2024暑假第三周总结
判断和循环
if语句,switch语句,for循环,while循环···
if语句三种格式
格式一:
if(关系表达式){
语句体;
}
格式二:
if (关系表达式)
{
语句体1;
}else{
语句体2
}
if 的嵌套实例
import java.util.Scanner;
public class shunxu {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter number: ");
int n = sc.nextInt();
//只有当n在0到100之间
if(n > 0 && n <= 100) {
if (n % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println("right");
} else {
System.out.println("left");
}
}else{
System.out.println("error");
}
}
}
格式三:
if(关系表达式1){
语句体1;
}else if (关系表达式2){
语句体2;
}
else{
语句体 n + 1;
}
应用1:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class shunxu {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter number: ");
int score = sc.nextInt();
if (score <= 100) {
if (score >= 95 && score <= 100) {
System.out.println("自行车");
} else if (score >= 90 && score <= 94) {
System.out.println("游乐场");
} else if (score >= 80 && score <= 89) {
System.out.println("变形金刚");
} else {
System.out.println("揍一顿");
}
}else{
System.out.println("error");
}
}
}
应用二:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class vip {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter score: ");
int score = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter price: ");
int price = sc.nextInt();
if (score <= 3) {
if (score == 1) {
System.out.println(price*0.9);
} else if (score == 2) {
System.out.println(price*0.8);
} else if (score == 3) {
System.out.println(price*0.7);
}
}else{
System.out.println("error");
}
}
}
选择结构
switch
switch(表达式){
case 值1(只能是字面量,不能是变量):
语句体1:
break:
case 值2:
语句体2:
break:
…
default:
语句体n+1:
break;
}
知识点:
default 的位置和省略
default不一定写在最下面
可以省略语法不出错
public class SwitchDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number = 100;
switch (number) {
case 1:
System.out.println("number为1");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("number为2");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("number为3");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("number为4");
break;
/*default:
System.out.println("default");
break;*/
}
}
case穿透
语句体中没有写break
使用场景:如果多个case 的语句体重复了,那么我们考虑利用case穿透去简化代码
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SwitchDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int day = sc.nextInt();
//1
/*switch (day) {
case 1:
case 2:
case 3:
case 4:
case 5:
System.out.println("work");
break;
case 6:
case 7:
System.out.println("rest");
break;
default:
System.out.println("default");
break;*/
//2
/*switch (day) {
case 1,2,3,4,5:
System.out.println("work");
break;
case 6,7:
System.out.println("rest");
break;
default:
System.out.println("default");
break;*/
//3最简写法
switch (day) {
case 1,2,3,4,5->System.out.println("work");
case 6,7->System.out.println("rest");
default->System.out.println("default");
}
}
}
switch的新特性(JDK12)
public class SwitchDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number = 1;
/*switch (number) {
case 1:
System.out.println("一");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("二");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("三");
