一、SocketChannel
Java NIO中的SocketChannel是一个连接到TCP网络套接字的通道。可以通过以下2种方式创建SocketChannel:
打开一个SocketChannel并连接到互联网上的某台服务器。
一个新连接到达ServerSocketChannel时,会创建一个SocketChannel。
打开 SocketChannel
下面是SocketChannel的打开方式:
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(); socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("http://jenkov.com", 80));
关闭 SocketChannel
当用完SocketChannel之后调用SocketChannel.close()关闭SocketChannel:
socketChannel.close();
从 SocketChannel 读取数据
要从SocketChannel中读取数据,调用一个read()的方法之一。以下是例子:
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48); int bytesRead = socketChannel.read(buf);
首先,分配一个Buffer。从SocketChannel读取到的数据将会放到这个Buffer中。
然后,调用SocketChannel.read()。该方法将数据从SocketChannel 读到Buffer中。read()方法返回的int值表示读了多少字节进Buffer里。如果返回的是-1,表示已经读到了流的末尾(连接关闭了)。
写入 SocketChannel
写数据到SocketChannel用的是SocketChannel.write()方法,该方法以一个Buffer作为参数。示例如下:
String newData = "New String to write to file..." + System.currentTimeMillis(); ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48); buf.clear(); buf.put(newData.getBytes()); buf.flip(); while(buf.hasRemaining()) { channel.write(buf); }
注意SocketChannel.write()方法的调用是在一个while循环中的。Write()方法无法保证能写多少字节到SocketChannel。所以,我们重复调用write()直到Buffer没有要写的字节为止。
非阻塞模式
可以设置 SocketChannel 为非阻塞模式(non-blocking mode).设置之后,就可以在异步模式下调用connect(), read() 和write()了。
connect()
如果SocketChannel在非阻塞模式下,此时调用connect(),该方法可能在连接建立之前就返回了。为了确定连接是否建立,可以调用finishConnect()的方法。像这样:
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false); socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("http://jenkov.com", 80)); while(! socketChannel.finishConnect() ){ //wait, or do something else... }
write()
非阻塞模式下,write()方法在尚未写出任何内容时可能就返回了。所以需要在循环中调用write()。前面已经有例子了,这里就不赘述了。
read()
非阻塞模式下,read()方法在尚未读取到任何数据时可能就返回了。所以需要关注它的int返回值,它会告诉你读取了多少字节。
非阻塞模式与选择器
非阻塞模式与选择器搭配会工作的更好,通过将一或多个SocketChannel注册到Selector,可以询问选择器哪个通道已经准备好了读取,写入等
二、Java NIO DatagramChannel
Java NIO中的DatagramChannel是一个能收发UDP包的通道。因为UDP是无连接的网络协议,所以不能像其它通道那样读取和写入。它发送和接收的是数据包。
打开 DatagramChannel
下面是 DatagramChannel 的打开方式:
DatagramChannel channel = DatagramChannel.open(); channel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(9999));
这个例子打开的 DatagramChannel可以在UDP端口9999上接收数据包。
接收数据
通过receive()方法从DatagramChannel接收数据,如:
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
buf.clear();
channel.receive(buf);
receive()方法会将接收到的数据包内容复制到指定的Buffer. 如果Buffer容不下收到的数据,多出的数据将被丢弃。
发送数据
通过send()方法从DatagramChannel发送数据,如:
String newData = "New String to write to file..." + System.currentTimeMillis(); ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48); buf.clear(); buf.put(newData.getBytes()); buf.flip(); int bytesSent = channel.send(buf, new InetSocketAddress("jenkov.com", 80));
这个例子发送一串字符到”jenkov.com”服务器的UDP端口80。 因为服务端并没有监控这个端口,所以什么也不会发生。也不会通知你发出的数据包是否已收到,因为UDP在数据传送方面没有任何保证。
连接到特定的地址
可以将DatagramChannel“连接”到网络中的特定地址的。由于UDP是无连接的,连接到特定地址并不会像TCP通道那样创建一个真正的连接。而是锁住DatagramChannel ,让其只能从特定地址收发数据。
这里有个例子:
channel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("jenkov.com", 80));
当连接后,也可以使用read()和write()方法,就像在用传统的通道一样。只是在数据传送方面没有任何保证。这里有几个例子:
int bytesRead = channel.read(buf); int bytesWritten = channel.write(but);
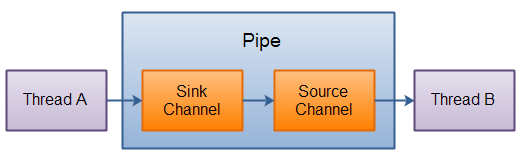
三、Pipe
Java NIO 管道是2个线程之间的单向数据连接。Pipe有一个source通道和一个sink通道。数据会被写到sink通道,从source通道读取。
这里是Pipe原理的图示:
创建管道
通过Pipe.open()方法打开管道。例如:
Pipe pipe = Pipe.open();
向管道写数据
要向管道写数据,需要访问sink通道。像这样:
Pipe.SinkChannel sinkChannel = pipe.sink();
通过调用SinkChannel的write()方法,将数据写入SinkChannel,像这样:
String newData = "New String to write to file..." + System.currentTimeMillis(); ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48); buf.clear(); buf.put(newData.getBytes()); buf.flip(); while(buf.hasRemaining()) { sinkChannel.write(buf); }
从管道读取数据
从读取管道的数据,需要访问source通道,像这样:
Pipe.SourceChannel sourceChannel = pipe.source();
调用source通道的read()方法来读取数据,像这样:
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48); int bytesRead = sourceChannel.read(buf);
read()方法返回的int值会告诉我们多少字节被读进了缓冲区。





