【转】Hostapd工作流程分析
【转】Hostapd工作流程分析
转自:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-30081165-id-5290531.html
Hostapd是一个运行在用户态的守护进程,可以通过Hostapd来读取配置文件,通过nl802.11来控制底层的状态如RTS/CTS beacon帧间隔等等信息;也可以读取相关的信息。
其代码框架如下图所示:hostapd_cli是基于文本的命令命令界面,GUI则是图形控制界面;event loop是一个死循环函数用于接收和处理各种事件信息。
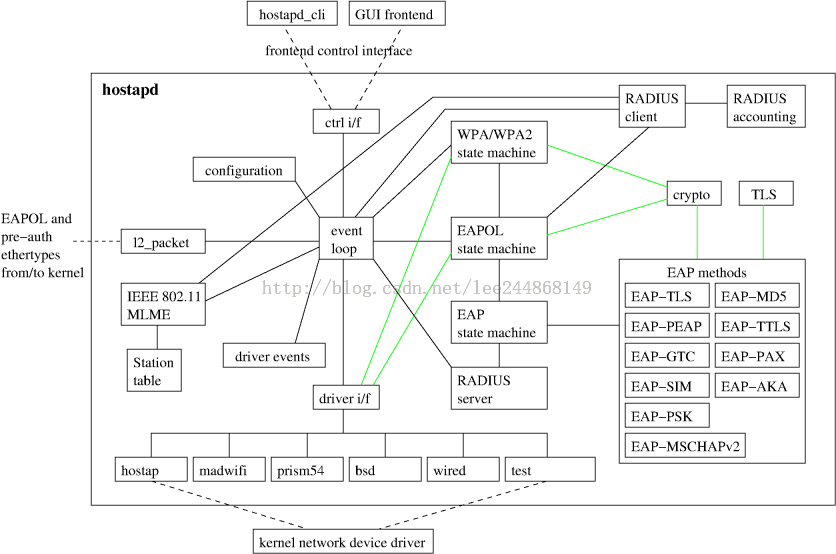
下图是各种命令配置工具以及无线工作流程:
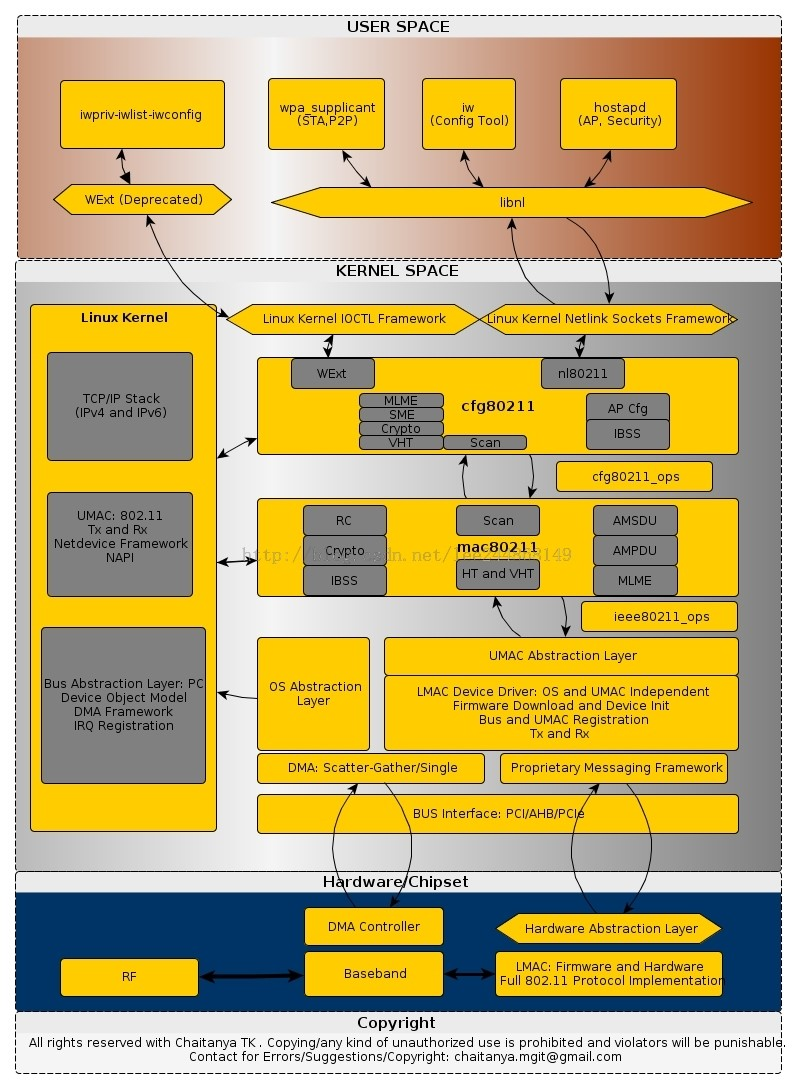
实际上可以看到无论是wpa_supplient iw还是hostapd工具都是通过调用libnl的相关方法来完成信息的配置预读取的。
接下来分析hostaod的主函数:
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { struct hapd_interfaces interfaces; int ret = 1; size_t i, j; int c, debug = 0; const char *log_file = NULL; const char *entropy_file = NULL; char **bss_config = NULL, **tmp_bss; size_t num_bss_configs = 0; #ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_LINUX_TRACING int enable_trace_dbg = 0; #endif /* CONFIG_DEBUG_LINUX_TRACING */ if (os_program_init()) return -1; os_memset(&interfaces, 0, sizeof(interfaces)); interfaces.reload_config = hostapd_reload_config; interfaces.config_read_cb = hostapd_config_read; interfaces.for_each_interface = hostapd_for_each_interface; interfaces.ctrl_iface_init = hostapd_ctrl_iface_init; interfaces.ctrl_iface_deinit = hostapd_ctrl_iface_deinit; interfaces.driver_init = hostapd_driver_init; interfaces.global_iface_path = NULL; interfaces.global_iface_name = NULL; interfaces.global_ctrl_sock = -1; wpa_supplicant_event = hostapd_wpa_event; //分析配置文件信息 for (;;) { c = getopt(argc, argv, "b:Bde:f:hKP:Ttu:g:G:v::"); if (c < 0) break; switch (c) { case 'h': usage(); break; case 'd': debug++; if (wpa_debug_level > 0) wpa_debug_level--; break; case 'B': daemonize++; break; case 'e': entropy_file = optarg; break; case 'f': log_file = optarg; break; case 'K': wpa_debug_show_keys++; break; case 'P': os_free(pid_file); pid_file = os_rel2abs_path(optarg); break; case 't': wpa_debug_timestamp++; break; #ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_LINUX_TRACING case 'T': enable_trace_dbg = 1; break; #endif /* CONFIG_DEBUG_LINUX_TRACING */ case 'v': if (optarg) exit(!has_feature(optarg)); show_version(); exit(1); break; case 'g': if (hostapd_get_global_ctrl_iface(&interfaces, optarg)) return -1; break; case 'G': if (hostapd_get_ctrl_iface_group(&interfaces, optarg)) return -1; break; case 'b': tmp_bss = os_realloc_array(bss_config, num_bss_configs + 1, sizeof(char *)); if (tmp_bss == NULL) goto out; bss_config = tmp_bss; bss_config[num_bss_configs++] = optarg; break; #ifdef CONFIG_WPS case 'u': return gen_uuid(optarg); #endif /* CONFIG_WPS */ default: usage(); break; } } if (optind == argc && interfaces.global_iface_path == NULL && num_bss_configs == 0) usage(); wpa_msg_register_ifname_cb(hostapd_msg_ifname_cb); if (log_file) wpa_debug_open_file(log_file); #ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_LINUX_TRACING if (enable_trace_dbg) { int tret = wpa_debug_open_linux_tracing(); if (tret) { wpa_printf(MSG_ERROR, "Failed to enable trace logging"); return -1; } } #endif /* CONFIG_DEBUG_LINUX_TRACING */ interfaces.count = argc - optind; if (interfaces.count || num_bss_configs) { interfaces.iface = os_calloc(interfaces.count + num_bss_configs, sizeof(struct hostapd_iface *)); if (interfaces.iface == NULL) { wpa_printf(MSG_ERROR, "malloc failed"); return -1; } } //初始化global context信息 if (hostapd_global_init(&interfaces, entropy_file)) { wpa_printf(MSG_ERROR, "Failed to initilize global context"); return -1; } /* Allocate and parse configuration for full interface files */ for (i = 0; i < interfaces.count; i++) { interfaces.iface[i] = hostapd_interface_init(&interfaces, argv[optind + i], debug); if (!interfaces.iface[i]) { wpa_printf(MSG_ERROR, "Failed to initialize interface"); goto out; } } /* Allocate and parse configuration for per-BSS files */ for (i = 0; i < num_bss_configs; i++) { struct hostapd_iface *iface; char *fname; wpa_printf(MSG_INFO, "BSS config: %s", bss_config[i]); fname = os_strchr(bss_config[i], ':'); if (fname == NULL) { wpa_printf(MSG_ERROR, "Invalid BSS config identifier '%s'", bss_config[i]); goto out; } *fname++ = '\0'; iface = hostapd_interface_init_bss(&interfaces, bss_config[i], fname, debug); if (iface == NULL) goto out; for (j = 0; j < interfaces.count; j++) { if (interfaces.iface[j] == iface) break; } if (j == interfaces.count) { struct hostapd_iface **tmp; tmp = os_realloc_array(interfaces.iface, interfaces.count + 1, sizeof(struct hostapd_iface *)); if (tmp == NULL) { hostapd_interface_deinit_free(iface); goto out; } interfaces.iface = tmp; interfaces.iface[interfaces.count++] = iface; } } /* * Enable configured interfaces. Depending on channel configuration, * this may complete full initialization before returning or use a * callback mechanism to complete setup in case of operations like HT * co-ex scans, ACS, or DFS are needed to determine channel parameters. * In such case, the