codeforces 459E
codeforces 459E
E. Pashmak and Graph
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Pashmak's homework is a problem about graphs. Although he always tries to do his homework completely, he can't solve this problem. As you know, he's really weak at graph theory; so try to help him in solving the problem.
You are given a weighted directed graph with n vertices and m edges. You need to find a path (perhaps, non-simple) with maximum number of edges, such that the weights of the edges increase along the path. In other words, each edge of the path must have strictly greater weight than the previous edge in the path.
Help Pashmak, print the number of edges in the required path.
Input
The first line contains two integers n, m (2 ≤ n ≤ 3·105; 1 ≤ m ≤ min(n·(n - 1), 3·105)). Then, m lines follows. The i-th line contains three space separated integers: ui, vi, wi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n; 1 ≤ wi ≤ 105) which indicates that there's a directed edge with weight wi from vertex ui to vertex vi.
It's guaranteed that the graph doesn't contain self-loops and multiple edges.
Output
Print a single integer — the answer to the problem.
Sample test(s)
input
3 3
1 2 1
2 3 1
3 1 1
output
1
input
3 3
1 2 1
2 3 2
3 1 3
output
3
input
6 7
1 2 1
3 2 5
2 4 2
2 5 2
2 6 9
5 4 3
4 3 4
output
6
Note
In the first sample the maximum trail can be any of this trails:
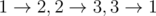
.
In the second sample the maximum trail is

.
In the third sample the maximum trail is
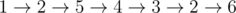
.
题目类型:DP
思路:1. dfs铁定超时,因为一开始没想到办法如何两条边去更新一个点时存储哪一个
2.看到排序之后立马有思路,但是还是超时?!为什么?因为我不是更新的点,是去更新的边,这样一条边可能会被访问很多很多次,而如果访问点的话,一条边只需要被访问一次(当然后来修改为AC的之后一条边可能被访问2次),当然就算不超时,后面也会wa的为什么呢?下面解释、、
3.修改为更新点,wa一次。。因为当更新第一次后,后面相同的wei可能会被放弃,最后面的一组样例就是这样错的,使用vector存储要更新的点
4.改了之后还是wa,因为要更新的点覆盖了之前这个点的更新信息,所以用pair存储就可以了
1 #include<iostream> 2 3 #include<cstdio> 4 5 #include<cstring> 6 7 #include<vector> 8 9 #include<cmath> 10 11 #include<map> 12 13 #include<algorithm> 14 15 #define M(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a)) 16 17 using namespace std; 18 19 20 21 int n,m; 22 23 int res; 24 25 int p[300005]; 26 27 int psave[300005]; 28 29 30 31 struct ed 32 33 { 34 35 int from; 36 37 int to; 38 39 int wei; 40 41 bool operator < (const ed& rhs) const 42 43 { 44 45 return wei<rhs.wei; 46 47 } 48 49 }edge[300005]; 50 51 52 53 vector<pair<int,int> > g; 54 55 56 57 void dp() 58 59 { 60 61 int pre = edge[0].wei; 62 63 //cout<<u<<'!'<<endl; 64 65 for(int i = 0;i<m;i++) 66 67 { 68 69 if(pre!=edge[i].wei) 70 71 { 72 73 pre = edge[i].wei; 74 75 for(int j = 0;j<g.size();j++) 76 77 if(g[j].second>p[g[j].first]) p[g[j].first] = g[j].second; 78 79 g.clear(); 80 81 } 82 83 //cout<<edge[i].from<<' '<<edge[i].to<<' '<<p[edge[i].from]<<' '<<pw[edge[i].from]<<endl; 84 85 if(p[edge[i].from]+1>p[edge[i].to]) 86 87 { 88 89 g.push_back(make_pair(edge[i].to,p[edge[i].from]+1)); 90 91 if(p[edge[i].from]+1>res) res = p[edge[i].from]+1; 92 93 } 94 95 } 96 97 for(int j = 0;j<g.size();j++) 98 99 if(psave[g[j].second]>p[g[j].first]) p[g[j].first] = psave[g[j].second]; 100 101 return; 102 103 } 104 105 106 107 int main() 108 109 { 110 111 while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)==2) 112 113 { 114 115 int u,v,w; 116 117 res = 1; 118 119 M(p,0); 120 121 for(int i = 0;i<m;i++) 122 123 { 124 125 scanf("%d%d%d",&u,&v,&w); 126 127 edge[i].from = u; 128 129 edge[i].to = v; 130 131 edge[i].wei = w; 132 133 } 134 135 sort(edge,edge+m); 136 137 // cout<<temu<<endl; 138 139 p[edge[0].from] = 0; 140 141 dp(); 142 143 for(int i = 0;i<n;i++) 144 145 { 146 147 if(p[i]>res) 148 149 res = p[i]; 150 151 } 152 153 printf("%d\n",res); 154 155 } 156 157 return 0; 158 159 } 160 161 /* 162 163 9 8 164 165 1 2 1 166 167 2 3 2 168 169 4 5 1 170 171 5 6 2 172 173 6 3 3 174 175 3 7 4 176 177 7 8 5 178 179 8 9 6 180 181 */ 182 183


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号