IPM简介逆透视变换
前言
原理
1. 二维坐标变换
关键是用已知角做出直角三角形,使用已知边作斜边进行计算。
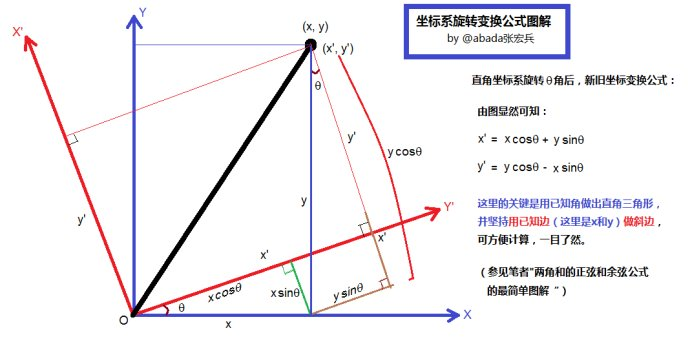
2. 三维图像坐标变换
假设固定一个(X,Y,Z)轴,旋转其他两个轴组成的平面。
3. 相机坐标系和图像平面坐标系(成像投影关系)
4. 图像平面坐标系XY到像素坐标系uv
图像平面坐标系:物理单位表示,比如mm;像素坐标系:以像素为单位表示;
假设每个像素在X轴和Y轴方向上的物理尺寸分别为dx、dy,则可以计算任意像素在两个坐标系下的关系。
5. 消失点(灭点)
注:逆透视变换的范围不能到达消失点,否则不能还原。
如果不存在俯仰角和偏航角,消失点就是光学中心位置,而存在俯仰角和偏航角后,消失点就会偏移,根据俯仰角和偏航角再计算变换后的消失点!
代码实现
1.IPM包含3个函数。
image2ground:将图像中的像素点(u, v)对应到地平面上(Z=1)IPM的像素点(x, y);
ground2image:将IPM中的像素点(x, y)基于IPM的最大范围转换为xygrid,从而转化为uvgrid;
src2ipm:基于uvgrid插值得到IPM中像素点(x, y)的的灰度值并显示,同时转换得到IPM中每个像素点的实际距离coord;
2.如何求解原图像中像素点的实际距离;
image2ground:uvp ——> xyp;
xyp2ipmp:xyp ——> ipmp;
xmin + x.ipmp * stepcol = x.xyp;
ymax - y.ipmp * steprow = y.xyp;
从而推导出,
x.ipmp = ( x.xyp - xmin ) / stepcol;
y.ipmp = ( ymax - y.xyp ) / steprow;
3.注意:
3.1.查看x.ipmp和y.ipm的结果是否越界,需要添加越界判断;
3.2.编码的时候需要非常注意各个参数的数据类型及格式是否匹配或者一致;
4. 单应矩阵
5. IPM的原理
6. 内参标定和外参标定
7.
1) 需要知道相机的内部参数(这个具体步骤可以找相关文档,这里就不具体展开说)。
我们这里假设已经获取内部参数:
内参:相机焦距,相机光学中心,畸变系数,
外参:相机高度, 相机的俯仰角, 相机的偏航角,
相机拍摄出的图像尺寸。
参数说明: 其中偏航角 和 俯仰角 就是所说的世界坐标经过旋转矩阵得到相应的相机坐标。 而偏航角和俯仰角将决定这个旋转矩阵。 而相机焦距 和相机光学中心 是可以从相机标定后得出 ,相机高度需要自己测量。而图像尺寸,是拍出图像的尺寸。
2) 设定逆透视变换的参数:
逆透视图像的尺寸,需要进行逆透视变换的区域,逆透视变换的差值算法。
逆透视变换的区域:原始图像中需要变换的区域(当然这个区域不能超过消失点区域,后面会说到)
逆透视图像的尺寸: 就是需要将逆透视变换区域映射到这个逆透视图像上。
差值算法:因为需要映射,所以某些数值需要估计出,这里用双线性差值。
code
measure_distance.cpp

/************************************************************************* * File Name: measure_distance.cpp * Author: * Mail: * Created Time: 09/17/18 ************************************************************************/ #include <iostream> #include <assert.h> #include <algorithm> #include "measure_distance.hpp" measureDistance::measureDistance(int camera_id, Dtype h, Dtype roll, Dtype pitch, Dtype yaw, double* camera_param_KK, double* camera_param_KC, int img_height, int img_width, int input_height, int input_width) { camera_id_ = camera_id; height_ = h; roll_ = roll; pitch_ = pitch; yaw_ = yaw; img_height_ = img_height; img_width_ = img_width; input_height_ = input_height; input_width_ = input_width; camera_matrix_ = cv::Mat(3, 3, CV_64FC1, camera_param_KK); distortion_coeff_ = cv::Mat(1, 5, CV_64FC1, camera_param_KC); // undistort image cv::Size img_size; img_size.width = img_width_; img_size.height = img_height_; mapx_ = cv::Mat(img_size, CV_64FC1); mapx_ = cv::Mat(img_size, CV_64FC1); cv::Mat R = cv::Mat::eye(3, 3, CV_64FC1); new_camera_matrix_ = cv::getOptimalNewCameraMatrix(camera_matrix_, distortion_coeff_, img_size, 0); cv::initUndistortRectifyMap(camera_matrix_, distortion_coeff_, R, camera_matrix_, img_size, CV_16SC2, mapx_, mapy_); // image coordinate matrix x_scale_ = static_cast<Dtype>(img_width_) / input_width_; y_scale_ = static_cast<Dtype>(img_height_) / input_height_; int pixel_num = img_height_ * img_width_; cv::Mat real_coords = cv::Mat::zeros(1, pixel_num, CV_64FC2); for (int i = 0; i < pixel_num; ++i) { real_coords.at<cv::Vec2d>(0, i)[0] = static_cast<double>(i % img_width_); real_coords.at<cv::Vec2d>(0, i)[1] = static_cast<double>(i / img_width_); } cv::Mat sum_map_matrix = camera_matrix_; double a11 = sum_map_matrix.at<double>(0, 0); double a13 = sum_map_matrix.at<double>(0, 2); double a22 = sum_map_matrix.at<double>(1, 1); double a23 = sum_map_matrix.at<double>(1, 2); double u = 0; double v = 0; double dis = 0; double fx = a11; double cx = a13; double fy = a22; double cy = a23; double s1 = sin(pitch_); double c1 = cos(pitch_); double s2 = sin(roll_); double c2 = cos(roll_); double s3 = sin(yaw_); double c3 = cos(yaw_); coords_distance_map_ = cv::Mat::zeros(img_height, img_width, CV_32FC2); for (int i = 0; i < img_height; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < img_width; ++j) { u = real_coords.at<cv::Vec2d>(0, i * img_width + j)[0]; v = real_coords.at<cv::Vec2d>(0, i * img_width + j)[1]; dis = -(h*c1*c1* c2*cy*fx*s3 - h*c2*c3*cx*fy*s1*s1 + h*c1*c1* c2*c3*fy*u + h*c2*cy*fx*s1*s1 * s3 + h*c2*c3*fy*s1*s1*u - h*c1*c1*c2*fx*s3*v - h*c2*fx*s1*s1 * s3*v + h*c1*c1 * c3*c3 * fx*fy*s2 + h*c1*c1 * fx*fy*s2*s3*s3 + h*c3*c3 * fx*fy*s1*s1 * s2 + h*fx*fy*s1*s1 * s2*s3*s3 - h*c1*c1 * c2*c3*cx*fy) / (c1*c3*cx*fy*s2 - c1*cy*fx*s2*s3 - c1*c3*fy*s2*u + c1*fx*s2*s3*v + c1*c2*c3*c3 * fx*fy - c2*c2 * c3*cy*fx*s1 + c1*c2*fx*fy*s3*s3 - c3*cy*fx*s1*s2*s2 - c2*c2 * cx*fy*s1*s3 + c2*c2 * c3*fx*s1*v - cx*fy*s1*s2*s2 * s3 + c2*c2 * fy*s1*s3*u + c3*fx*s1*s2*s2 * v + fy*s1*s2*s2 * s3*u); coords_distance_map_.at<cv::Vec2f>(i, j)[0] = static_cast<float>(dis); dis = (h*c1*c3*cy*fx*s2*s2 + h*c1*c2*c2 * cx*fy*s3 - h*c1*c2*c2 * c3*fx*v + h*c2*c3*c3 * fx*fy*s1 + h*c1*cx*fy*s2*s2 * s3 - h*c1*c2*c2 * fy*s3*u - h*c1*c3*fx*s2*s2 * v + h*c2*fx*fy*s1*s3*s3 - h*c1*fy*s2*s2 * s3*u + h*c3*cx*fy*s1*s2 - h*cy*fx*s1*s2*s3 - h*c3*fy*s1*s2*u + h*fx*s1*s2*s3*v + h*c1*c2*c2 * c3*cy*fx) / (c1*c3*cx*fy*s2 - c1*cy*fx*s2*s3 - c1*c3*fy*s2*u + c1*fx*s2*s3*v + c1*c2*c3*c3 * fx*fy - c2*c2 * c3*cy*fx*s1 + c1*c2*fx*fy*s3*s3 - c3*cy*fx*s1*s2*s2 - c2*c2 * cx*fy*s1*s3 + c2*c2 * c3*fx*s1*v - cx*fy*s1*s2*s2 * s3 + c2*c2 * fy*s1*s3*u + c3*fx*s1*s2*s2 * v + fy*s1*s2*s2 * s3*u); if (dis<0) dis = 200; dis = dis > 200 ? 