interface will be enabled from eloop context within * hostapd_global_run(). */ interfaces.terminate_on_error = interfaces.count; for (i = 0; i < interfaces.count; i++) { //根据配置文件设置iface信息 if (hostapd_driver_init(interfaces.iface[i]) || //将配置文件通过写入驱动 hostapd_setup_interface(interfaces.iface[i])) goto out; } hostapd_global_ctrl_iface_init(&interfaces); // hostapd_global_run死循环,接收处理信息 if (hostapd_global_run(&interfaces, daemonize, pid_file)) { wpa_printf(MSG_ERROR, "Failed to start eloop"); goto out; } ret = 0; out: hostapd_global_ctrl_iface_deinit(&interfaces); /* Deinitialize all interfaces */ for (i = 0; i < interfaces.count; i++) { if (!interfaces.iface[i]) continue; interfaces.iface[i]->driver_ap_teardown = !!(interfaces.iface[i]->drv_flags & WPA_DRIVER_FLAGS_AP_TEARDOWN_SUPPORT); hostapd_interface_deinit_free(interfaces.iface[i]); } os_free(interfaces.iface); hostapd_global_deinit(pid_file); os_free(pid_file); if (log_file) wpa_debug_close_file(); wpa_debug_close_linux_tracing(); os_free(bss_config); os_program_deinit(); return ret; }
分析:
1) 函数主要分为三部分,第一部是读取命令行参数作相应的处理。
2) 第二部分主要是根据配置文件设置hapd_interface的参数然后通过一系列的函数调用进入内核态设置相应的内核参数。核心代码如下:
首先是通过调用函数hostapd_driver_init获取配置信息保存在iface[i]中,然后通过调用函数hostapd_setup_interface函数将其配置信息写入内核。
for (i = 0; i < interfaces.count; i++) { //根据配置文件设置iface信息 if (hostapd_driver_init(interfaces.iface[i]) || //将配置文件通过写入驱动 hostapd_setup_interface(interfaces.iface[i])) goto out; }
下面来跟一下写入的过程:
通过依次调用
hostapd_setup_interface
------>setup_interface
------>hostapd_set_country
------>setup_interface2
------>hostapd_setup_interface_complete
------>hostapd_set_freq
------>hostapd_set_rts
------>hostapd_set_state
------>hostapd_tx_queue_para,
通过这几个调用进入netlink层,后面的过程此处不做详解。
全局变量eloop是执行这个死循环的重要结构体,其定义如下所示:
struct eloop_sock { int sock; void *eloop_data; void *user_data; eloop_sock_handler handler; WPA_TRACE_REF(eloop); WPA_TRACE_REF(user); WPA_TRACE_INFO }; struct eloop_sock_table { int count; struct eloop_sock *table; #ifdef CONFIG_ELOOP_EPOLL eloop_event_type type; #else /* CONFIG_ELOOP_EPOLL */ int changed; #endif /* CONFIG_ELOOP_EPOLL */ }; struct eloop_data { int max_sock; int count; /* sum of all table counts */ #ifdef CONFIG_ELOOP_POLL int max_pollfd_map; /* number of pollfds_map currently allocated */ int max_poll_fds; /* number of pollfds currently allocated */ struct pollfd *pollfds; struct pollfd **pollfds_map; #endif /* CONFIG_ELOOP_POLL */ #ifdef