Day09-集合
集合
-
可以动态的保存任意多个类型,使用比较方便
-
提供了一系列方便的操作对象:add、remove、set、get等
-
使用集合添加,删除新元素的示意代码简洁了
-
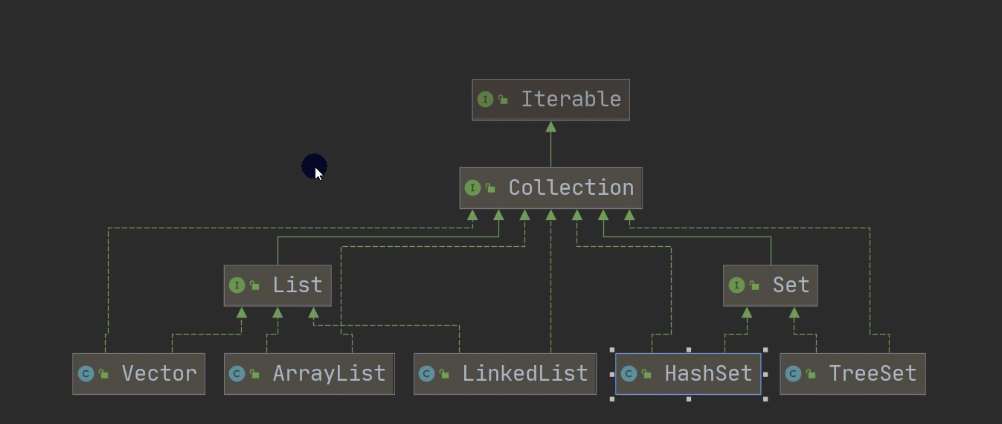
集合主要是两组(单列集合、双列集合)
-
collection接口有两个重要的子接口List Set ,他们的实现子类都是单列集合
-
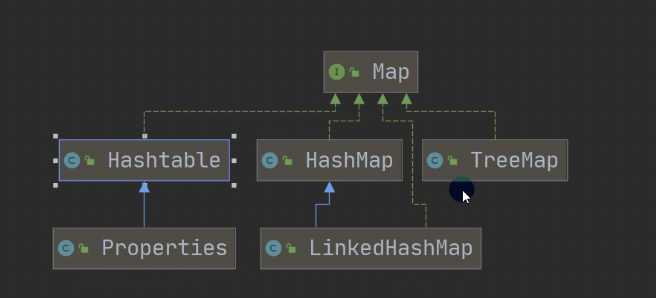
Map接口的实现子类是双列集合,存放的K-V
-
-
Iterator对象称为迭代器,主要用于遍历Collection集合中的的元素
-
所有实现了Collection接口的集合类都有一个it erator()方法,用以返回一个实现了Iterator接口的对象,即可以返 回一个迭代器
-
当退出while循环后,这时iterator迭代器,指向最后的元素
-
iterator.next();//NosuchElementException
-
如果希望再次遍历,需要重置我们的迭代器
package 集合;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collection;import java.util.Iterator;public class Demo01 {public static void main(String[] args) {Collection col = new ArrayList();col.add(new Book("红楼梦","曹雪芹",10));col.add(new Book("三国演义","施耐庵",6));Iterator iterator = col.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {Object obj = iterator.next();System.out.println(obj);}iterator=col.iterator();//重置迭代器}}class Book{private String name;private String author;private double price;public Book(String name, String author, double price) {this.name = name;this.author = author;this.price = price;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public String getAuthor() {return author;}public void setAuthor(String author) {this.author = author;}public double getPrice() {return price;}public void setPrice(double price) {this.price = price;}public String toString() {return "Book{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", author='" + author + '\'' +", price=" + price +'}';}}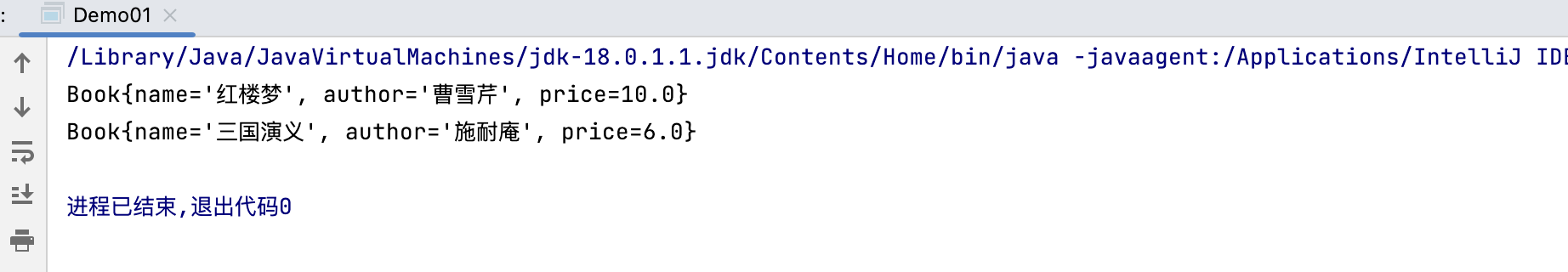
-
package 集合;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection col = new ArrayList();
col.add(new Book("红楼梦","曹雪芹",10));
col.add(new Book("三国演义","施耐庵",6));
Iterator iterator = col.iterator();
//增强for循环
for (Object o : col) {
System.out.println(o);
}
}
}
class Book{
private String name;
private String author;
private double price;
public Book(String name, String author, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
例题1
分别用增强for循环和迭代器遍历集合元素
package 集合;
import java.sql.Array;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list =new ArrayList();
list.add(new Dog("阿黄",1));
list.add(new Dog("旺财",2));
list.add(new Dog("来福",3));
Iterator iterator = list.iterator();
//迭代器
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object obj = iterator.next();
System.out.println(obj);
}
System.out.println("====分割线====");
//增强for循环
for (Object o :list) {
System.out.println(o);
}
}
}
class Dog{
private String name;
private int age;
public Dog(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
-
List集合类中元素
-
List集合中的每个元素都尤其对应的顺序索引,即支持索引
例题2
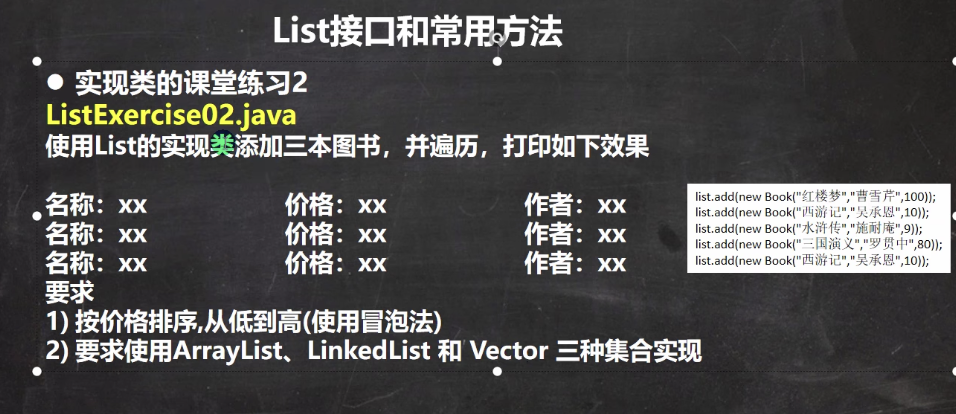
package 集合;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.time.temporal.Temporal;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool;
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//方式1
List list = new ArrayList();
//方式2
List list = new LinkedList();
//方式3
List list = new Vector();
list.add(new Book("红楼梦", "林黛玉", 13));
list.add(new Book("三国演义", "曹操", 17));
list.add(new Book("水浒传", "宋江", 11));
Iterator iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object obj = iterator.next();
System.out.println(obj);
}
System.out.println("==========排序后===========");
bubble(list);
iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object obj = iterator.next();
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
public static void bubble(List list) {
int count = list.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < count - 1 - i; j++) {
Book book1 = (Book) list.get(j);
Book book2 = (Book) list.get(j + 1);
if (book1.getPrice() > book2.getPrice()) {
list.set(j, book2);
list.set(j + 1, book1);
}
}
}
}
}

