Pintos Project 1
序:
这是我第二次写Pintos内核,第一次上这课的时候由于刚接触操作系统,这个project难度又是非常大,所以其实写出的代码有很多bug,一些测试也没有通过,希望通过这次重写Pintos,加深对操作系统内核的理解,并力争通过所有测试。代码完整部分在我的github里,如果觉得有帮助的话记得star我一下哦。
Part1:
第一部分的目的是让我们修改timer_sleep(int64_t ticks)函数的忙等机制。thread结构体如下
1 struct thread 2 { 3 /* Owned by thread.c. */ 4 tid_t tid; /* Thread identifier. */ 5 enum thread_status status; /* Thread state. */ 6 char name[16]; /* Name (for debugging purposes). */ 7 uint8_t *stack; /* Saved stack pointer. */ 8 int priority; /* Priority. */ 9 struct list_elem allelem; /* List element for all threads list. */ 10 11 /* Shared between thread.c and synch.c. */ 12 struct list_elem elem; /* List element. */ 13 14 #ifdef USERPROG 15 /* Owned by userprog/process.c. */ 16 uint32_t *pagedir; /* Page directory. */ 17 #endif 18 19 /* Owned by thread.c. */ 20 unsigned magic; /* Detects stack overflow. */ 21 22 int64_t ticks_blocked; /* Time for blocked. */ 23 };
这里我们添加了一个变量ticks_blocked用于记录剩余阻塞时间。在timer_sleep函数中,将该线程阻塞并设置阻塞时间。注意这一过程需要解除中断。
1 /* Sleeps for approximately TICKS timer ticks. Interrupts must 2 be turned on. */ 3 void 4 timer_sleep (int64_t ticks) 5 { 6 if(ticks <= 0) return; 7 ASSERT (intr_get_level () == INTR_ON); 8 enum intr_level old_level = intr_disable (); 9 struct thread *current_thread = thread_current (); 10 current_thread->ticks_blocked = ticks; 11 thread_block (); 12 intr_set_level (old_level); 13 }
thread_block()的底层实现是将当前线程的状态设置为THREAD_BLOCKED,然后重新调度。状态为THREAD_BLOCKED的线程将从就绪队列中移除。
1 /* Puts the current thread to sleep. It will not be scheduled 2 again until awoken by thread_unblock(). 3 4 This function must be called with interrupts turned off. It 5 is usually a better idea to use one of the synchronization 6 primitives in synch.h. */ 7 void 8 thread_block (void) 9 { 10 ASSERT (!intr_context ()); 11 ASSERT (intr_get_level () == INTR_OFF); 12 13 thread_current ()->status = THREAD_BLOCKED; 14 schedule (); 15 }
接下来就是在适当的时间唤醒线程。我们在每个tick内遍历所有线程,并将ticks_blocked值减一,如果该值小于等于0,则将其从阻塞队列中移除重新参与调度。每次时间片轮转时都会调度timer_interrupt函数。
1 /* Timer interrupt handler. */ 2 static void 3 timer_interrupt (struct intr_frame *args UNUSED) 4 { 5 ticks++; 6 thread_tick (); 7 thread_foreach(check_blocked_time,NULL); 8 }
thread_foreach函数的作用是对每个线程调用func函数,thread_action_func是用户定义类型typedef void thread_action_func (struct thread *t, void *aux);它规定了函数的返回值为void且有struct thread和void*两个参数。
1 /* Invoke function 'func' on all threads, passing along 'aux'. 2 This function must be called with interrupts off. */ 3 void 4 thread_foreach (thread_action_func *func, void *aux) 5 { 6 struct list_elem *e; 7 8 ASSERT (intr_get_level () == INTR_OFF); 9 10 for (e = list_begin (&all_list); e != list_end (&all_list); 11 e = list_next (e)) 12 { 13 struct thread *t = list_entry (e, struct thread, allelem); 14 func (t, aux); 15 } 16 }
每次时间片用完时,我们都需要将每个线程的ticks_blocked减1,如果该线程ticks_blocked小于0,则将其唤醒,因此我们实现函数如下。
