pytest+allure(allure-pytest基于这个插件)设计定制化报告
一:环境准备
- 1.python3.6
- 2.windows环境
- 3.pycharm
- 4.allure-pytest
- 5.allure2.8.0
- 6.java1.8
allure-pytest快速安装
在cmd中输入 pip install allure-pytest,回车
二:报告生成
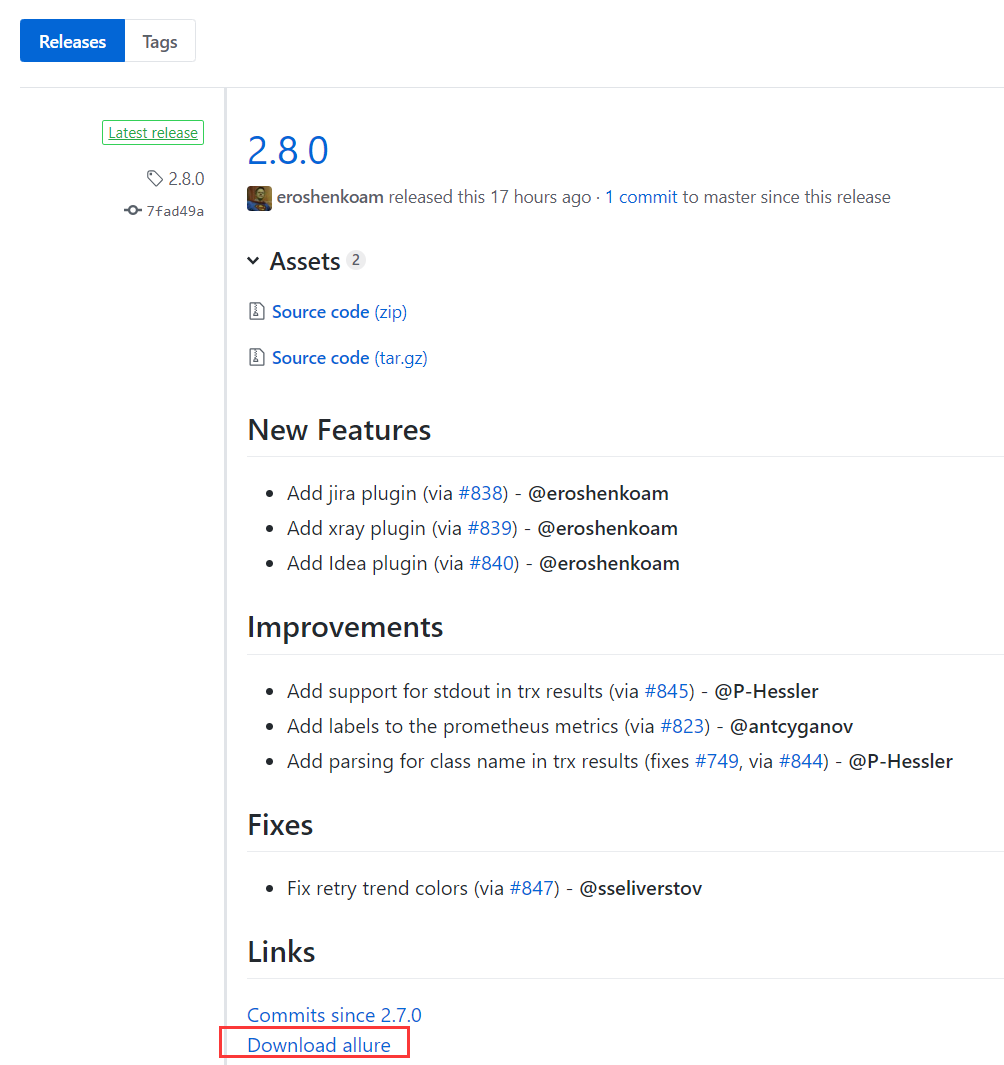
第1步:下载allure.zip,下载地址:allure-github: https://github.com/allure-framework/allure2 ,找到对应版本,并下载
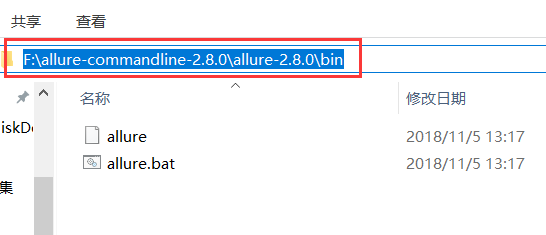
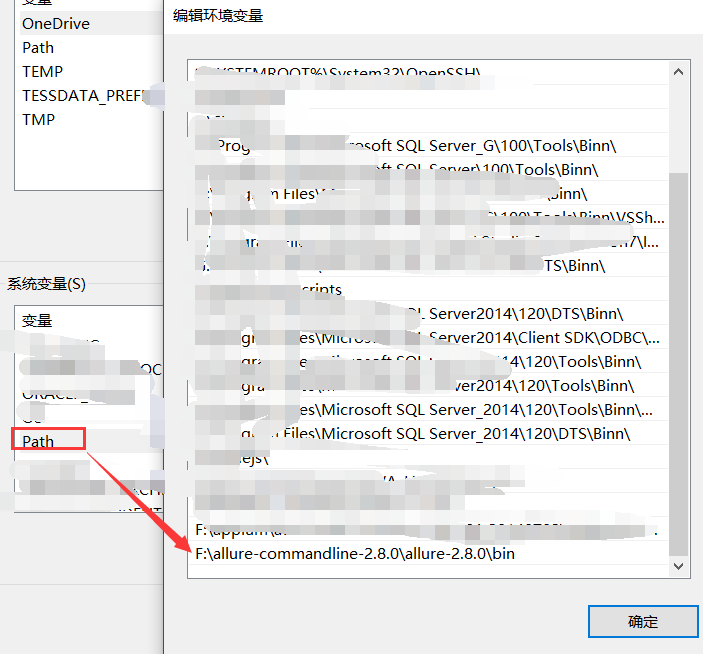
第2步:解压allure.zip,将路径添加环境变量,path中,记得需要重启电脑
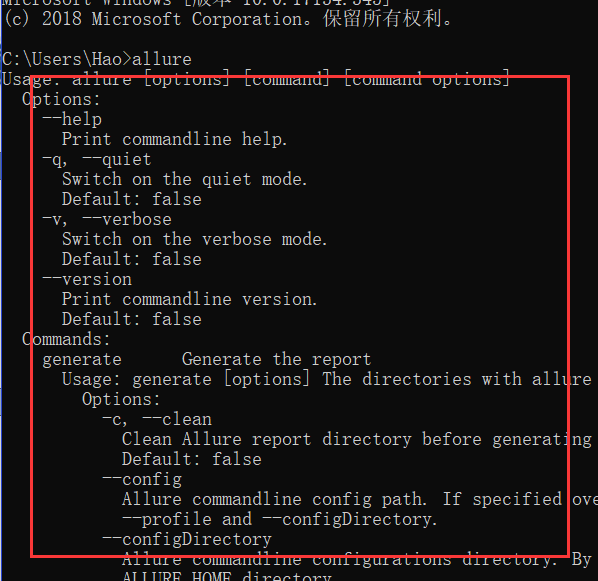
第3步:验证allure,在cmd中输入allure,然后回车,如果可以看到一下,说明配置完成