-
transient:表示该属性不会被序列化
-
在开发中,需要线程同步时,考虑使用vector
| 底层结构 | 版本 | 线程安全(同步) | 扩容倍数 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ArrayList | 可变数组 | jdk1.2 | 不安全,效率高 | 如果是有参构造1.5倍,如果是无参构造第一次10,从第二次开始按1.5扩 |
| Vector | 可变数组Object[] | jdk1.0 | 安全,效率不高 | 如果是无参,默认10,满后就按照2倍扩容,如果指定大小,则每次直接按2倍扩 |
| 底层结构 | 增删的效率 | 改查的效率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ArrayList | 可变数组 | 较低,数组扩容 | 较高 |
| LinkedList | 双向链表 | 较高,通过链表追加 | 较低 |
3.
-
-
不允许重复元素,最多包含一个null
-
和List接口一样,set接口也是collection的子接口,因此,常用方法和collection接口一样
-
可以使用迭代器
-
增强for
-
不能使用索引的方式来获取(普通for循环无法实现 )
HashSet的底层机制
-
HashSet底层是HashMap,HashMap底层是(数组+
-
添加一个元素是,先得到hash值-》会转成索引值
-
找到存储数据表table,看这个索引位置是否已经存放的有元素,如果没有直接加入,如果有,调用equals比较,如果相同,就放弃添加,如果不相同,则添加到最后
-
在java8中,如果一条链表的元素个数到达TREEIFY_THRESHOLD(默认是8),并且table大小>=MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY(默认64),就会进行树化(红黑树)
例题1