200 : dis; coords_distance_map_.at<cv::Vec2f>(i, j)[1] = static_cast<float>(dis); } } } Distance measureDistance::getDistance(const int x, const int y) { Distance dis; #if 0 int sy = y * y_scale_; int sx = x * x_scale_; sy = sy < img_height_ ? sy : img_height_ - 1; sx = sx < img_width_ ? sx : img_width_ - 1; cv::Vec2f p_dis = coords_distance_map_.at<cv::Vec2f>(sy, sx); dis.x_dis = p_dis[0] - 0.12; dis.y_dis = p_dis[1] - 1.85; #endif #if 1 int yy = floor(y * y_scale_), xx = floor(x * x_scale_); Dtype delta_y = y * y_scale_ - yy, delta_x = x * x_scale_ - xx; yy = yy < img_height_ ? yy : img_height_ - 1; xx = xx < img_width_ ? xx : img_width_ - 1; int y_add = yy + 1, x_add = xx + 1; y_add = y_add < img_height_ ? y_add : img_height_ - 1; x_add = x_add < img_width_ ? x_add : img_width_ - 1; dis.x_dis = (1 - delta_x) * (1 -delta_y) * coords_distance_map_.at<cv::Vec2f>(yy, xx)[0] + delta_x * (1 - delta_y) * coords_distance_map_.at<cv::Vec2f>(yy, x_add)[0] + (1 - delta_x) * delta_y * coords_distance_map_.at<cv::Vec2f>(y_add, xx)[0] + delta_x * delta_y * coords_distance_map_.at<cv::Vec2f>(y_add, x_add)[0] + 0.16;// -0.12 dis.y_dis = (1 - delta_x) * (1 -delta_y) * coords_distance_map_.at<cv::Vec2f>(yy, xx)[1] + delta_x * (1 - delta_y) * coords_distance_map_.at<cv::Vec2f>(yy, x_add)[1] + (1 - delta_x) * delta_y * coords_distance_map_.at<cv::Vec2f>(y_add, xx)[1] + delta_x * delta_y * coords_distance_map_.at<cv::Vec2f>(y_add, x_add)[1] - 1.75; #endif return dis; }
measure_distance.hpp

#ifndef __MEASURE_DISTANCE__ #define __MEASURE_DISTANCE__ #include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp> #include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp> #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> #include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp> #define PI 3.1415926535898 typedef float Dtype; struct Distance { float x_dis; float y_dis; }; class measureDistance { public: measureDistance(int camera_id, Dtype h, Dtype roll, Dtype pitch, Dtype yaw, double* camera_param_KK, double* camera_param_KC, int img_height = 720, int img_width = 1280, int input_height = 448, int input_width = 800); Distance getDistance(const int x, const int y); cv::Mat get_mapx() { return mapx_; } cv::Mat get_mapy() { return mapy_; } ~measureDistance(){}; private: int camera_id_; Dtype height_; Dtype roll_; Dtype pitch_; Dtype yaw_; cv::Mat camera_matrix_; cv::Mat new_camera_matrix_; cv::Mat distortion_coeff_; cv::Mat mapx_, mapy_; cv::Mat coords_distance_map_; int img_height_, img_width_, input_height_, input_width_; Dtype x_scale_; Dtype y_scale_; }; #endif
参考
1.matlab理解IPM;
2.opencv函数;
3. IPM_opencv;
4. 【智能驾驶】车道线检测中的新IPM(逆透视变换)算法实验效果;
完
心正意诚,做自己该做的事情,做自己喜欢做的事情,安静做一枚有思想的技术媛。
版权声明,转载请注明出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/happyamyhope/





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· .NET周刊【3月第1期 2025-03-02】