Java教程01-基础语法
目录
1. 基本概念
1.1. 环境变量
环境变量通常是指在操作系统(win10,win7)中,用来指定操作系统运行时需要的一些参数(比如一个国家需要人民,货币,货物...),一般为一些键值对

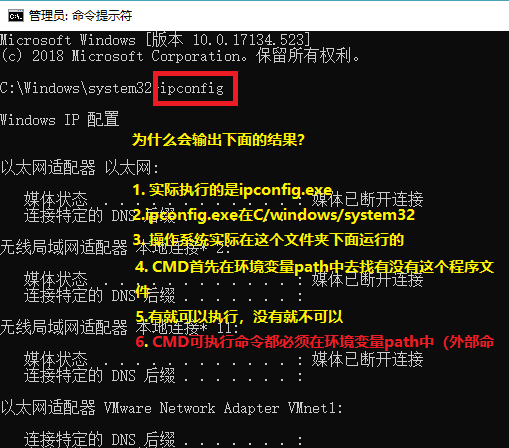
Path环境变量的作用->寻找命令
Path环境变量是操作系统外部命令搜索路径
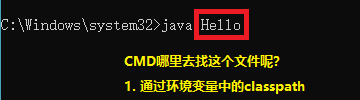
classpath变量的作用->寻找类文件
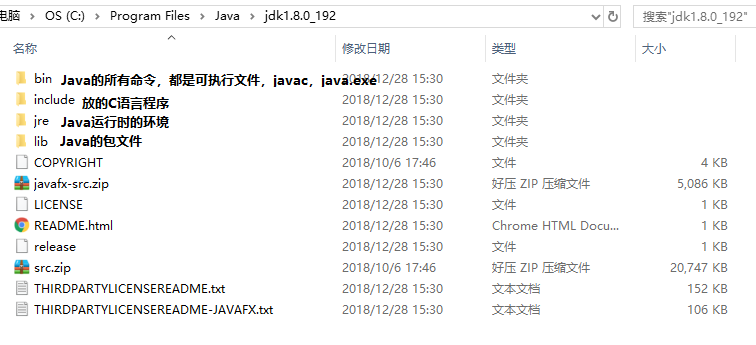
1.2. JDK里面有什么?
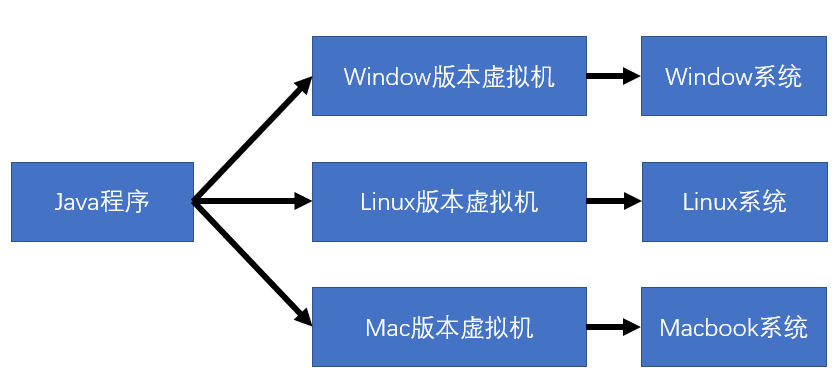
1.3. 什么是JRE?