package Set;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
hashSet.add(new Employee("小明",3));
hashSet.add(new Employee("小红",4));
hashSet.add(new Employee("小明",3));
System.out.println("hashSet:"+hashSet);
}
}
class Employee{
private String name;
private int age;
public Employee(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Employee employee = (Employee) o;
return age == employee.age && Objects.equals(name, employee.name);
}
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
}

例题2

package Set;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
hashSet.add(new Employee_("小刘",20000,new MyDate(1999,9,12)));
hashSet.add(new Employee_("小张",15000,new MyDate(1998,10,20)));
hashSet.add(new Employee_("小刘",15000,new MyDate(1999,9,12)));
System.out.println("hashSet:"+hashSet);
}
}
class Employee_{
private String name;
private double sal;
private MyDate birthday;
public Employee_(String name, double sal, MyDate birthday) {
this.name = name;
this.sal = sal;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getSal() {
return sal;
}
public void setSal(double sal) {
this.sal = sal;
}
public MyDate getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(MyDate birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public String toString() {
return "Employee_{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", sal=" + sal +
", birthday=" + birthday +
'}';
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Employee_ employee = (Employee_) o;
return Objects.equals(name, employee.name) && Objects.equals(birthday, employee.birthday);
}
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, birthday);
}
}
class MyDate{
private long year;
private int month;
private int day;
public MyDate(long year, int month, int day) {
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
public long getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(long year) {
this.year = year;
}
public int getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(int month) {
this.month = month;
}
public int getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(int day) {
this.day = day;
}
public String toString() {
return "'"+ year +
"-" + month +
"-" + day+"'";
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
MyDate myDate = (MyDate) o;
return year == myDate.year && month == myDate.month && day == myDate.day;
}
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(year, month, day);
}
}

LinkedHashSet
-
LinkedHashSet是HashSet的子类
-
LinkedHashSet底层是一个LinkedHashMap,底层维护了一个数组+
-
LinkedHashSet根据元素的hashCode值来决定元素的存储位置,同时是用链表维护元素的次序(图),
-
LinkedHashSet不允许添加重复元素
例题1

package Set;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashSet linkedHashSet = new LinkedHashSet();
linkedHashSet.add(new Car("大众",15_0000));
linkedHashSet.add(new Car("比亚迪",12_0000));
linkedHashSet.add(new Car("大众",15_0000));
System.out.println("linkedHashSet:"+ linkedHashSet);
}
}
class Car{
private String name;
private double price;
public Car(String name, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Car car = (Car) o;
return Double.compare(car.price, price) == 0 && Objects.equals(name, car.name);
}
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, price);
}
public String toString() {
return "Car{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}