1 /* Check every threads whether they should be awaked. */ 2 void check_blocked_time(struct thread *t, void *aux){ 3 if (t->status == THREAD_BLOCKED && t->ticks_blocked > 0){ 4 t->ticks_blocked--; 5 if (t->ticks_blocked == 0) 6 thread_unblock(t); 7 } 8 }
别忘记在头文件里添加定义
1 void check_blocked_time(struct thread *t, void *aux);
至此,part1通过大半部分
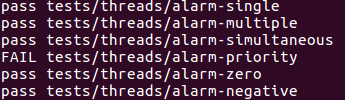
下面来部署线程的优先级系统,我们发现thread.c里面有那么一个函数,看名字就知道它返回下一个要执行的线程,那么我们只要在ready_list中找到优先级最高的线程并将其返回即可。
1 /* Chooses and returns the next thread to be scheduled. Should 2 return a thread from the run queue, unless the run queue is 3 empty. (If the running thread can continue running, then it 4 will be in the run queue.) If the run queue is empty, return 5 idle_thread. */ 6 static struct thread * 7 next_thread_to_run (void) 8 { 9 if (list_empty (&ready_list)) 10 return idle_thread; 11 else 12 return list_entry (list_pop_front (&ready_list), struct thread, elem); 13 }
查找list.c文件,我发现了list_max函数,用于根据比较函数查找ready_list中优先级最高的线程,然后将其从ready_list中移除并返回。这里的list_entry用于将链表节点类型转换为线程结构体类型。
1 bool thread_compare_priority (const struct list_elem *a,const struct list_elem *b,void *aux UNUSED){ 2 return list_entry(a,struct thread,elem)->priority < list_entry(b,struct thread,elem)->priority; 3 } 4 5 /* Chooses and returns the next thread to be scheduled. Should 6 return a thread from the run queue, unless the run queue is 7 empty. (If the running thread can continue running, then it 8 will be in the run queue.) If the run queue is empty, return 9 idle_thread. */ 10 static struct thread * 11 next_thread_to_run (void) 12 { 13 if (list_empty (&ready_list)) 14 return idle_thread; 15 else{ 16 struct list_elem *max_priority = list_max (&ready_list,thread_compare_priority,NULL); 17 list_remove (max_priority); 18 return list_entry (max_priority,struct thread,elem); 19 } 20 }
至此,part1所有test cases全部pass
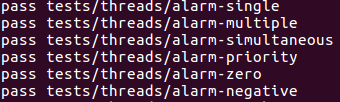
Part2:
第二部分有以下测试
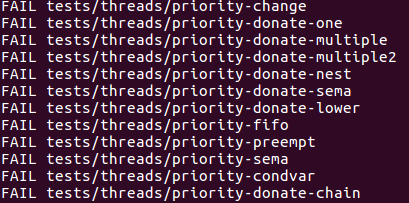
我们先看除去donation以外的测试,先看priority-fifo的源代码
1 void 2 test_priority_fifo (void) 3 { 4 struct simple_thread_data data[THREAD_CNT]; 5 struct lock lock; 6 int *output, *op; 7 int i, cnt; 8 9 /* This test does not work with the MLFQS. */ 10 ASSERT (!thread_mlfqs); 11 12 /* Make sure our priority is the default. */ 13 ASSERT (thread_get_priority () == PRI_DEFAULT); 14 15 msg ("%d threads will iterate %d times in the same order each time.", 16 THREAD_CNT, ITER_CNT); 17 msg ("If the order varies then there is a bug."); 18 19 output = op = malloc (sizeof *output * THREAD_CNT * ITER_CNT * 2); 20 ASSERT (output != NULL); 21 lock_init (&lock); 22 23 thread_set_priority (PRI_DEFAULT + 2); 24 for (i = 0; i < THREAD_CNT; i++) 25 { 26 char name[16]; 27 struct simple_thread_data *d = data + i; 28 snprintf (name, sizeof name, "%d", i); 29 d->id = i; 30 d->iterations = 0; 31 d->lock = &lock; 32 d->op = &op; 33 thread_create (name, PRI_DEFAULT + 