基于开源模型搭建实时人脸识别系统(三):人脸关键点、对齐模型概览与模型选型
续 基于开源模型搭建实时人脸识别系统(二):人脸检测概览与模型选型_CodingInCV的博客-CSDN博客
摘要
人脸对齐(face alignment)或者人脸关键点(face alignment)是定位人脸上的关键点,是很多基于人脸的任务的前置步骤,比如人脸识别、表情分析、人脸变装(makeup)等。人脸对齐有2D和3D对齐,本篇主要讲2D对齐。
- 人脸姿态对齐:人脸识别等算法都需要对人脸的姿态进行对齐从而提高模型的精度。
- 人脸美颜与编辑:基于关键点可以精确分析脸型、眼睛形状、鼻子形状等,从而对人脸的特定位置进行修饰加工,实现人脸特效美颜,贴片等娱乐功能。
- 人脸表情分析与嘴型识别:基于关键点可以对人的面部表情进行分析,从而用于互动娱乐,行为预测等场景。
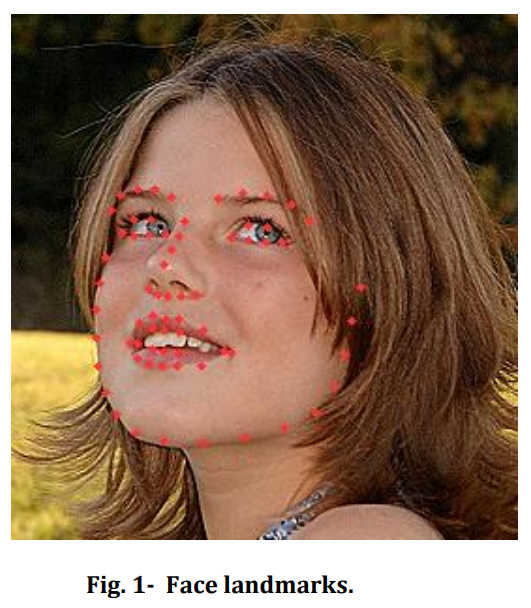

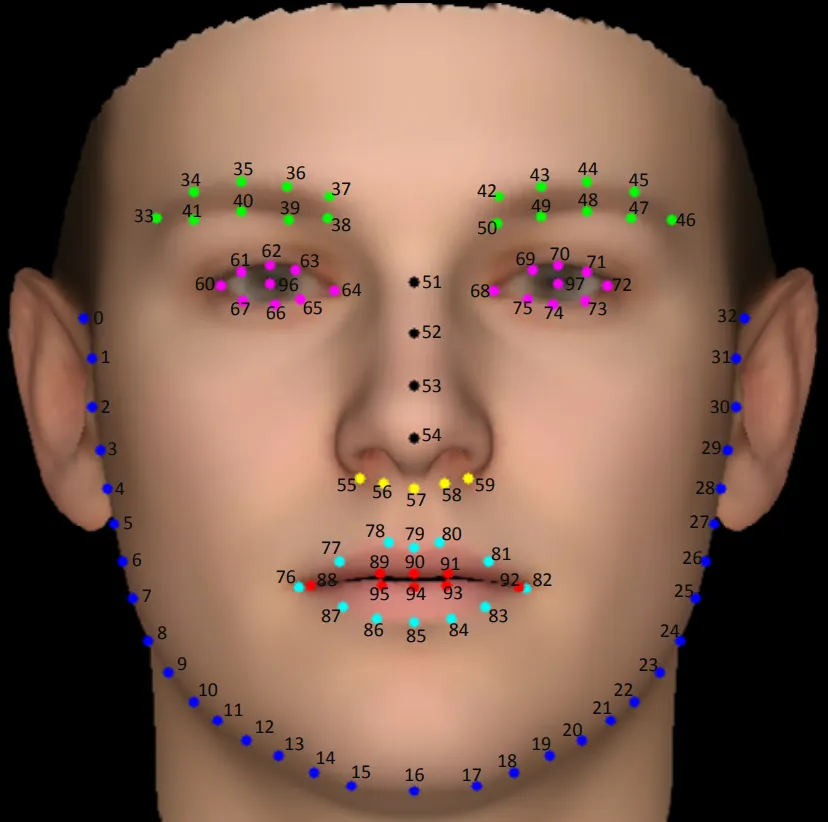
根据关键点个数,主要分为5点、68点、98点、106点等。

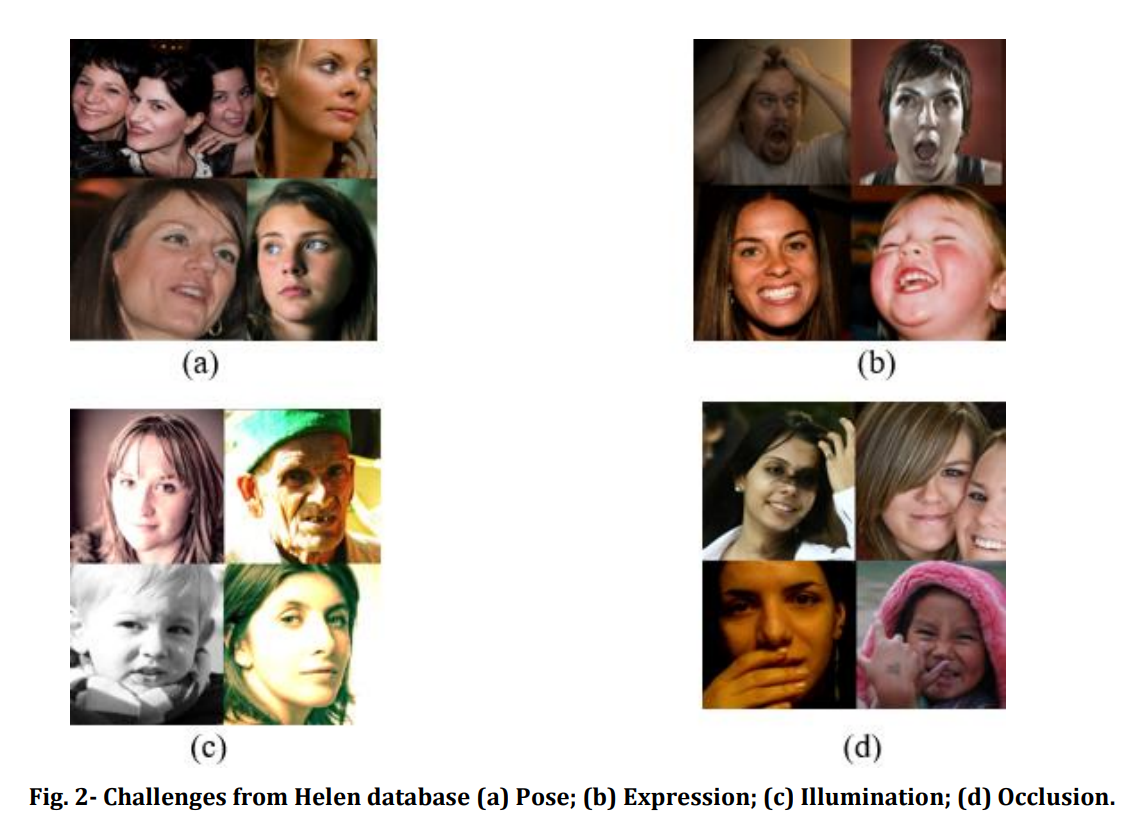
人脸关键点定位的困难主要来源于以下几个方面: - 人脸姿态
- 人脸遮挡
- 人脸表情
- 环境光照

人脸关键点算法概览
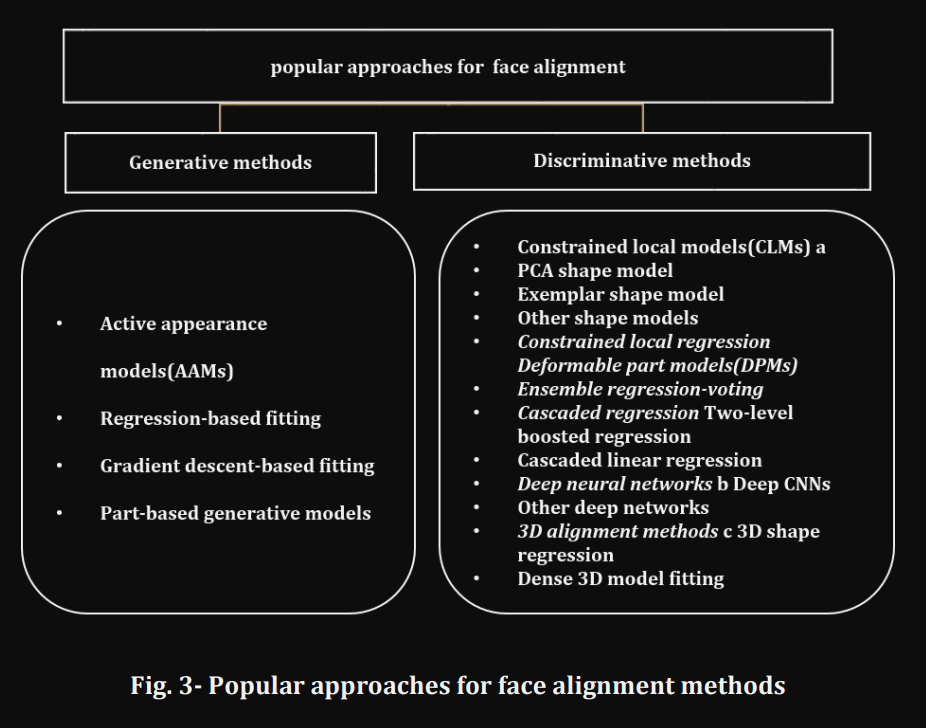
同样的人脸关键点算法也分为传统和深度学习时期,目前主要使用深度学习。
