2023/02/19刷题+Educational Codeforces Round 143
Educational Codeforces Round 143
链接
Educational Codeforces Round 143
A题
这个题,打比赛的时候看错了,考试结束补题的时候才发现,这个题其实很简单因为我们只能从栈顶获取元素,所以我们将第二个方块倒着接在第一个的上面然后判断一下连着的是不是超过1个,因为如果只有一个连着的可以分成两个方块,大于等于两个就输出no
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <sstream>
#include <queue>
#define int long long
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<'\n'
#define no cout<<"NO"<<'\n'
using namespace std;
signed main () {
//ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
string s1, s2;
int l1, l2;
cin >> l1 >> l2;
cin >> s1 >> s2;
reverse(s2.begin(), s2.end()); //反转一下
string s;
s = s1 + s2; //倒着接入
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < (int)s.size(); i++) {
if (s[i - 1] == s[i]) { //如果前面的和后面的颜色一样让cnt++
cnt++;
}
}
if (cnt > 1) { //cnt>1输出no
printf("NO\n");
} else {
printf("YES\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
B题
这个题就是说我们要删除只能删除一行,判断一下能不能通过任意的删除让k变成下面的区间里面出现最多的元素,我们可以发现k+1和k-1是离k最近的元素我们判断一下k+1和k-1如果不能通过删除可以变得比k少就输出no否则输出yes
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <sstream>
#include <queue>
#define int long long
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<'\n'
#define no cout<<"NO"<<'\n'
using namespace std;
signed main () {
//ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
int n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
int st[60] = {0};
while (n--) {
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
if (k >= l && k <= r) {//当k在这个区间里面的时候,然后再判断k+1和k-1在不在里面
st[k]++;//先让s[k]++
if (k + 1 >= l && k + 1 <= r) {//然后判断k+1和k-1在不在区间里面并计数
st[k + 1]++;
}
if (k - 1 >= l && k - 1 <= r) {
st[k - 1]++;
}
}
}
if (st[k] > st[k - 1] && st[k] > st[k + 1]) {//如果st[k]大于st[k-1]并且st[k]大于st[k+1]说明可以通过删除满足题目要求
yes;
} else {
no;
}
}
return 0;
}
B. Bad Prices
链接
这个题是我看了别人的题解才会,思路是倒着从前向后进行扫描,先让最后一个元素定义为最低的价格,向前扫描只要前面的比当前最小的大就让答案加1,遇到比最小值小的,就更新最小值,继续向前扫描.直到最后打印结果
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <sstream>
#include <queue>
#define int long long
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<'\n'
#define no cout<<"NO"<<'\n'
using namespace std;
int a[150005];
signed main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
int mmin = a[n - 1]; //将最小值赋值为最后一个
int res = 0;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) { //倒着扫描
if (a[i] > mmin) { //如果a[i]大于最小值就让res++
res++;
} else {
mmin = a[i]; //否则更新最小值,继续向前扫描
}
}
cout << res << '\n'; //打印res
}
return 0;
}
B. Bogosort
链接
这个题我们先对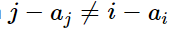 这个式子进行变形变成j+a_i不等于i+a_j从题目上面我们可以发现j>i如果我们让ai>=aj就永远不可能相等.我们对数组从大到小进行排序,因为j大于i的话,a[i]就会大于等于a[j].这样就永远不可能相等.
这个式子进行变形变成j+a_i不等于i+a_j从题目上面我们可以发现j>i如果我们让ai>=aj就永远不可能相等.我们对数组从大到小进行排序,因为j大于i的话,a[i]就会大于等于a[j].这样就永远不可能相等.