1, simple_thread_func, d); 34 } 35 36 thread_set_priority (PRI_DEFAULT); 37 /* All the other threads now run to termination here. */ 38 ASSERT (lock.holder == NULL); 39 40 cnt = 0; 41 for (; output < op; output++) 42 { 43 struct simple_thread_data *d; 44 45 ASSERT (*output >= 0 && *output < THREAD_CNT); 46 d = data + *output; 47 if (cnt % THREAD_CNT == 0) 48 printf ("(priority-fifo) iteration:"); 49 printf (" %d", d->id); 50 if (++cnt % THREAD_CNT == 0) 51 printf ("\n"); 52 d->iterations++; 53 } 54 }
这个测试创建了一个优先级PRI_DEFAULT+2的主线程,并用这个线程创建了16个优先级PRI_DEFAULT+1的子线程,然后把主线程的优先级设置为优先级PRI_DEFAULT,所以现在pintos内有16个优先级PRI_DEFAULT+1的线程和1个优先级PRI_DEFAULT的线程在跑,测试需要把16个线程跑完再结束那一个线程,看起来没什么问题,但注意OS中线程是并行执行的,有可能最开始的一个线程在设置完优先级之后立刻结束了,而此时其他线程并未结束,即37行的注释,因此在线程设置完优先级之后应该立刻重新调度,因此只需要在thread_set_priority()函数里添加thread_yield()函数即可。
1 /* Sets the current thread's priority to NEW_PRIORITY. */ 2 void 3 thread_set_priority (int new_priority) 4 { 5 thread_current ()->priority = new_priority; 6 thread_yield(); 7 }
接下来看priority-preempt测试了什么
1 void 2 test_priority_preempt (void) 3 { 4 /* This test does not work with the MLFQS. */ 5 ASSERT (!thread_mlfqs); 6 7 /* Make sure our priority is the default. */ 8 ASSERT (thread_get_priority () == PRI_DEFAULT); 9 10 thread_create ("high-priority", PRI_DEFAULT + 1, simple_thread_func, NULL); 11 msg ("The high-priority thread should have already completed."); 12 }
这个就很简单了,创建一个新的高优先级线程抢占当前线程,因此在thread_create中,如果新线程的优先级高于当前线程优先级,调用thread_yield()函数即可。
1 tid_t 2 thread_create (const char *name, int priority, 3 thread_func *function, void *aux) 4 { 5 struct thread *t; 6 struct kernel_thread_frame *kf; 7 struct switch_entry_frame *ef; 8 struct switch_threads_frame *sf; 9 tid_t tid; 10 11 ASSERT (function != NULL); 12 13 /* Allocate thread. */ 14 t = palloc_get_page (PAL_ZERO); 15 if (t == NULL) 16 return TID_ERROR; 17 18 /* Initialize thread. */ 19 init_thread (t, name, priority); 20 tid = t->tid = allocate_tid (); 21 22 /* Stack frame for kernel_thread(). */ 23 kf = alloc_frame (t, sizeof *kf); 24 kf->eip = NULL; 25 kf->function = function; 26 kf->aux = aux; 27 28 /* Stack frame for switch_entry(). */ 29 ef = alloc_frame (t, sizeof *ef); 30 ef->eip = (void (*) (void)) kernel_thread; 31 32 /* Stack frame for switch_threads(). */ 33 sf = alloc_frame (t, sizeof *sf); 34 sf->eip = switch_entry; 35 sf->ebp = 0; 36 37 /* Add to run queue. */ 38 thread_unblock (t); 39 40 if (thread_current ()->priority < priority) 41 thread_yield (); 42 43 return tid; 44 }
意外发现priority-change也过了,顺便看看这个测试在做什么
1 void 2 test_priority_change (void) 3 { 4 /* This test does not work with the MLFQS. */ 5 ASSERT (!thread_mlfqs); 6 7 msg ("Creating a high-priority thread 2."); 8 thread_create ("thread 2", PRI_DEFAULT + 1, changing_thread, NULL); 9 msg ("Thread 2 should have just lowered its priority."); 10 thread_set_priority (PRI_DEFAULT - 2); 11 msg ("Thread 2 should have just exited."); 12 }