对于关键点任务,一般将其作为一个回归任务,即目标是回归每个关键点的位置;另一种方式是引入heatmap。这里不展开阐述,需要更深入了解,可以阅读下面的链接。
更多:
人脸关键点综述 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
Article (iasj.net)
算法选型
Face Alignment | Papers With Code
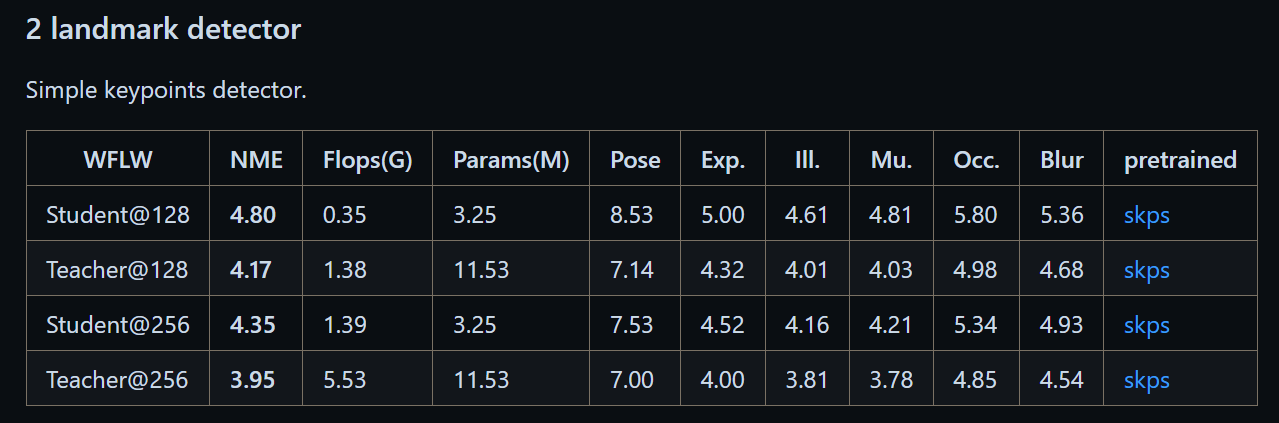
人脸对齐开源的算法还挺多,但是这sota算法开源的权重都太大,无法达到我们的轻量化要求。人脸对齐作为人脸质量筛选和人脸识别前的步骤,不能计算量太大。
按照计算量要求,我们选择了这一算法(选择其中的Student@128):
人脸关键点模型的输入是人脸区域,具体而言是对人脸检测模型得到的人脸框进行一定的放大后的区域。
修改后模型的推理代码如下:
class FaceLandmarks(BaseModel):
def __init__(self, model_path, device="cpu", **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(model_path, device, **kwargs)
self.input_size = 128
self.extend = [0.2, 0.3]
def preprocess(self, image: np.ndarray, bbox: np.ndarray):