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <sstream>
#include <queue>
#define int long long
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<'\n'
#define no cout<<"NO"<<'\n'
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int a[N];
bool cmp(int a, int b) {
return a > b;
}
signed main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
sort(a, a + n, cmp); //从大到小排序
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << a[i] << ' '; //打印结果
}
cout << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
C. Challenging Cliffs
链接
A. Boboniu Likes to Color Balls
链接
A. Boboniu Likes to Color Balls
这个题写的代码有点长,感觉不是正解,具体看一下代码的注释
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <sstream>
#include <queue>
#define int long long
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<'\n'
#define no cout<<"NO"<<'\n'
using namespace std;
signed main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t;
cin >> t;
int a[4];
while (t--) {
int r, g, b, w;
cin >> r >> g >> b >> w;
a[0] = r;
a[1] = g;
a[2] = b;
a[3] = w;//读入数据赋值给数组
int x = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= 2; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0) {
x++;
}
}//判断前面三种颜色有多少个是0
if (x > 0) {//在前三种颜色有0的情况下判断有多少奇数和偶数
//因为不能变换最多只能有一个奇数
int num = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= 3; i++) {
if (a[i] % 2 == 1) {
num++;
}
if (num > 1) {//大于一个奇数
printf("NO\n");//打印no
goto out;//跳出
}
}
}
//如果前三个都不上0
if (w % 2 == 0) {//如果白色为偶数
int flag = 0;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= 2; i++) {//判断前三种颜色有几个奇数
if (a[i] % 2 == 1) {
cnt++;
}
}
if (cnt > 1) {//如果奇数大于1,不满足条件
flag++;
}
cnt = 0;
//下面判断转移之后的情况,转移之后w肯定是奇数
for (int i = 0; i <= 2; i++) {
if ((a[i] - 1) % 2 == 1) {//判断转移之后的奇数数量
cnt++;
}
}
if (cnt > 0) {//如果奇数大于1不满足条件
flag++;
}
if (flag < 2) {//满足两个判断的其中之一就打印yes
printf("YES\n");
} else {
printf("NO\n");
};
} else {//如果是奇数
int flag = 0;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= 2; i++) {
if (a[i] % 2 == 1) {//判断前三个有几个是奇数
cnt++;
}
}
if (cnt > 0) {//大于0就不满足条件
flag++;
}
cnt = 0;
//转移之后肯定是偶数
for (int i = 0; i <= 2; i++) {
if ((a[i] - 1) % 2 == 1) {
cnt++;
}
}
if (cnt > 1) {//奇数大于1不满足条件
flag++;
}
if (flag < 2) {
printf("YES\n");
} else {
printf("NO\n");
}
}
out:
int n;
n++;//两串无用代码
}
return 0;
}
B. Caisa and Pylons
链接
这个题我想了很长时间,其实就是从前向后进行扫描,用一个res进行累加,如果小于0就补上这个数字,然后继续扫描,再碰到负的就再次补上这个数字,最后打印结果
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <sstream>
#include <queue>
#define int long long
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<'\n'
#define no cout<<"NO"<<'\n'
using namespace std;
const int N = 100000 + 5;
int a[N];
signed main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n;
cin >> n;
int res = 0;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
//从1开始默认a[0]为0
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
res = res + (a[i - 1] - a[i]);//每次计算累加.加到res里面
//如果res小于0的话就让res=0,并且将这个答案加到结果
if (res < 0) {
cnt = cnt + (-res);
res = 0;
}
}
cout << cnt;//打印结果
return 0;
}
B. GCD Compression
链接
这个题看着比较复杂其实我们只需要分别输出奇数和偶数的下标(因为两个偶数的最大公约数不可能为1),肯定就可以满足条件.因为两个奇数相加是偶数,两个偶数相加还是偶数,在题目满足的条件下总是满足的.
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <sstream>
#include <queue>
#define int long long
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<'\n'
#define no cout<<"NO"<<'\n'
using namespace std;
signed main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
int js[10000 + 5] = {0};
int os[10000 + 5] = {0};
int n;
cin >> n;
int a;
int k1 = 0;
int k2 = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i++) {
cin >> a;
if (a % 2 == 1) {
js[k1++] = i;
} else {
os[k2++] = i;
}
}//记录奇数和偶数的下表进数组里面
if (k1 % 2 == 1) {//如果为奇数就减一
k1--;
}
if (k2 % 2 == 1) {
k2--;
}
int num = 0;//判断输出的多少个数了
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < k1; i++) {
printf("%lld ", js[i]);//输出
num++;
cnt++;
if (cnt % 2 == 0) {//控制换行
printf("\n");
}
if (num == 2 * (n - 1)) {//如果num==2*(n-1)就直接跳出
goto out;
}
}
cnt = 0;
//下面输出偶数
for (int i = 0; i < k2; i++) {
printf("%lld ", os[i]);
cnt++;
num++;
if (cnt % 2 == 0) {
printf("\n");
}
//条件成立直接跳出
if (num == 2 * (n - 1)) {
goto out;
}
}
out:
int x = 0;
x++;//无效代码
}
return 0;
}
C. Challenging Cliffs
链接
这个题我也不会,看了别人的题解,分享一下别人的观点,先取出两个相差的最小的元素放到数组的最前面和最后面,然后先打印后半部分的数组再打印前半部分的数组,最后输出
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <sstream>
#include <queue>
#define int long long
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<'\n'
#define no cout<<"NO"<<'\n'
using namespace std;
const int N = 200000 + 6;
signed main () {
bool st[N] = {0};
int a[N] = {0};
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
sort(a, a + n);//排序
int mmin = 9999999999999;
memset(st, false, sizeof st);//初始化
int x, y;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] - a[i - 1] < mmin) {//寻找最小差值
mmin = a[i] - a[i - 1];//更新最小差值
x = i - 1;//更新x,y下标
y = i;
}
}
st[x] = true;
st[y] = true;//表姐为已经使用
int res[N] = {0};//结果数组
res[0] = a[x];
res[n - 1] = a[y];//先赋值
int k = 1;
for (int i = y + 1; i < n; i++) {//先从后面开始接到数组上面这样可能让第0个小于第1个加上一分
res[k++] = a[i];
}//先加上y后面的
//在加上x前面的
for (int i = 0; i <= x - 1; i++) {
res[k++] = a[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {//打印结果
cout << res[i] << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
}
return 0;
}