很明显,这个测试创建了一个新线程并要这个线程立刻调用,然后在降低优先级之后它就不应该继续执行了,这正好对应于之前修改的两处,所以自然能通过测试。
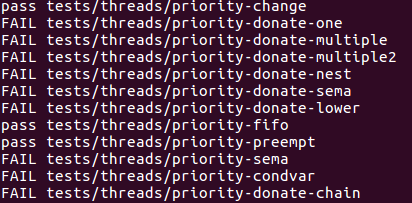
通过了三个简单测试,接下来处理线程同步问题
先来看看priority-seme这个测试
1 void 2 test_priority_sema (void) 3 { 4 int i; 5 6 /* This test does not work with the MLFQS. */ 7 ASSERT (!thread_mlfqs); 8 9 sema_init (&sema, 0); 10 thread_set_priority (PRI_MIN); 11 for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) 12 { 13 int priority = PRI_DEFAULT - (i + 3) % 10 - 1; 14 char name[16]; 15 snprintf (name, sizeof name, "priority %d", priority); 16 thread_create (name, priority, priority_sema_thread, NULL); 17 } 18 19 for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) 20 { 21 sema_up (&sema); 22 msg ("Back in main thread."); 23 } 24 }
这个测试创建了10个优先级不等的线程,并且每个线程调用sema_down函数,其他得不到信号量的线程都得阻塞,而每次运行的线程释放信号量时必须确保优先级最高的线程继续执行,因此修改sema_up。查到semaphore结构体如下,waiters为阻塞队列
1 /* A counting semaphore. */ 2 struct semaphore 3 { 4 unsigned value; /* Current value. */ 5 struct list waiters; /* List of waiting threads. */ 6 };
再来看pintos的sema_up是如何设计的,他只是把waiters最前面的线程取出来加入到ready_list而已。
1 /* Up or "V" operation on a semaphore. Increments SEMA's value 2 and wakes up one thread of those waiting for SEMA, if any. 3 4 This function may be called from an interrupt handler. */ 5 void 6 sema_up (struct semaphore *sema) 7 { 8 enum intr_level old_level; 9 10 ASSERT (sema != NULL); 11 12 old_level = intr_disable (); 13 if (!list_empty (&sema->waiters)) 14 thread_unblock (list_entry (list_pop_front (&sema->waiters), 15 struct thread, elem)); 16 sema->value++; 17 intr_set_level (old_level); 18 }
现在问题很简单了,就是把14和15行修改一下,在waiters中取出优先级最高的thread,并yield()即可即可,修改如下
1 /* Up or "V" operation on a semaphore. Increments SEMA's value 2 and wakes up one thread of those waiting for SEMA, if any. 3 4 This function may be called from an interrupt handler. */ 5 void 6 sema_up (struct semaphore *sema) 7 { 8 enum intr_level old_level; 9 10 ASSERT (sema != NULL); 11 12 old_level = intr_disable (); 13 if (!list_empty (&sema->waiters)) { 14 struct list_elem *max_priority = list_max (&sema->waiters,thread_compare_priority,NULL); 15 list_remove (max_priority); 16 thread_unblock(list_entry (max_priority,struct thread,elem)); 17 }18 sema->value++; 19 intr_set_level (old_level); 20 thread_yield(); 21 }
接下来看priority-condvar测试,
1 void 2 test_priority_condvar (void) 3 { 4 int i; 5 6 /* This test does not work with the MLFQS. */ 7 ASSERT (!thread_mlfqs); 8 9 lock_init (&lock); 10 cond_init (&condition); 11 12 thread_set_priority (PRI_MIN); 13 for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) 14 { 15 int priority = PRI_DEFAULT - (i + 7) % 10 - 1; 16 char name[16]; 17 snprintf (name, sizeof name, "priority %d", priority); 18 thread_create (name, priority, priority_condvar_thread, NULL); 19 } 20 21 for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) 22 { 23 lock_acquire (&lock); 24 msg ("Signaling..."); 25 cond_signal (&condition, &lock); 26 lock_release (&lock); 27 } 28 }