JRE是JAVA运行的环境,包括以下几个部分:
- Java虚拟机: 它是由一个软件虚拟出来的计算机
- Java平台核心类文件
- 其他支持文件
2. Java的基础
2.1. Java的写法
// 类名与文件名必须一致
public class Main {
// Java虚拟机将从指定类的main方法执行
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}
2.2. 变量和常量
2.2.1. Java的变量类型
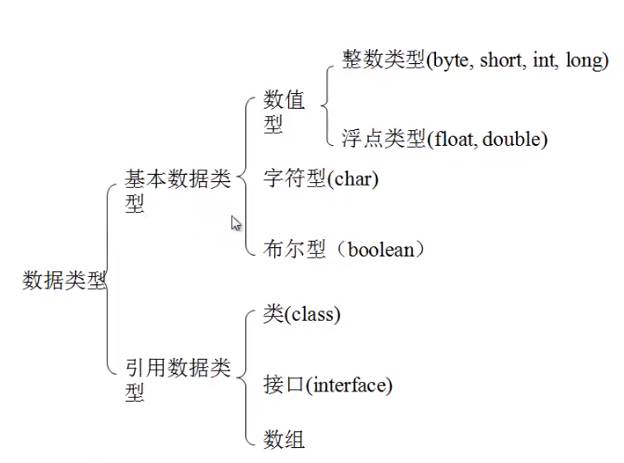
2.2.2. Java的变量声明
- 变量
int a = 10;
double salary = 12.23;
boolean done = true;
- 常量
public class Main {
// 类常量用static final定义
public static final double PRESEM = 2.54;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//基本常量用final定义
final int jbg = 12;
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}
2.3. Java的运算符
2.3.1. 数学函数
+、-、*、/Math.sqrt(x)/.pow(x,a)/.sin/.cos/.tan/.exp/.log/.log10/.PI/.E
2.3.2. 强制数值转换
double x = 9.997;
//在圆括号中给出需要转换的目标类型
int nx = (int) x;
2.3.3. 关系和boolean运算符
| 逻辑运算符 | 含义 |
|---|---|
&& |
and |
| ` | |
!= |
not |
condition? exp1: exp2 |
如果condition为真,执行exp1 |
2.3.4. 枚举类型
enum Size {SMALL, MEDIUM, LARGE};
Size s = Size.MEDIUM;
2.4. 字符串
String g = "Hello";
String w = "world";
// 子串
String s = g.substring(0,3);
//拼接
String m0 = g + w;
int val = 20;
String m1 = g + 20; //自动转为string
String m2 = String.join("/", "S", "M", "L"); // 转为S/M/L/XL
// 修改字符串: 注意: 字符串是不可变的
g = g.substring(0,3) + "p!"; // help!
// 检测字符串是否相等
"Hello".equals(g);
"Hello".equalsIgnoreCase(g); //忽略大小写
// 检测字符串既不是null也不是空串
if (g!=null && g.length()!=0);
// 构建字符串
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append(g);
builder.apend(w);
String finishedmsg = builder.toString();
2.5. 输入和输出
2.5.1. 输入
| 语句 | 含义 |
|---|---|
Scanner(InputStream in) |
用给定输入流创建一个Scanner对象 |
String nextLine() |
读取输入的下一行内容 |
String next() |
读取输入的下一个单词 |
int nextInt() |
读取整数 |
double nextDouble() |
读取浮点数 |
boolean hasNext() |
检测是否还有其他单词 |
boolean hasNextInt() |
其他整数 |
boolean hasNextDouble() |
其他浮点数 |
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("what is your name?");
String name = in.nextLine();
System.out.print("youge age?");
int age = in.nextInt();
System.out.println("your name is " + name + ". Your age is " + age);
}
}
2.5.2. 格式化输出
System.out.println("Hello, %s, Your age is %d", name, age);
2.5.3. 文件的输入输出
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 读取文件内容
Scanner in = new Scanner(Paths.get("C:\\Users\\haoch\\Desktop\\Programming\\untitled\\test.txt"), "UTF-8");
System.out.println(in.nextLine());
// 将内容写入文件
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter("C:\\Users\\haoch\\Desktop\\Programming\\untitled\\test.txt", "UTF-8");
out.println("写入内容");
}
}
2.6. Java的控制流程

2.7. 数组
数组是用来储存同一数据类型的集合
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建数组,指定数组长度(不可更改),创建后,所有元素初始化为0,布尔为false, 对象数组为null
int[] a = new int[10];
// 给数组赋值
for (int i=0; i<a.length; i++){
a[i] = i;
}
// foreach循环
for (int element: a){
System.out.println(element);
}
// 数组初始化(无需指定长度)
int[] b = {1,3,5,8,6,12};
// 数组拷贝(指向内存同一个区域)
int[] c = b;
int[] c_hard_copy = Arrays.copyOf(b, b.length);
// 数组排序
Arrays.sort(b);
// 命令行参数 在main方法中的String[] args就是一个字符串数组,接收一系列命令行参数
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号