Java字符串
Java字符串
String的特点
程序当中所有用双引号括起来的东西都说字符串不管有没有生成String类
1. 字符串的内容永不可变(重点)
2.字符串永不可变,所以可以共享使用
3.字符串效果相当于char[]数组,但是底层原理是byte[]字节数组

创建字符串
创建字符串的3+1种方法
构造方法:
1.创建一个空白串
2.用字符数组来创建字符串
3.byte数组来创建字符串
直接创建:
直接使用双引号创建

代码示例
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String();//空构造方法
System.out.println("第一个字符串:" + str1);
char charArray[] = {'A', 'B', 'C', 'D'};
String str2 = new String(charArray);//使用字符数组创建
System.out.println("第二个字符串:" + str2);
byte byteArray[] = {97, 98, 99, 100};
String str3 = new String(byteArray);//使用字节数组创建
System.out.println("第三个字符串:" + str3);
//直接创建(创建的也是String对象)
String str4 = "hello,world!!!";
System.out.println("第4个字符串:" + str4);
}
}
字符串常量池
当程序中直接写上双引号字符串,这个字符串就在字符串常量池中
1.对应基本数据类型==比较的是值的大小
2.对于引用数据类型==比较的是地址值

字符串常量池的内存示意图
1.如果用双引号直接创建字符串对象就会放入池中,并且字符串底层使用byte数组是实现,常量池中的字符串对象是一个指向byte数组的引用.
2.当再次使用双引号直接创建相同的字符串对象会直接把原本已经有的字符串对象赋值给新生成的对象
3.如果使用了new关键字就不会创建在字符串常量池当中了,会在堆当中开辟空间.如果使用字符数组创建会把字符数组转化为byte数组
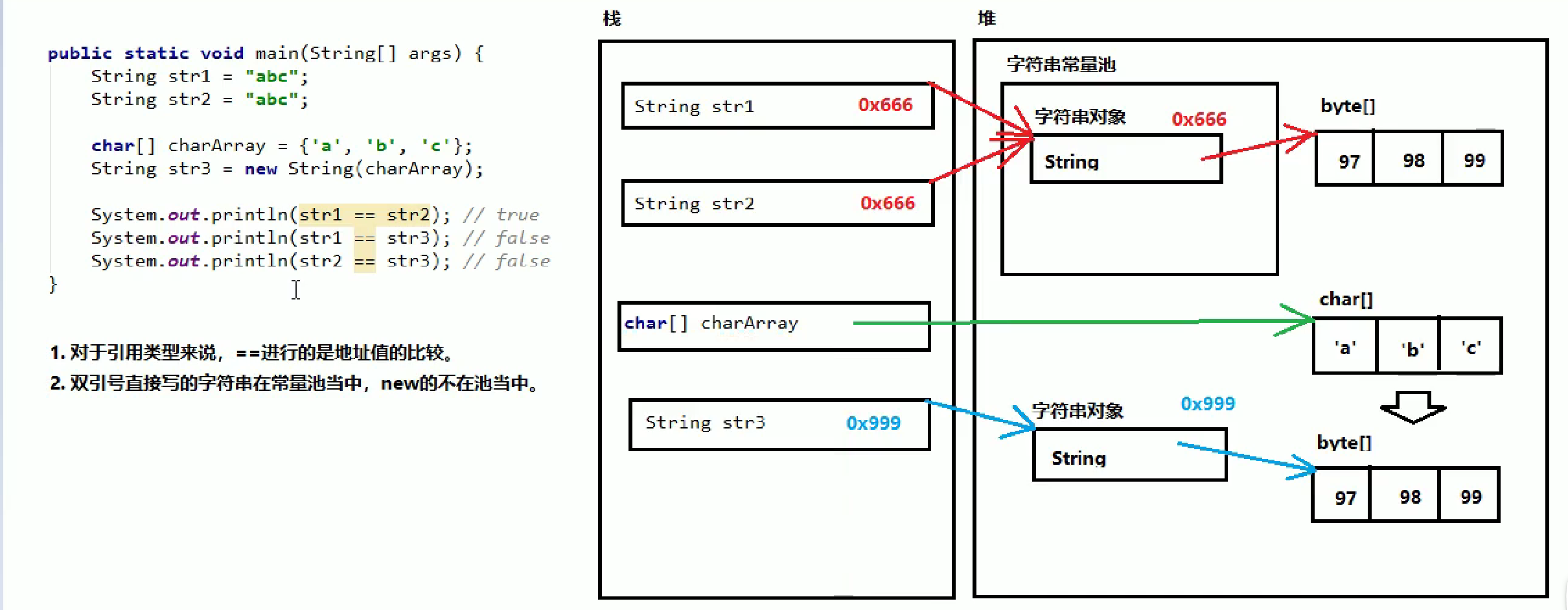
代码示例
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "abc";
String str2 = "abc";
char[] charArry = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
String str3 = new String(charArry);
System.out.println(str1 == str2);
System.out.println(str1 == str3);
System.out.println(str2 == str3);
}
}
字符串比较
字符串比较相关方法
-
==是进行地址值的比较
-
字符串的比较需要用str.equals(),进行比较.字符串相同为true.字符串不同为false
注意事项
- 任何对象队可以用Object接收
- equals具有对称性a.equals(b)和b.equals(a)相同
- 如果比较的是一个常量和一个变量,推荐把常量写在前面
str.equalsIgnoreCase为字符串忽略大小写比较