和前面的信号量机制类似,条件变量也维护了一个waiters用于存储等待接受条件变量的线程,那么就修改cond_signal()函数唤醒优先级最高的线程即可,和priority-sema类似,直接上代码。值得注意的是,这里的cond->waiters推入的是semaphore_elem而不是thread,这是为了等待不同信号量的线程直接互不影响,
1 bool cond_compare_priority (const struct list_elem *a,const struct list_elem *b,void *aux UNUSED){ 2 struct semaphore_elem *sa = list_entry(a,struct semaphore_elem,elem); 3 struct semaphore_elem *sb = list_entry(b,struct semaphore_elem,elem); 4 return list_entry(list_front(&sa->semaphore.waiters),struct thread,elem)->priority < 5 list_entry(list_front(&sb->semaphore.waiters),struct thread,elem)->priority; 6 } 7 8 /* If any threads are waiting on COND (protected by LOCK), then 9 this function signals one of them to wake up from its wait. 10 LOCK must be held before calling this function. 11 12 An interrupt handler cannot acquire a lock, so it does not 13 make sense to try to signal a condition variable within an 14 interrupt handler. */ 15 void 16 cond_signal (struct condition *cond, struct lock *lock UNUSED) 17 { 18 ASSERT (cond != NULL); 19 ASSERT (lock != NULL); 20 ASSERT (!intr_context ()); 21 ASSERT (lock_held_by_current_thread (lock)); 22 23 if (!list_empty (&cond->waiters)){ 24 struct list_elem *max_priority = list_max (&cond->waiters,cond_compare_priority,NULL); 25 list_remove (max_priority); 26 sema_up(&list_entry(max_priority,struct semaphore_elem,elem)->semaphore); 27 } 28 }
线程同步测试至此结束
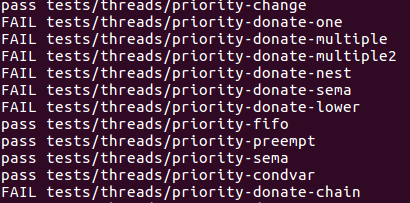
接下来处理优先级捐赠的问题,这里七个测试用例我就不一一解释了,但是我强烈建议把七个测试的内容仔细看一遍,这里我从七个测试中提取要点进行解释,因为前几个测试比较简单,实际上处理完复杂的测试之后简单的测试必然能通过,因此这里我专门挑选复杂的测试进行讲解。
这七个测试有两个关键点,一个是priority-donate-multiple这个测试它给了我们一个关键信息,一个线程可能有多个锁,然后多个其他线程会因为这个线程而阻塞,这是第一个要点。第二个要点是priority-donate-chain这个测试,这个测试比较复杂,是个优先级嵌套的问题。如下图
thread_0(has lock[0]) thread_3(has lock[1], blocked by lock[0]) thread_6(has lock[2], blocked by lock[1]) thread_9(has lock[3], blocked by lock[2])
0 3 6 9
3 6 9
6 9
9
分析一下这张图,thread_0的线程拥有了lock[0],thread_3的线程拥有lock[1],并因为thread_0的lock[0]而阻塞,因此将thread_0优先级提升到3,thread_6因为hread_3的lock[1]而阻塞,所以thread_3和thread_0将优先级提升到6,以此类推。这里我们提取到的关键信息是,优先级的更新操作是需要循环的,而循环的关键点在于知道当前锁的拥有者,如thread_9就需要知道lock[2]的所有者是谁(thread_6),以及thread_6在等待哪个锁(lock[1])。
因此我们修改thread和lock结构体。
1 struct thread 2 { 3 /* Owned by thread.c. */ 4 tid_t tid; /* Thread identifier. */ 5 enum thread_status status; /* Thread state. */ 6 char name[16]; /* Name (for debugging purposes). */ 7 uint8_t *stack; /* Saved stack pointer. */ 8 int priority; /* Priority. */ 9 struct list_elem allelem; /* List element for all threads list. */ 10 11 /* Shared between thread.c and synch.c. */ 12 struct list_elem elem; /* List element. */ 13 14 #ifdef USERPROG 15 /* Owned by userprog/process.c. */ 16 uint32_t *pagedir; /* Page directory. */ 17 #endif 18 19 /* Owned by thread.c. */ 20 unsigned magic; /* Detects stack overflow. */ 21 22 int64_t ticks_blocked; /* Time for blocked. */ 23 struct list locks; /* Locks this thread holds */ 24 struct lock *waiting_lock; /* The lock this thread is waiting for */ 25 int original_priority; /* Original priority of this thread */ 26 };