Map
-
Map与Collection并列存在,用于保存具有映射关系的数据:Key-value(双列元素)
-
Map中的key和value可以是任何引用类型,会封装到hashMap$Node对象中
-
Map中的key不允许重复,原因和hashSet一样
-
Map的key可以为null,value也可以为null,注意key为空,只能有一个,value为空可以有多个
-
常用String类作为Map的key
-
key和value之间存在单向一对一关系,即通过指定的key总能找到对应的value
-
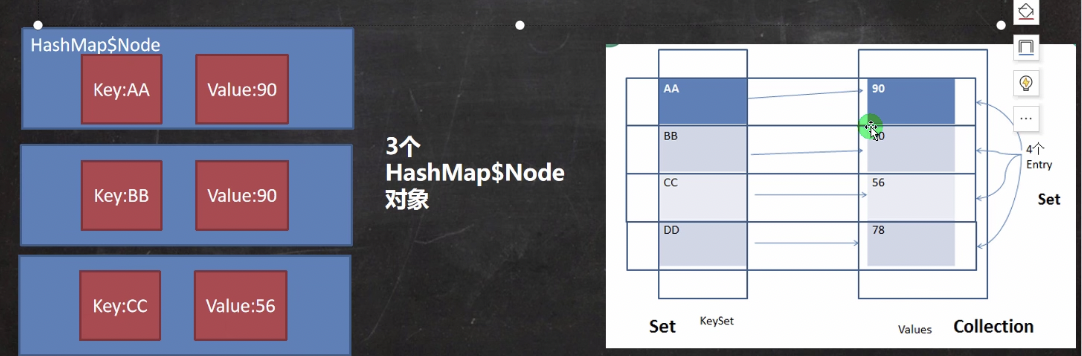
Map存放数据的key-value示意图,一对k-v是放在一个HashMap$Node中的,有因为Node实现了Entry接口,有些书上也说一对k-v就是一个Entry(如图)
-
entrySet中,定义的类型是Map.Entry,但是实际上存放的还是HashMap$Node,这是因为static class Node<K,V>implements Map.Entry<K,V>
-
当把HashMap$Node对象存到entrySet就方便我们的遍历,因为Map.Entry提供了重要方法,K getKey();V getValue();
-
containsKey:查找键是否存在
-
keySet:获取所有的键
-
entrySet:获取所有关系k-v
-
values:获取所有的值
package Set;
import java.rmi.MarshalledObject;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("蔡徐坤", "杨颖");
map.put(null, "张无忌");
map.put("赵敏", null);
map.put("袁湘琴", "江直树");
//keySet获取所有键:先取出所有的key,再通过key取出对应的value
//1. 增强for
System.out.println("======keySet方式中的使用增强for遍历=========");
Set keyset = map.keySet();
for (Object key : keyset) {
System.out.println(key + "-" + map.get(key));
}
System.out.println("======keySet方式中的使用迭代器遍历=========");
//2.迭代器
Iterator iterator =keyset.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object key = iterator.next();
Object value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key+"-"+ value);
}
//entrySet获取所有的k-v
//1.增强for
Set entryset = map.entrySet(); //EntrySet<Map.Entry<k,v>>
System.out.println("======entrySet方式中的使用增强for遍历=========");
for (Object entry :entryset) {
Map.Entry m =(Map.Entry) entry;
System.out.println(m.getKey()+"-"+m.getValue());
}
//2.迭代器
System.out.println("======entrySet方式中的使用迭代器遍历=========");
Iterator iterator1 = entryset.iterator();
while (iterator1.hasNext()) {
Object entry = iterator1.next();
Map.Entry m=(Map.Entry) entry;
System.out.println(m.getKey()+"-"+m.getValue());
System.out.println(entry.getClass()); //HashNode$Node--->实现了Map.Entry(getKey,getValue)
}
//values获取所有的值
//1.增强for
Collection values = map.values();
System.out.println("======values方式中的使用增强for遍历=========");
for (Object val :values) {
System.out.println(val);
}
//2.迭代器
System.out.println("======values方式中的使用迭代器遍历=========");
Iterator iterator2 = values.iterator();
while (iterator2.hasNext()) {
Object val = iterator2.next();
System.out.println(val);
}
}
}