break;
default:
System.out.println("无选项");
break;*/
switch (number) {
case 1 ->{
System.out.println("一");
}
case 2 ->{
System.out.println("二");
}
//只有一行代码大括号可以省略
case 3 -> System.out.println("三");
default -> {
System.out.println("无选项");
}
}
}
}
switch 用于把有限个数据一一列举,任选其一
if的第三种格式 用于对范围的判断
循环
for(){
循环语句体;
}
public class ForDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//打印1~5
for (int i = 1 ; i <=5; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
public class ForDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//打印10~1
for (int i = 10 ; i > 0 ; i--) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
统计数字
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ForDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//键盘录入两个数字,表示一个范围
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请录入一个数字表示范围的开始:");
int number1 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请录入一个数字表示范围的结束:");
int number2 = sc.nextInt();
//统计范围所有满足条件的数字
int count = 0;
for (int i = number1; i <= number2; i++) {
if (i % 3 == 0 && i % 5 == 0) {
count++;
System.out.println(i);
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
循环语句
while (){
循环语句体;
条件控制语句;
}
for和whlie对比
相同点:运行规则一致
区别:使用习惯
for循环 知道循环的次数或者范围
whil循环 不知道循环的次数和范围,只知道循环的结束条件
例子:
public class WhileDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//记录纸张的初始厚度
double i = 0.1;
//记录折叠次数
int count = 0;
//循环次数和范围未知
while (i < 8844430) {
i = i * 2;
System.out.println(i);
count++;
}
System.out.println("折叠次数"+ count);
}
}
回文数
import java.util.Scanner;
public class WhileDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请录入被除数: ");
int a = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请录入除数: ");
int b = sc.nextInt();
/*int num = a;
//统计相减次数
int count = 0;
while(num > 0){
num = num-b;
count++;
}
//余数
System.out.println(num+b);
//商
System.out.println(count-1);*/
int count = 0;
while (a >= b) {
a = a - b;
count++;
}
//余数
System.out.println(a);
//商
System.out.println(count);
}
}
do-while
do{
循环体;
}while();
循环高级
无限循环:循环一直停不下来
无限循环下面不能再写其他代码,因为循环永远停不下来,下面的代码永远执行不到
for
public class ForDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (;;) {
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}
}
while
public class WhileDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//while无限循环
while(true){
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}
}
跳转控制语句
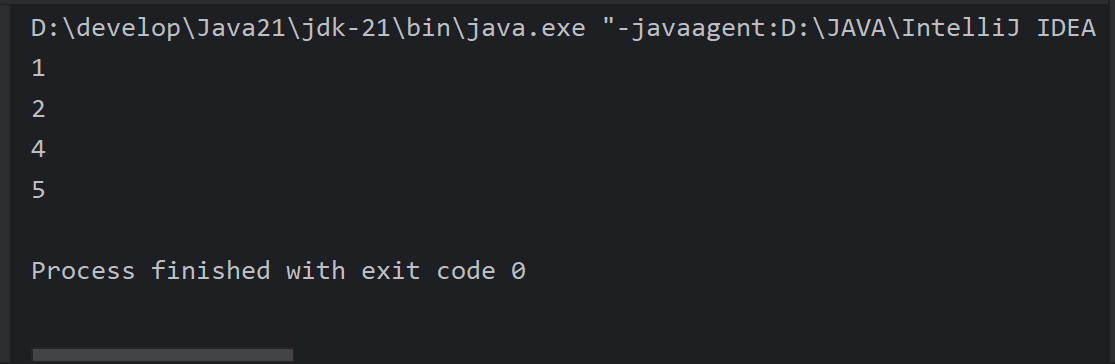
continue跳过本次循环,继续执行下次循环
public class ForDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
if (i == 3) {
continue;
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
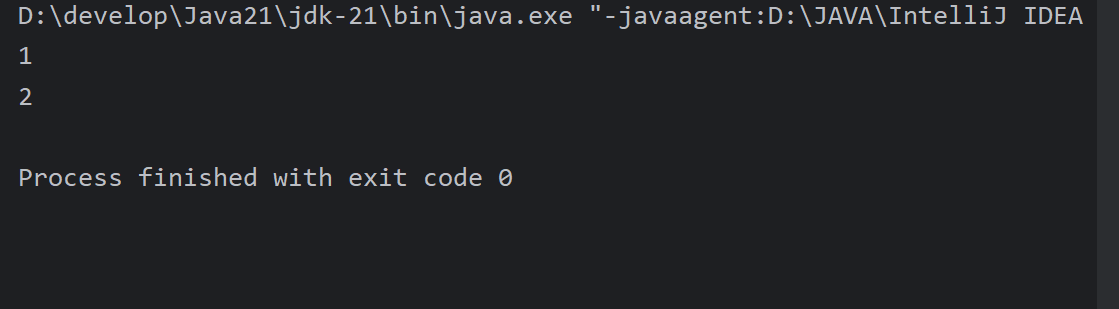
break 结束整个循环
public class ForDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
if (i == 3) {
break;
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
总结
本周是继续对java的基本语法进行学习,并认真阅读《大道至简》
整理了有关顺序、选择、循环的相关语法知识,并做了一定的练习。
下周深入学习面向对象和方法的相关语法知识,并进行一定的训练,并继续阅读《大道至简》