1 struct lock 2 { 3 int max_priority; /* Max priority of all threads aquiring this lock */ 4 struct list_elem elem; /* Used in thread.c */ 5 struct thread *holder; /* Thread holding lock (for debugging). */ 6 struct semaphore semaphore; /* Binary semaphore controlling access. */ 7 };
接下来处理lock_acquire(),为了区别与第三部分的mlfqs,所有添加部分都进行了thread_mlfqs判断(我是做了第三部分才改了第二部分,因此提前在这里作出修改)。在获取锁之前,根据前面的分析,循环更新所有参与嵌套的线程的优先级。
1 /* Acquires LOCK, sleeping until it becomes available if 2 necessary. The lock must not already be held by the current 3 thread. 4 5 This function may sleep, so it must not be called within an 6 interrupt handler. This function may be called with 7 interrupts disabled, but interrupts will be turned back on if 8 we need to sleep. */ 9 void 10 lock_acquire (struct lock *lock) 11 { 12 ASSERT (lock != NULL); 13 ASSERT (!intr_context ()); 14 ASSERT (!lock_held_by_current_thread (lock)); 15 16 if(lock->holder != NULL && !thread_mlfqs){ 17 thread_current()->waiting_lock = lock; 18 struct lock *wlock = lock; 19 while(wlock != NULL && thread_current()->priority > wlock->max_priority){ 20 wlock->max_priority = thread_current()->priority; 21 struct list_elem *max_priority_in_locks = list_max(&wlock->holder->locks,lock_compare_max_priority,NULL); 22 int maximal = list_entry(max_priority_in_locks,struct lock,elem)->max_priority; 23 if(wlock->holder->priority < maximal) 24 wlock->holder->priority = maximal; 25 wlock = wlock->holder->waiting_lock; 26 } 27 } 28 29 sema_down (&lock->semaphore); 30 lock->holder = thread_current (); 31 32 if(!thread_mlfqs){ 33 thread_current()->waiting_lock = NULL; 34 lock->max_priority = thread_current()->priority; 35 list_push_back(&thread_current()->locks,&lock->elem); 36 if(lock->max_priority > thread_current()->priority){ 37 thread_current()->priority = lock->max_priority; 38 thread_yield(); 39 } 40 } 41 }
处理lock_release()函数,在释放锁之前,对该线程的优先级进行更新,如果他没有拥有的锁,就直接更新为original_priority,否则从所有锁的max_priority中找到最大值进行更新。
1 void 2 lock_release (struct lock *lock) 3 { 4 ASSERT (lock != NULL); 5 ASSERT (lock_held_by_current_thread (lock)); 6 7 if(!thread_mlfqs){ 8 list_remove(&lock->elem); 9 int maximal = thread_current()->original_priority; 10 if(!list_empty(&thread_current()->locks)){ 11 struct list_elem *max_priority_in_locks = list_max(&thread_current()->locks,lock_compare_max_priority,NULL); 12 int p = list_entry(max_priority_in_locks,struct lock,elem)->max_priority; 13 if(p > maximal) 14 maximal = p; 15 } 16 thread_current()->priority = maximal; 17 } 18 19 lock->holder = NULL; 20 sema_up (&lock->semaphore); 21 }