例题1

package Set;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class Demo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map=new HashMap();
map.put(1,new Worker(1,"文姬",21000));
map.put(2,new Worker(2,"允浩",12000));
map.put(3,new Worker(3,"民勇",18000));
//keySet方式获取所有的key,并通过key获取values值
//1.迭代器
Set keyset = map.keySet();
System.out.println("==========迭代器==========");
Iterator iterator = keyset.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object key = iterator.next();
Worker worker = (Worker)map.get(key);
if (worker.getSal()>18000) {
System.out.println(map.get(key));
}
}
//2.增强for
System.out.println("=========增强for===========");
for (Object key :keyset) {
Worker worker=(Worker)map.get(key);
if (worker.getSal()>18000) {
System.out.println(map.get(key));
}
}
}
}
class Worker {
private int id;
private String name;
private double sal;
public Worker(int id, String name, double sal) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.sal = sal;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getSal() {
return sal;
}
public void setSal(double sal) {
this.sal = sal;
}
public String toString() {
return "Worker{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", sal=" + sal +
'}';
}
}

HashMap
-
HashMap是Map接口使用频率最高的实现类
-
HashMap是以key -val对的方式来存储数据(HashMap$Node类型)
-
key不能重复,但是值可以重复,允许使用null键和null值
-
如果添加相同的key,则会覆盖原来的key-val,等同于修改(key不会替换,val会替换)
-
与HashSet一样,不保证映射的顺序,因为底层是以hash表的方式来存储的
-
HashMap没有实现同步,因此是线程不安全的,方法没有做同步互斥的操作,即没有synchronized
HashTable
-
如果添加相同的key,则会覆盖原来的key-val,等同于修改(key不会替换,val会替换),不允许使用null键和null值
-
底层数组Hashtable$Entry[],初始化大小为11
-
临界值threshold 8=11*0.75
-
扩容:按照自己的扩容机制来进行即可
-
执行方法addEntry(hash,key,value,index),添加k-v封装到Entry
-
当if(count>=threshold)满足时 ,就进行扩容,按照int newCapacity=(oldCapacity<<1)+1;的大小扩容
| 版本 | 线程安全(同步) | 效率 | 允许null键null值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hashMap | 1.2 | 不安全 | 高 | 可以 |
| hashTable | 1.0 | 安全 | 较低 | 不可以 |
Properties
-
Properties类继承自HashTable类并实现了Map接口,也是使用一种键值对的形式来保存数据
-
他的使用特点和HashTable类似
-
Properties还可以用于从x x x.properties文件中,加载数据到Properties类对象,并进行读取和修改
-
说明:工作后x x x.properties文件通常作为配置文件
-
先判断存储的类型(一组对象【单列】或一组键值对【双列】)
-
一组对象:Collection接口
-
允许重复:List
-
增删多:LinkedList(底层维护了一一个双向链表)
-
改查多:ArrayList(底层维护Object类型的可变数组,索引来定位速度快)
-
-
不允许重复:Set
-
无序:HashSet(底层是HashMap,维护了一个哈希表,即(数组+链表+红黑树))
-
排序:TreeSet
-
当我们使用无参构造器,创建TreeSet时,仍然是无序的
-
希望添加的元素按照字符串大小来排序,使用TreeSet提供的一个构造器,可以传入一个比较器(匿名内部类),并指定排序
-
-
插入和取出顺序一致:LinkedHashSet(底层LinkedHashMap--》底层HashMap),维护数组+双向链表
-
-
一组键值对:Map
-
键无序:HashMap【底层是:哈希表 jdk7:数组+链表,jdk8:数组+链表+红黑树】
-
键排序:TreeMap
-
键插入和取出顺序一致:LinkedHashMap
-
读取文件:P roperties
例题1

package 集合;
import java.util.*;
public class Demo04 {
private static List list;
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(new News("新冠确诊病例超千万,数百万印度教徒赴恒河\"圣浴\"引民众担忧"));
list.add(new News("男子突然想起2个月前钓的鱼还在网兜里,捞起一看赶紧放生"));
int size = list.size();
for (int i = size-1; i >=0 ; i--) {
Object o = list.get(i);
News news=(News)o;
System.out.println(sortReverse(news.getTittle()));
}
}
public static String sortReverse(String value){
if(value.length()>15){
value=value.substring(0,15)+"...";
}else {
value=value;
}
return value;
}
}
class News{
private String tittle;
private String content;
public News(String tittle) {
this.tittle = tittle;
}
public String getTittle() {
return tittle;
}
public void setTittle(String tittle) {
this.tittle = tittle;
}
public String getcontent() {
return content;
}
public void setcontent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public String toString() {
return "tittle='" + tittle;
}
}