bbox_width = bbox[2] - bbox[0]
bbox_height = bbox[3] - bbox[1]
face_size = bbox_width
# face_size = int(max(bbox_width, bbox_height))
face_width = (1 + 2 * self.extend[0]) * face_size
center = [(bbox[0] + bbox[2]) // 2, (bbox[1] + bbox[3]) // 2]
### make the box as square
crop_bbox = np.zeros(4, dtype=np.int32)
crop_bbox[0] = center[0] - face_width // 2
crop_bbox[1] = center[1] - face_width // 2
crop_bbox[2] = center[0] + face_width // 2
crop_bbox[3] = center[1] + face_width // 2
# limit the box in the image
crop_bbox[0] = max(0, crop_bbox[0])
crop_bbox[1] = max(0, crop_bbox[1])
crop_bbox[2] = min(image.shape[1], crop_bbox[2])
crop_bbox[3] = min(image.shape[0], crop_bbox[3])
# crop
crop_bbox = crop_bbox.astype(np.int32)
crop_image = image[crop_bbox[1] : crop_bbox[3], crop_bbox[0] : crop_bbox[2], :]
crop_image = cv2.resize(crop_image, (self.input_size, self.input_size))
return crop_image, crop_bbox
def run(self, image: np.ndarray, bbox: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
input, crop_box = self.preprocess(image, bbox)
input = input.astype(np.float32)
input = input / 255.0
input = input.transpose((2, 0, 1))
input = np.expand_dims(input, axis=0)
output, _ = self.inference(input)
landmarks = np.array(output)[:98*2].reshape(-1, 2)
landmarks = self.postprocess(landmarks, crop_box)