最后需要对thread_set_priority (int new_priority)进行更新,如果没有锁,那优先级捐赠的情况根本不用考虑,直接更新,或者更新的优先级大于当前线程的优先级,则更新当前线程优先级,但无论如何,original_priority都需要进行更新。
1 void 2 thread_set_priority (int new_priority) 3 { 4 thread_current ()->original_priority = new_priority; 5 if(list_empty(&thread_current()->locks) || new_priority > thread_current()->priority){ 6 thread_current()->priority = new_priority; 7 thread_yield(); 8 } 9 }
还有个list_max中的比较函数
1 /* Compare function in list of a lock */ 2 bool lock_compare_max_priority (const struct list_elem *a,const struct list_elem *b,void *aux UNUSED){ 3 return list_entry(a,struct lock,elem)->max_priority < list_entry(b,struct lock,elem)->max_priority; 4 }
至此第二部分完全通过,该部分是project1最难的一部分,代码量不大,但需要从七大测试中提取出最难的测试并解决,其余简单的测试都迎刃而解。
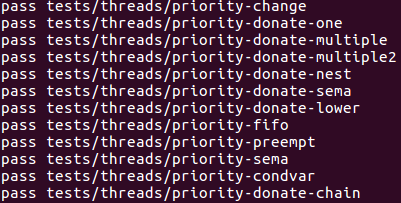
Part3:
第三部分主要让我们实现多级反馈队列调度算法,文档中有这么一句话:Unfortunately, Pintos does not support floating-point arithmeticin the kernel, because it would complicate and slow the kernel.所以说我们先不管算法什么的,先部署这个浮点类型的计算部分,依据文档95页的要求,编写下面的文件fixed-point.h
1 #ifndef FIXED_POINT_H 2 #define FIXED_POINT_H 3 4 #define p 17 5 #define q 14 6 #define f (1<<q) 7 8 #define CONVERT_N_TO_FIXED_POINT(n) ((n)*(f)) 9 #define CONVERT_X_TO_INTEGER_ZERO(x) ((x)/(f)) 10 #define CONVERT_X_TO_INTEGER_NEAREST(x) (((x)>=0)?(((x)+(f)/2)/(f)):(((x)-(f)/2)/(f))) 11 12 #define ADD_X_AND_Y(x,y) ((x)+(y)) 13 #define SUBTRACT_Y_FROM_X(x,y) ((x)-(y)) 14 #define ADD_X_AND_N(x,n) ((x)+(n)*(f)) 15 #define SUBTRACT_N_FROM_X(x,n) ((x)-(n)*(f)) 16 #define MULTIPLY_X_BY_Y(x,y) (((int64_t) (x))*(y)/(f)) 17 #define MULTIPLY_X_BY_N(x,n) ((x)*(n)) 18 #define DIVIDE_X_BY_Y(x,y) (((int64_t) (x))*(f)/(y)) 19 #define DIVIDE_X_BY_N(x,n) ((x)/(n)) 20 21 #endif
接下来实现算法部分,在此之前,先理解这个算法是咋回事。阅读文档BSD4.4部分,我们得到以下信息:
1. 该算法的优先级是动态变化的,主要动态修改Niceness, Priority, recent_cpu, load_avg四大变量
2. Priority的计算公式为:priority= PRI_MAX - (recent_cpu/ 4) - (nice*2),每四个clock tick对所有线程更新一次
3. recent_cpu的计算公式为recent_cpu= (2*load_avg)/(2*load_avg+ 1) *recent_cpu+nice,当timer_ticks () % TIMER_FREQ == 0时对所有线程更新,每个tick对当前线程的recent_cpu加1。
4. load_avg的计算公式为load_avg= (59/60)*load_avg+ (1/60)*ready_threads,当timer_ticks () % TIMER_FREQ == 0时对所有线程更新
现在问题就很简单了,首先在在thread结构体中添加成员,
1 struct thread 2 { 3 /* Owned by thread.c. */ 4 tid_t tid; /* Thread identifier. */ 5 enum thread_status status; /* Thread state. */ 6 char name[16]; /* Name (for debugging purposes). */ 7 uint8_t *stack; /* Saved stack pointer. */ 8 int priority; /* Priority. */ 9 struct list_elem allelem; /* List element for all threads list. */ 10 11 /* Shared between thread.c and synch.c. */ 12 struct list_elem elem; /* List element. */ 13 14 #ifdef USERPROG 15 /* Owned by userprog/process.c. */ 16 uint32_t *pagedir; /* Page directory. */ 17 #endif 18 19 /* Owned by thread.c. */ 20 unsigned magic; /* Detects stack overflow. */ 21 22 int64_t ticks_blocked; /* Time for blocked. */ 23 struct list locks; /* Locks this thread holds */ 24 struct lock *waiting_lock; /* The lock this thread is waiting for */ 25 int original_priority; /* Original priority of this thread */ 26 27 int nice; /* Niceness of thread used in mlfqs */ 28 int64_t recent_cpu; /* Used in mlfqs */ 29 };