第4步:运行测试用例 pytest.main(["-m","login","-s","-q","--alluredir=./report"])
"-m": 标记用例
"login": 被标记需要执行用例
"-s":允许终端在测试运行时输出某些结果,例如你想输入print的内容,可以加上-s
"-q"简化输出结果
"--alluredir": 生成allure指定语法
"./report":生成报告的路径
"--clean-alluredir" :因为这个插件库allure-pytest生成的报告文件,你第二次运行时候不会清理掉里面的东西,所以你需要删除这个report文件夹,然后运行重新新建reoprt文件夹
说明:运行后,会在report文件夹里面生成文件
三.allure定制化报告
第1步:一些词语解释
一、feature: 标注主要功能模块。
二、story: 标注Features功能模块下的分支功能。
三、severity: 标注测试用例的重要级别。
1)blocker级别:中断缺陷(客户端程序无响应,无法执行下一步操作)
2)critical级别:临界缺陷(功能点缺失)
3)normal级别:正常 默认为这个级别
4)minor级别:次要缺陷(界面错误与UI需求不符)
5)trivial级别:轻微缺陷(必输项无提示,或者提示不规范)
四、step: 标注测试用例的重要步骤。
五、attach:用于向测试报告中输入一些附加的信息,通常是一些测试数据信息。

1)name就是附件名称,body就是数据,attachment_type就是传类型
2)附件支持的类型(TEXT,HTML,XML,PNG,JPG,JSON,OTHER)
六、issue:这里传的是一个连接,记录的是你的问题。
七、testcase:这里传的是一个连接,记录的是你的用例。
八、description:描述用例信息
第2步:代码展示+报表展示
feature方法的演示
代码:
1 import pytest,allure
2 @allure.feature("测试") #标记代码
3 class Test_Demo():
4
5 # @allure.story("test_demo_1")
6 # @allure.severity("trivial")
7 def test_demo_1(self):
8 # """
