM默认处理
- 自己处理
- 抛出异常
JVM默认处理方式

public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("你好");
System.out.println("小明");
System.out.println(2 / 0);
System.out.println("我是小黑");
}
}
自己处理(捕获异常)

好处:可以让程序继续向下执行,不会停止.
public class Main2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
try {
System.out.println(arr[6]);//数组越界产生异常
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {//如果出现了ArrayIndexOutofBoundsException异常,我该如何处理
//此处出现了异常,程序就会在这里创建一个ArrayIndexOutofBoundsException对象
// new ArrayIndexoutofBoundsException();
//拿着这个对象到catch的小括号中对比,看括号中的变量是否可以接收这个对象
//如果能被接收,就表示该异常就被捕获(抓住),执行catch里面对应的代码
//当catch里面所有的代码执行完毕,继续执行try.·.catch体系下面的其他代码
System.out.println("数组越界了");
}
//程序会继续向下执行
System.out.println("你好呀");
/*
*/
}
}