CONFIG_ELOOP_EPOLL int epollfd; int epoll_max_event_num; int epoll_max_fd; struct eloop_sock *epoll_table; struct epoll_event *epoll_events; #endif /* CONFIG_ELOOP_EPOLL */ struct eloop_sock_table readers; struct eloop_sock_table writers; struct eloop_sock_table exceptions; struct dl_list timeout; int signal_count; struct eloop_signal *signals; int signaled; int pending_terminate; int terminate; };
也就是说其主要定义了reader,wri
首先是对sock timeout 和event三个函数table的初始化,在main中调用函数
hostapd_global_init完成,其代码如下:首先通过调用eloop_init完成了对eloop这个全局变量的初始化。
static int hostapd_global_init(struct hapd_interfaces *interfaces, const char *entropy_file) { int i; os_memset(&global, 0, sizeof(global)); hostapd_logger_register_cb(hostapd_logger_cb); if (eap_server_register_methods()) { wpa_printf(MSG_ERROR, "Failed to register EAP methods"); return -1; } if (eloop_init()) { wpa_printf(MSG_ERROR, "Failed to initialize event loop"); return -1; } random_init(entropy_file); #ifndef CONFIG_NATIVE_WINDOWS eloop_register_signal(SIGHUP, handle_reload, interfaces); eloop_register_signal(SIGUSR1, handle_dump_state, interfaces); #endif /* CONFIG_NATIVE_WINDOWS */ eloop_register_signal_terminate(handle_term, interfaces); #ifndef CONFIG_NATIVE_WINDOWS openlog("hostapd", 0, LOG_DAEMON); #endif /* CONFIG_NATIVE_WINDOWS */ for (i = 0; wpa_drivers[i]; i++) global.drv_count++; if (global.drv_count == 0) { wpa_printf(MSG_ERROR, "No drivers enabled"); return -1; } global.drv_priv = os_calloc(global.drv_count, sizeof(void *)); if (global.drv_priv == NULL) return -1; return 0; }
接着是对各个事件的注册,如下所示即为注册socket的函数:
int eloop_register_sock(int sock, eloop_event_type type,
eloop_sock_handler handler,
void *eloop_data, void *user_data)
{
struct eloop_sock_table *table;
assert(sock >= 0);
table = eloop_get_sock_table(type);
return eloop_sock_table_add_sock(table, sock, handler,
eloop_data, user_data);
}
分析代码即为将相应的handler和data放进sock_table表中即可。
最后是在函数hostapd_global_run中死循环来检测socket或者timeout或者event的相关量是否发生变化进而调用相应的提前注册到该事件上的函数。
其处理socket事件的核心代码如下:将其添加进相应的表中
eloop_sock_table_set_fds(&eloop.readers, rfds); eloop_sock_table_set_fds(&eloop.writers, wfds); eloop_sock_table_set_fds(&eloop.exceptions, efds); res = select(eloop.max_sock + 1, rfds, wfds, efds, timeout ? &_tv : NULL);
最后执行相应的提前注册的函数:
eloop_sock_table_dispatch(&eloop.readers, rfds); eloop_sock_table_dispatch(&eloop.writers, wfds); eloop_sock_table_dispatch(&eloop.exceptions, efds);
至此hostapd的基本流程分析完了。