9 # 用例描述:22222222222222
10 # """
11 #allure.MASTER_HELPER.description("11111111111111")
12 assert 1 == 1
报告展示:
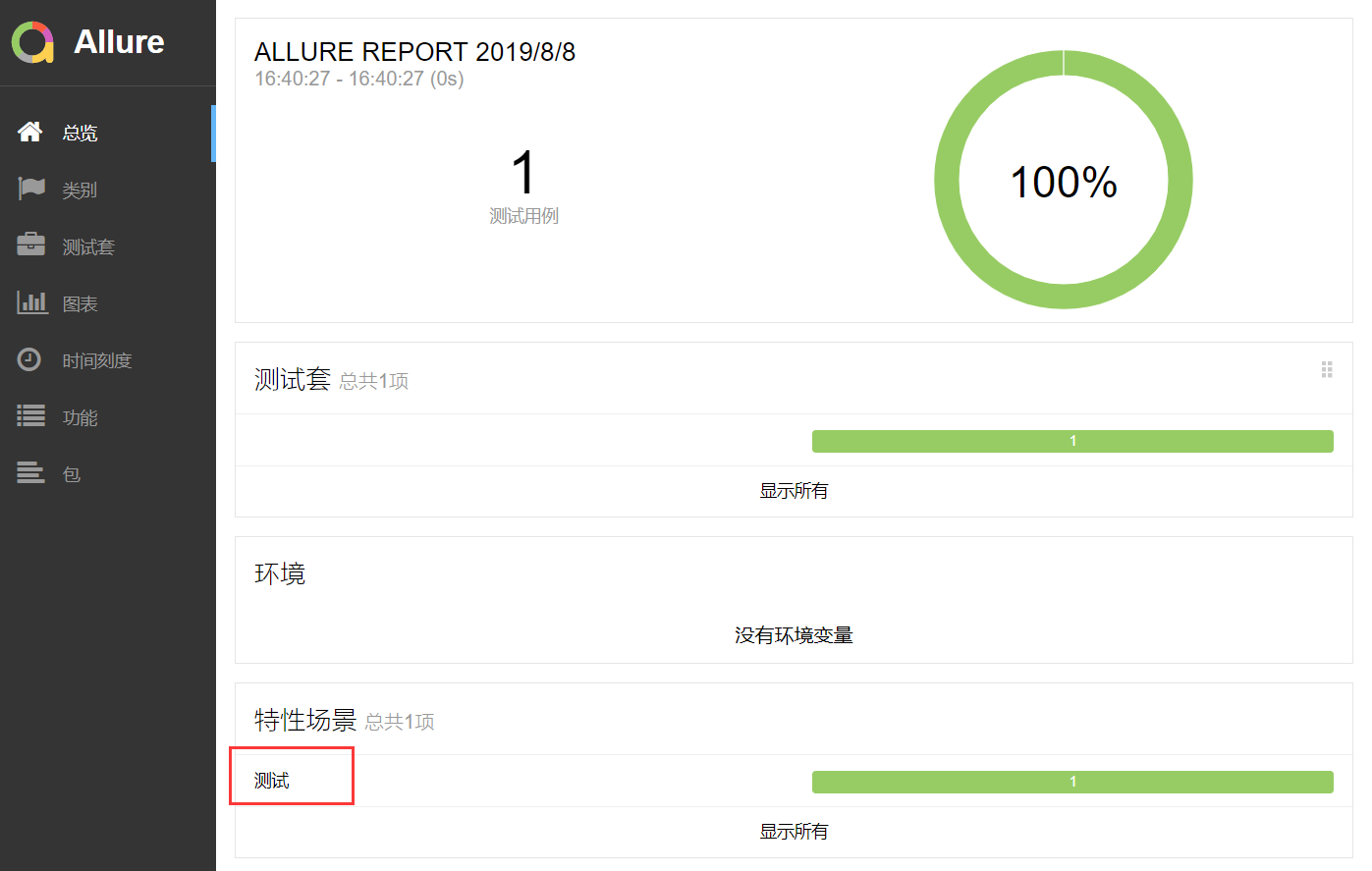
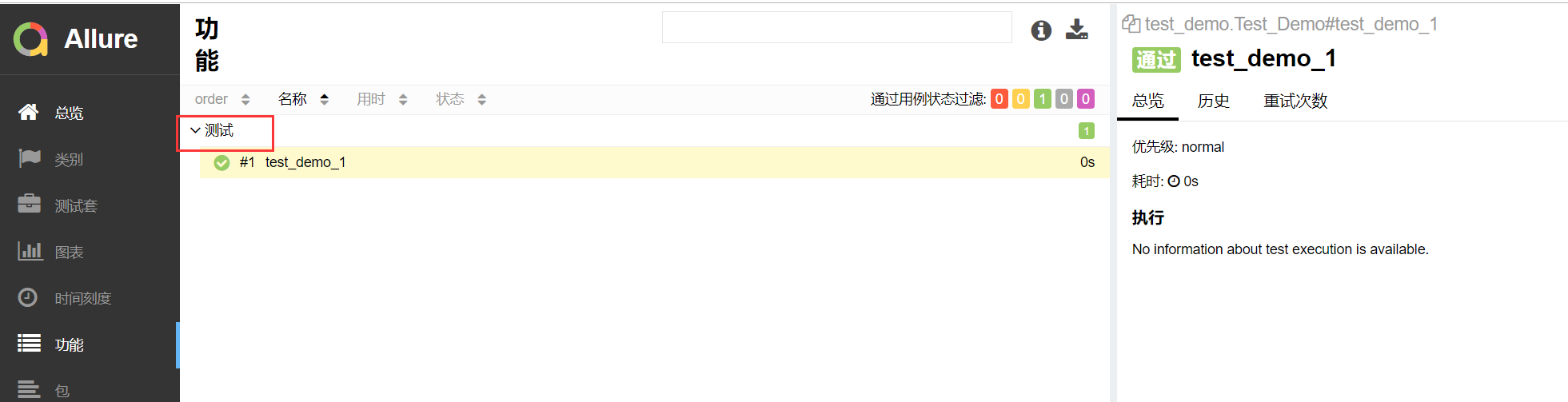
story方法的演示
代码:
1 import pytest,allure 2 @allure.feature("测试") 3 class Test_Demo(): 4 5 @allure.story("test_demo_1") #标记代码 6 # @allure.severity("trivial") 7 def test_demo_1(self): 8 # """ 9 # 用例描述:22222222222222 10 # """ 11 #allure.MASTER_HELPER.description("11111111111111") 12 assert 1 == 1 13 @allure.story("test_demo_4") 标记代码 14 #@allure.severity("minor") 15 def test_demo_4(self): 16 assert 3 == 3