例题2

package 集合;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Demo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
Car 宝马 = new Car("宝马", 400000);
list.add(宝马);
Car 宾利 = new Car("宾利", 5000000);
list.add(宾利);
System.out.println("list:"+list);
list.remove(1);
System.out.println("删除宾利:"+list);
System.out.println("是否包含\"宝马\":"+list.contains(宝马));
System.out.println("获取元素个数:"+list.size());
System.out.println("是否为空:"+list.isEmpty());
list.clear();
ArrayList list1 = new ArrayList();
list1.add(new Car("大众",140000));
list1.add(new Car("比亚迪",1500000));
System.out.println("list1:"+list1);
list.addAll(list1);
list.add(new Car("兰博基尼",4000000));
list.add(new Car("五菱",100000));
System.out.println("list:"+list);
System.out.println("查找list1中的元素是否存在:"+list.containsAll(list1));
System.out.println("删除list中的list1元素:"+list.removeAll(list1));
for (Object o :list) {
System.out.println(o);
}
}
}
class Car{
private String name;
private double price;
public Car(String name, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String toString() {
return "Car{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}

例题3

//方式1
package 集合;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class Demo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
Emp jack = new Emp("jack", 650);
Emp tom = new Emp("tom", 1200);
Emp smith = new Emp("smith", 2900);
map.put(1,jack);
map.put(2,tom);
map.put(3,smith);
System.out.println("当前员工信息为:"+map);
Set keyset = map.keySet();
for (Object key : keyset) {
Object o = map.get(key);
Emp emp=(Emp)o;
if (emp.getName()=="jack"){
emp.setSal(2600);
}
emp.setSal(emp.getSal()+100);
System.out.println("修改后:"+key+"-"+map.get(key));
}
}
}
class Emp{
private String name;
private double sal;
public Emp(String name, double sal) {
this.name = name;
this.sal = sal;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getSal() {
return sal;
}
public void setSal(double sal) {
this.sal = sal;
}
public String toString() {
return "Emp{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", sal=" + sal +
'}';
}
}
//方式2
package 集合;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class Demo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("jack", 650);
map.put("tom", 1200);
map.put("smith", 2900);
System.out.println("当前员工信息为:"+map);
map.put("jack",2600);
Set keyset = map.keySet();
for (Object key : keyset) {
map.put(key,(Integer)map.get(key)+100);
System.out.println("修改后:"+key+"-"+map.get(key));
}
}
}