代码示例
public class Demo01Str {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "abc";
String str2 = "abc";
char[] charArray = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
String str3 = new String(charArray);
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));//true
System.out.println(str2.equals(str3));//true;
System.out.println("abc".equals(str3));//ture
//如果字符串为一个常量和一个变量推荐把常量写在前面
String str4 = "abc";
System.out.println(str4.equals("abc"));//不推荐
System.out.println("abc".equals(str4));//推荐
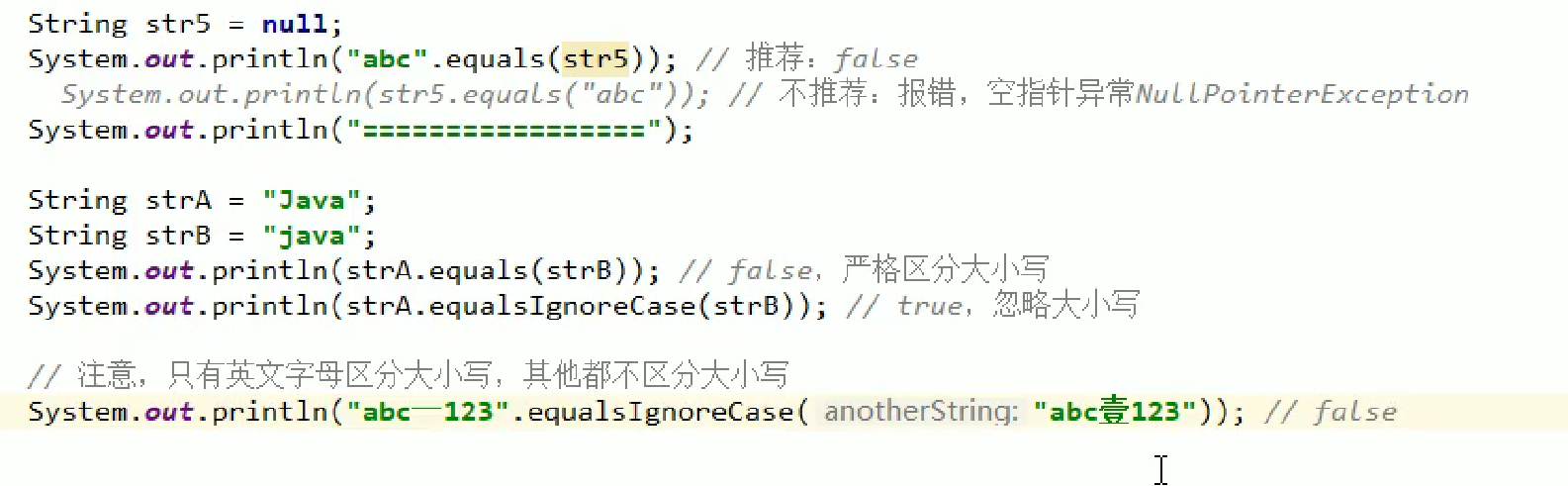
//如果str4=NULL的话不推荐的写法会报错,而推荐的写法是false
str4=null;
// System.out.println(str4.equals("abc"));//不推荐..Cannot invoke "String.equals(Object)" because "str4" is null
System.out.println("abc".equals(str4));//推荐
}
}
public class Demo01Str {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "abc";
String str2 = "abc";
char[] charArray = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
String str3 = new String(charArray);
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));//true
System.out.println(str2.equals(str3));//true;
System.out.println("abc".equals(str3));//ture
//如果字符串为一个常量和一个变量推荐把常量写在前面
String str4 = "abc";
System.out.println(str4.equals("abc"));//不推荐
System.out.println("abc".equals(str4));//推荐
//如果str4=NULL的话不推荐的写法会报错,而推荐的写法是false
str4=null;
// System.out.println(str4.equals("abc"));//不推荐..Cannot invoke "String.equals(Object)" because "str4" is null
System.out.println("abc".equals(str4));//推荐
}
}
字符串忽略大小比较
只忽略英文大小写
代码示例
import java.sql.SQLOutput;
public class Demo01Str {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "abc";
String str2 = "abc";
char[] charArray = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
String str3 = new String(charArray);
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));//true
System.out.println(str2.equals(str3));//true;
System.out.println("abc".equals(str3));//ture
//如果字符串为一个常量和一个变量推荐把常量写在前面
String str4 = "abc";
System.out.println(str4.equals("abc"));//不推荐
System.out.println("abc".equals(str4));//推荐
//如果str4=NULL的话不推荐的写法会报错,而推荐的写法是false
str4=null;
// System.out.println(str4.equals("abc"));//不推荐..Cannot invoke "String.equals(Object)" because "str4" is null
System.out.println("abc".equals(str4));//推荐
String str5="ABC";
//字符串忽略大小比较
System.out.println("ABC".equalsIgnoreCase(str5));//true
System.out.println("Abc".equalsIgnoreCase(str5));//true
}
}
字符串获取
字符串获取函数
- 获取字符串长度
- 连接两个字符串并返回新的字符串(!!!重点!!!在Java中字符串是不可改变的)
- 获取索引位置的单个字符
- 字串查找返回第一次出现的索引,没有返回-1

