SpringBoot-自动装配
SSM为项目的开发提供了一定的便捷,但随着技术的发展,我们发现其实SSM还是不够便捷!
也正是为了更高效便捷的开发项目,SpringBoot横空出世!
SpringBoot 约定大于配置、简化了开发流程、开箱即用、也很容易集成其他框架
SpringBoot的核心是自动装配,开发时根据需要,简单配置即可等效于SSM时代中的各种繁琐配置。
pom.xml
父依赖
新建的Springboot中,其实也是带有父项目的,从pom中可以看出:
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.5.5</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent>
点击 spring-boot-starter-parent 进去父项目:
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId> <version>2.5.5</version> </parent>
发现spring-boot-starter-parent还有一层父项目:spring-boot-dependencies
spring-boot-dependencies是管理SpringBoot应用里面所有依赖版本的地方,是SpringBoot的版本控制中心。
例如一些已经被配置的组件的版本:
<javax-websocket.version>1.1</javax-websocket.version> <jaxen.version>1.2.0</jaxen.version> <jaybird.version>4.0.3.java8</jaybird.version> <jboss-logging.version>3.4.2.Final</jboss-logging.version> <jboss-transaction-spi.version>7.6.1.Final</jboss-transaction-spi.version> <jdom2.version>2.0.6</jdom2.version> <jedis.version>3.6.3</jedis.version> <jersey.version>2.33</jersey.version>
所以,以后我们导入依赖默认是不需要写版本;但是如果导入的包没有在依赖中管理着就需要手动配置版本了;
启动器 spring-boot-starter
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency>
springboot-boot-starter-xxx:就是spring-boot的场景启动器
spring-boot-starter-web:帮我们导入了web模块正常运行所依赖的组件;
SpringBoot将所有的功能场景都抽取出来,做成一个个的starter (启动器),只需要在项目中引入这些starter即可,所有相关的依赖都会导入进来 , 我们要用什么功能就导入什么样的场景启动器即可 ;我们未来也可以自己自定义 starter;
主启动类
分析完了 pom.xml 来看看这个启动类
默认的的主启动类:
@SpringBootApplication //说明这是一个Spring Boot应用
public class Boot01Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Boot01Application.class, args); //不是简单地启动了一个方法,而是启动了一个服务
}
}
这个并不简单,来分析:
@SpringBootApplication
作用:标注在某个类上说明这个类是SpringBoot的主配置类 , SpringBoot就应该运行这个类的main方法来启动SpringBoot应用;
进入这个注解:可以看到上面还有很多其他注解!
@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @SpringBootConfiguration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan( excludeFilters = {@Filter( type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class} ), @Filter( type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class} )} ) public @interface SpringBootApplication { ...... }
除了4个标准注解,还有@SpringBootConfiguration、@EnableAutoConfiguration、@ComponetScan
@ComponentScan
这个注解在Spring中很重要 ,它对应XML配置中的元素。
作用:自动扫描并加载符合条件的组件或者bean , 将这个bean定义加载到IOC容器中
@SpringBootConfiguration
作用:SpringBoot的配置类 ,标注在某个类上 , 表示这是一个SpringBoot的配置类;
我们继续进去这个注解查看
@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Configuration @Indexed public @interface SpringBootConfiguration { @AliasFor( annotation = Configuration.class ) boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true; }
这里的 @Configuration,说明这是一个配置类 ,配置类就是对应Spring的xml 配置文件;
进去@Configuration
@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Component public @interface Configuration { @AliasFor( annotation = Component.class ) String value() default ""; boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true; }
除开标准注解,只有@Component ,这说明启动类本身也是Spring中的一个组件而已,负责启动应用!
我们回到 SpringBootApplication 注解中继续看。
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration :开启自动配置功能
以前我们需要自己配置的东西,而现在SpringBoot可以自动帮我们配置 ;@EnableAutoConfiguration告诉SpringBoot开启自动配置功能,这样自动配置才能生效;
点进注解接续查看:
@AutoConfigurationPackage @Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}) public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration { String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration"; Class<?>[] exclude() default {}; String[] excludeName() default {}; }
@AutoConfigurationPackage :自动配置包
进入:
@Import({Registrar.class})
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
String[] basePackages() default {};
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {};
}
@import :Spring底层注解, 给容器中导入一个组件
Registrar.class 作用:将主启动类的所在包及包下面所有子包里面的所有组件扫描到Spring容器 ;
这个分析完了,退到上一步,继续看
@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}) :给容器导入组件 ;
AutoConfigurationImportSelector :自动配置导入选择器,那么它会导入哪些组件的选择器呢?我们点击去这个类看源码:
这个类中有一个这样的方法
// 获得候选的配置
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
//这里的getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass()方法List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader());
//返回的就是我们最开始看的启动自动导入配置文件的注解类;EnableAutoConfiguration
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
2、这个方法又调用了 SpringFactoriesLoader 类的静态方法!我们进入SpringFactoriesLoader类loadFactoryNames() 方法
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName(); //这里它又调用了 loadSpringFactories 方法 return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList()); }
我们继续点击查看 loadSpringFactories 方法:
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) { Map<String, List<String>> result = (Map)cache.get(classLoader); if (result != null) { return result; } else { HashMap result = new HashMap(); try { Enumeration urls = classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories"); while(urls.hasMoreElements()) { URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement(); UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url); Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator(); while(var6.hasNext()) { Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next(); String factoryTypeName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim(); String[] factoryImplementationNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue()); String[] var10 = factoryImplementationNames; int var11 = factoryImplementationNames.length; for(int var12 = 0; var12 < var11; ++var12) { String factoryImplementationName = var10[var12]; ((List)result.computeIfAbsent(factoryTypeName, (key) -> { return new ArrayList(); })).add(factoryImplementationName.trim()); } } } result.replaceAll((factoryType, implementations) -> { return (List)implementations.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), Collections::unmodifiableList)); }); cache.put(classLoader, result); return result; } catch (IOException var14) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var14); } } }
发现一个多次出现的文件:spring.factories,全局搜索它
spring.factories
我们根据源头打开spring.factories , 看到了很多自动配置的文件;这就是自动配置根源所在!