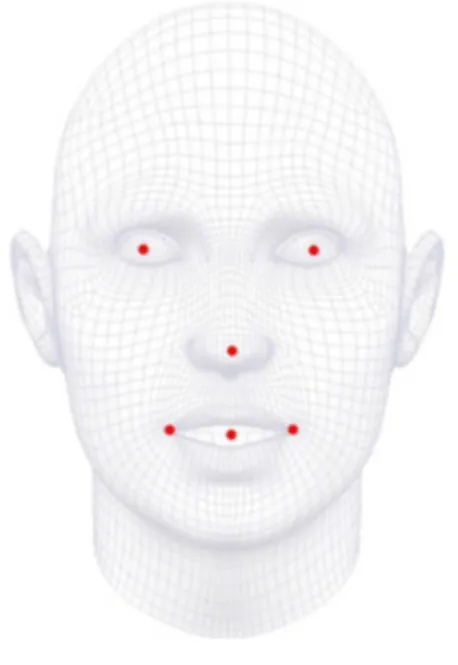
#change 98 points to 5 points
landmarks = landmarks[[96, 97, 54, 88, 92], :]
return landmarks
def postprocess(self, landmarks: np.ndarray, crop_box)->np.ndarray:
h = crop_box[3] - crop_box[1]
w = crop_box[2] - crop_box[0]
landmarks[:, 0] = landmarks[:, 0] * w + crop_box[0]
landmarks[:, 1] = landmarks[:, 1] * h + crop_box[1]
return landmarks
测试
得到的关键点如下(为了方便后续的使用,我们将98关键点转换为了5个关键点):
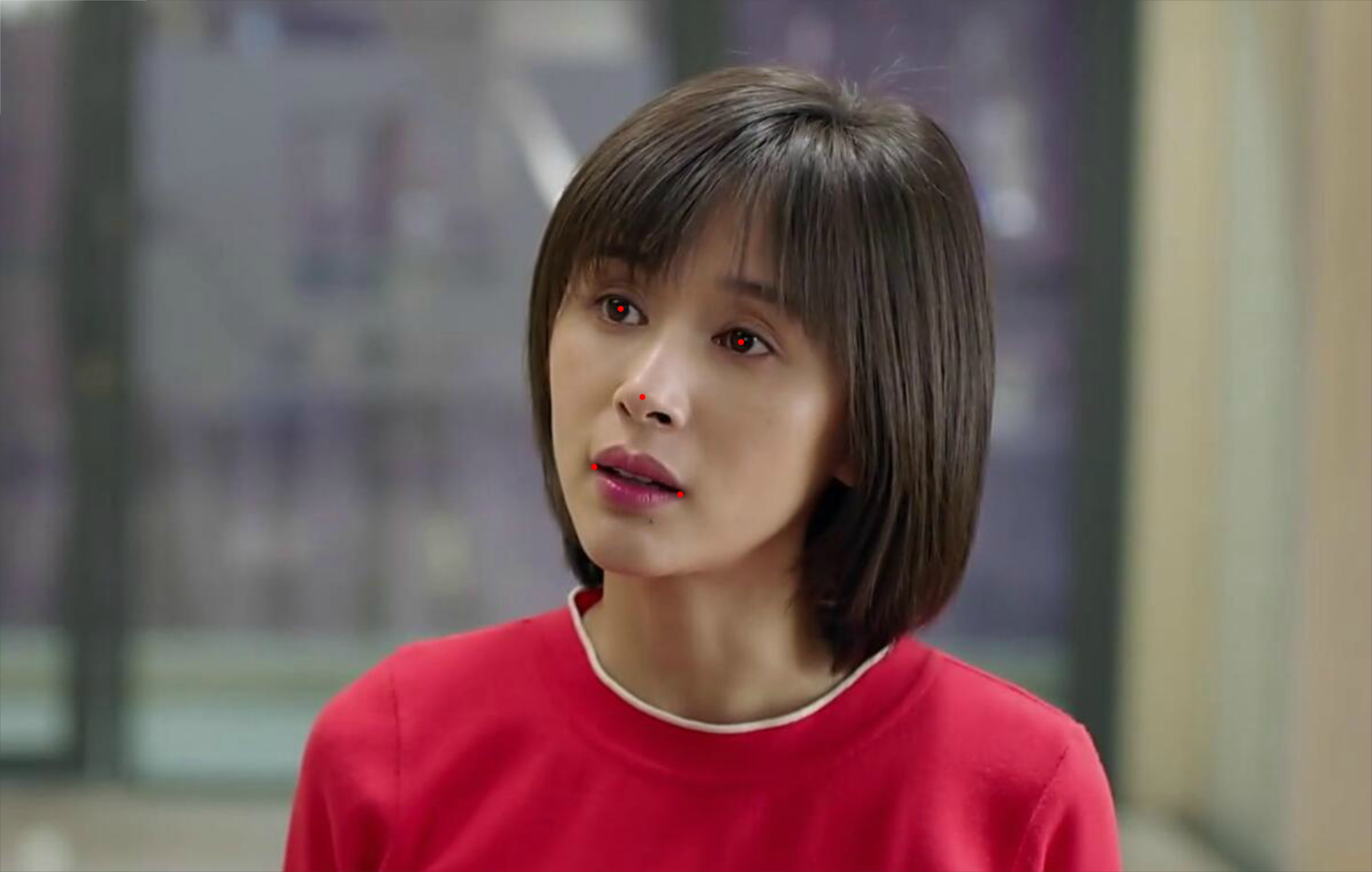

CPU上的平均耗时为8ms, 还是非常快的。
结语
本篇简单介绍了人脸对齐,但只是从实用的角度浅尝辄止,感兴趣的还是需要搜索相关文献进一步学习。
源码欢迎光临我的面包多:CoderInCV的个人主页 (mbd.pub)
本文来自博客园,作者:CoderInCV,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/haoliuhust/p/17723486.html