然后在thread.c中定义一个全局变量load_avg,根据2,3,4条我们在thread.c中编写以下函数,记得在thread.h中添加声明
1 /* Increment by 1 for each clock tick */ 2 void increase_recent_cpu(void){ 3 if (thread_current()!=idle_thread) 4 thread_current()->recent_cpu = ADD_X_AND_N(thread_current()->recent_cpu,1); 5 } 6 7 /* Modify Priority */ 8 void modify_priority(struct thread *t,void *aux UNUSED){ 9 if (t!=idle_thread){ 10 //priority = PRI_MAX - (recent_cpu / 4) - (nice * 2) 11 t->priority = CONVERT_X_TO_INTEGER_NEAREST(CONVERT_N_TO_FIXED_POINT(PRI_MAX)- 12 t->recent_cpu/4-CONVERT_N_TO_FIXED_POINT(2*t->nice)); 13 if (t->priority < PRI_MIN) 14 t->priority = PRI_MIN; 15 if (t->priority > PRI_MAX) 16 t->priority = PRI_MAX; 17 } 18 } 19 20 /* Modify recent_cpu */ 21 void modify_cpu(struct thread *t,void *aux UNUSED){ 22 if (t != idle_thread){ 23 int64_t fa = MULTIPLY_X_BY_N(load_avg,2); 24 int64_t fb = MULTIPLY_X_BY_N(load_avg,2)+CONVERT_N_TO_FIXED_POINT(1); 25 t->recent_cpu = MULTIPLY_X_BY_Y(DIVIDE_X_BY_Y(fa,fb),t->recent_cpu)+ 26 CONVERT_N_TO_FIXED_POINT(t->nice); 27 } 28 } 29 30 /* Modify load average */ 31 void modify_load_avg(void){ 32 int ready_threads = list_size(&ready_list); 33 if (thread_current()!=idle_thread){ 34 ready_threads++; 35 } 36 int64_t fa = MULTIPLY_X_BY_N(load_avg,59); 37 int add1 = DIVIDE_X_BY_N(fa,60); 38 int add2 = DIVIDE_X_BY_N(CONVERT_N_TO_FIXED_POINT(ready_threads),60); 39 load_avg = ADD_X_AND_Y(add1,add2); 40 }
接下来就是在每次中断时对这些值进行更新,修改timer.c文件
1 /* Timer interrupt handler. */ 2 static void 3 timer_interrupt (struct intr_frame *args UNUSED) 4 { 5 ticks++; 6 thread_tick (); 7 thread_foreach(check_blocked_time,NULL); 8 9 if(thread_mlfqs){ 10 increase_recent_cpu(); 11 if (timer_ticks() % TIMER_FREQ == 0){ 12 modify_load_avg(); 13 thread_foreach(modify_cpu,NULL); 14 } 15 if (timer_ticks() % 4 == 0){ 16 thread_foreach(modify_priority,NULL); 17 } 18 } 19 }
最后,把原框架留给我们的几个函数补全
1 /* Sets the current thread's nice value to NICE. */ 2 void 3 thread_set_nice (int nice UNUSED) 4 { 5 thread_current()->nice = nice; 6 modify_priority(thread_current(),NULL); 7 thread_yield(); 8 } 9 10 /* Returns the current thread's nice value. */ 11 int 12 thread_get_nice (void) 13 { 14 return thread_current()->nice; 15 } 16 17 /* Returns 100 times the system load average. */ 18 int 19 thread_get_load_avg (void) 20 { 21 int temp = MULTIPLY_X_BY_N(load_avg,100); 22 return CONVERT_X_TO_INTEGER_NEAREST(temp); 23 } 24 25 /* Returns 100 times the current thread's recent_cpu value. */ 26 int 27 thread_get_recent_cpu (void) 28 { 29 return CONVERT_X_TO_INTEGER_NEAREST(MULTIPLY_X_BY_N(thread_current()->recent_cpu,100)); 30 }
至此,project 1所有测试通过
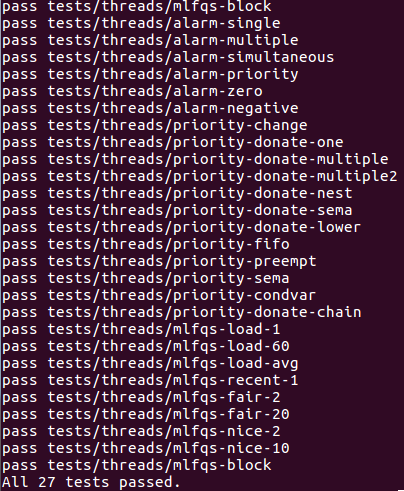
------------------------
未完待续