代码示例
public class Demo02Str {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("jdoljdofjaofeyrowefjljcdxc".length());//获取字符串长度
String str1 = "hello";
String str2 = "world";
String str3 = str1.concat(str2);
//在java中字符串不可改变
System.out.println(str1);//hello
System.out.println(str2);//world
System.out.println(str3);
String str4 = "abcdefg";
for (int i = 0; i < str4.length(); i++) {
char ch = str4.charAt(i);
System.out.println("第" + i + "个位置是字母" + ch);
}
System.out.println("abcdefabcdef".indexOf("bcde"));//1
System.out.println("abcdef".indexOf("aaaa"));//-1
}
}
字符串转换方法
字符串转换函数
-
转换为字符数组
-
转换为字节数组
-
将旧字符串替换为新字符串

代码示例
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//替换为字符数组
//使用toCharArray方法
char[] chars = "abcdef".toCharArray();
System.out.println(chars.length);
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
System.out.println(chars[i]);
}
//替换为字节数组
//使用getBytes方法
byte[] bytes = "ABC".getBytes();
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
System.out.println(bytes[i]);
}
//字符串替换函数
String str1 = "how how how how";
System.out.println(str1);
String str2 = str1.replace("o", "&");
System.out.println(str2);
String str3 = str1.replace("ow", "%");
System.out.println(str3);
}
}
字符串截取
字符串截取方法
splist()方法,将字串切割为若干部分,返回值为一个字符串数组.()里面其实是一个正则表达式.
注意,如果要按照.切分需要两个(反斜杠)

代码示例
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "abc,def,ghi";
String arr1[] = str1.split(",");
for (int i = 0; i < arr1.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr1[i]);
}
System.out.println("===================");
String str2 = "abc def ghi";
String arr2[] = str2.split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr2[i]);
}
System.out.println("===================");
String str3 = "abc.abc.abc";
String arr3[] = str3.split(".");
System.out.println(arr3.length);
for (int i = 0; i < arr3.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr3[i]);
}
System.out.println("===================");
String str4 = "VVV.VVV.VVV";
String arr4[] = str4.split("\\.");//需要两个\\
System.out.println(arr4.length);
for (int i = 0; i < arr4.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr4[i]);
}
}
}
Java字符串练习
题目要求

代码实现
public class toArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
String res = fromArrayToString(arr);
System.out.println(res);
}
public static String fromArrayToString(int[] arr) {
String str = "[";
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (i != arr.length - 1) {
str += "world" + arr[i] + "#";
} else {
str += "world" + arr[i] + "]";
}
}
return str;
}
}
题目要求

代码实现
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Count {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = sc.next();
int countUpper = 0;
int countNumber = 0;
int countLower = 0;
int countOther = 0;
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
if (chars[i] >= 'A' && chars[i] <= 'Z') {
countUpper++;
} else if (chars[i] >= 'a' && chars[i] <= 'z') {
countLower++;
} else if (chars[i] >= '0' && chars[i] <= '9') {
countNumber++;
} else {
countOther++;
}
}
System.out.println("大写字母:" + countUpper);
System.out.println("小写字母:" + countLower);
System.out.println("数字:" + countNumber);
System.out.println("其他字符:" + countOther);
}
}