WebMvcAutoConfiguration
我们在上面的自动配置类随便找一个打开看看,比如 :WebMvcAutoConfiguration
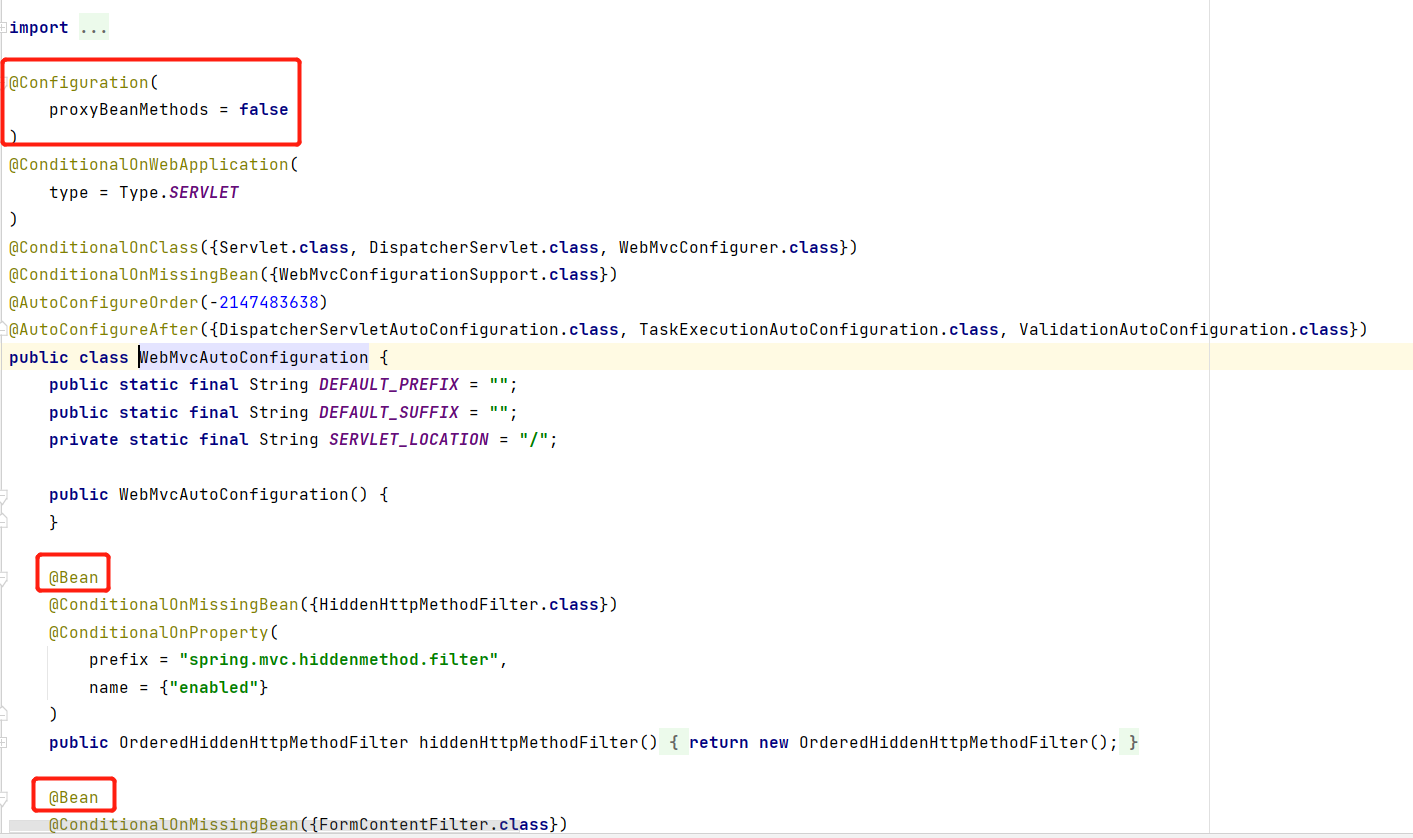
可以看到这些一个个的都是JavaConfig配置类,而且都注入了一些Bean,可以找一些自己认识的类,看着熟悉一下!
所以,自动配置真正实现是从classpath中搜寻所有的META-INF/spring.factories配置文件 ,并将其中对应的 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure. 包下的配置项,通过反射实例化为对应标注了 @Configuration的JavaConfig形式的IOC容器配置类 , 然后将这些都汇总成为一个实例并加载到IOC容器中。
结论:
-
SpringBoot在启动的时候从类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories中获取EnableAutoConfiguration指定的值
-
将这些值作为自动配置类导入容器 , 自动配置类就生效 , 帮我们进行自动配置工作;
-
整个J2EE的整体解决方案和自动配置都在springboot-autoconfigure的jar包中;
-
它会给容器中导入非常多的自动配置类 (xxxAutoConfiguration), 就是给容器中导入这个场景需要的所有组件 , 并配置好这些组件 ;
-
有了自动配置类 , 免去了我们手动编写配置注入功能组件等的工作;
以上就是自动装配的原理,现在应该大概的了解了SpringBoot的运行原理。
最后得出这些注解的关系:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号