例题4
试分析HashSet和TreeSet分别如何实现去重的?
-
HashSet的去重机制:hashCode()+equals(),底层先通过存入对象,进行运算得到一个hash值,通过hash值得到对应的索引,如果发现table索引所在的位置,没有数据,就直接存放,如果有数据,就进行equals比较【遍历比较】,如果比较后,不相同就加入,否则就不加入
-
TreeSet去重机制:如果你传入了一个Comparator匿名对象,就是用实现的conpare去重,如果方法返回0,就认为是相同的元素/数据,就不添加,如果你没有传入一个Comparator匿名对象,则以你添加的对象实现的Compareable接口的compareTo去重
例题5
下面代码运行会不会抛出异常,并从源码层面说明原因
TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet();
treeSet.add(new Person());
例题6
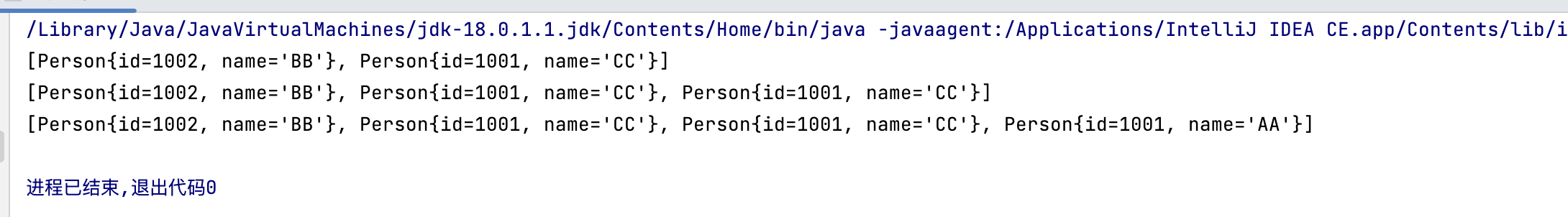
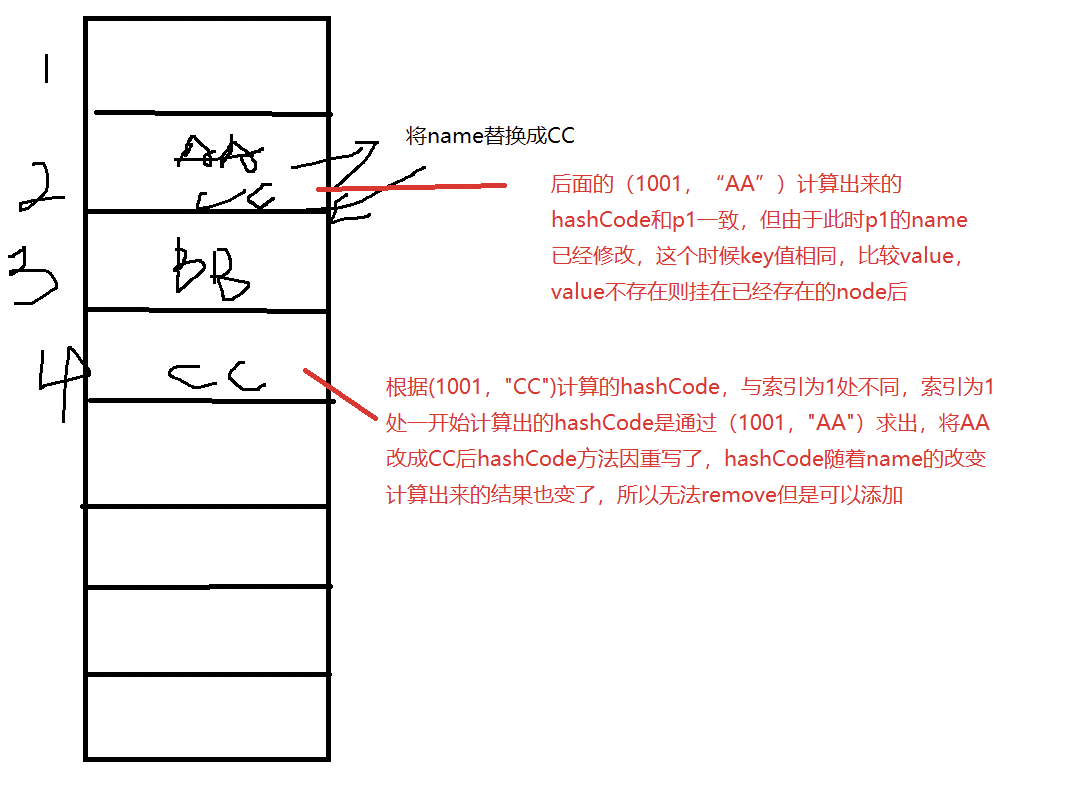
下面的代码输出什么?
已知:Person类按照id和name重写了hashCode和equals方法,问下面代码输出什么?
HashSet set = new HashSet();
Person p1 = new Person(1001,"AA");
Person p2 = new Person(1002,"BB");
set.add(p1);
set.add(p2);
p1.name = "CC";
set.remove(p1);
System.out.println(set);
set.add(new Person(1001,"CC"));
System.out.println(set);
set.add(new Person(1001,"AA"));
System.out.println(set);
//代码实现
package 集合;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Demo07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet set = new HashSet();
Person p1 = new Person(1001,"AA");
Person p2 = new Person(1002,"BB");
set.add(p1);//成功
set.add(p2);//成功
p1.name = "CC";
set.remove(p1); //失败
System.out.println(set);
set.add(new Person(1001,"CC")); //成功
System.out.println(set);
set.add(new Person(1001,"AA")); //成功
System.out.println(set);
}
}
class Person{
public int id;
public String name;
public Person(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Person person = (Person) o;
return id == person.id && Objects.equals(name, person.name);
}
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(id, name);
}
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}