报告展示:
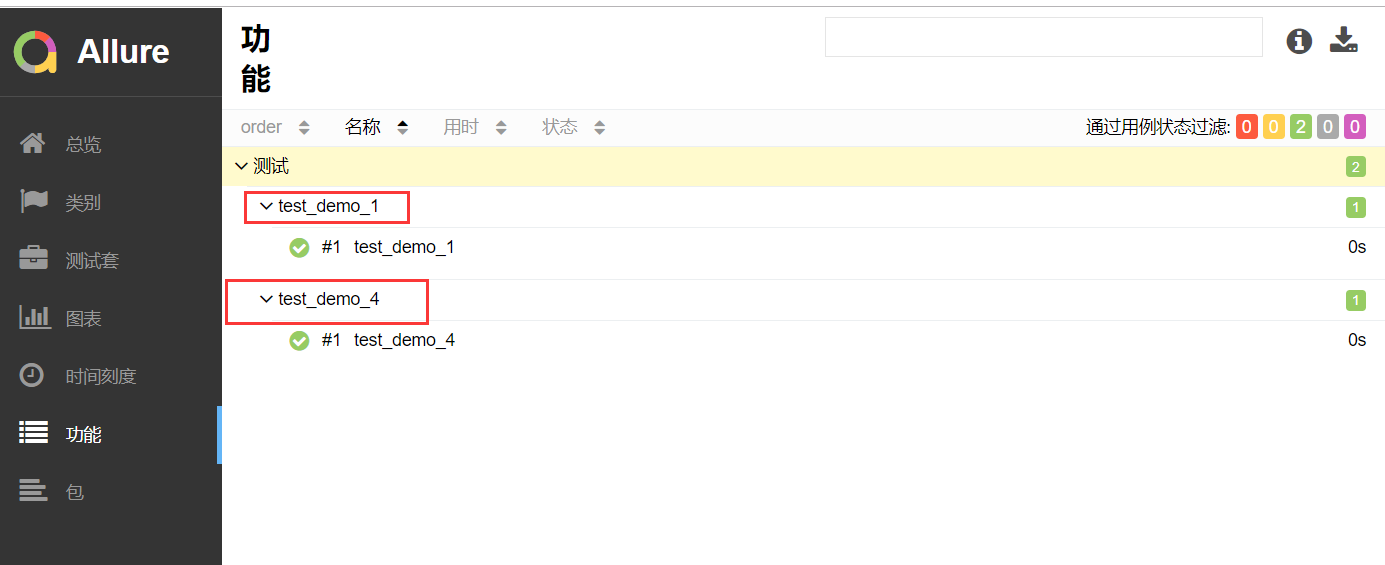
severity方法的演示:
代码:
1 import pytest,allure 2 @allure.feature("测试") 3 class Test_Demo(): 4 5 #@allure.story("test_demo_1") 6 @allure.severity("trivial") #标记代码 7 def test_demo_1(self): 8 # """ 9 # 用例描述:22222222222222 10 # """ 11 #allure.MASTER_HELPER.description("11111111111111") 12 assert 1 == 1 13 #@allure.story("test_demo_4") 14 @allure.severity("minor") #标记代码 15 def test_demo_4(self): 16 assert 3 == 3
报告展示:
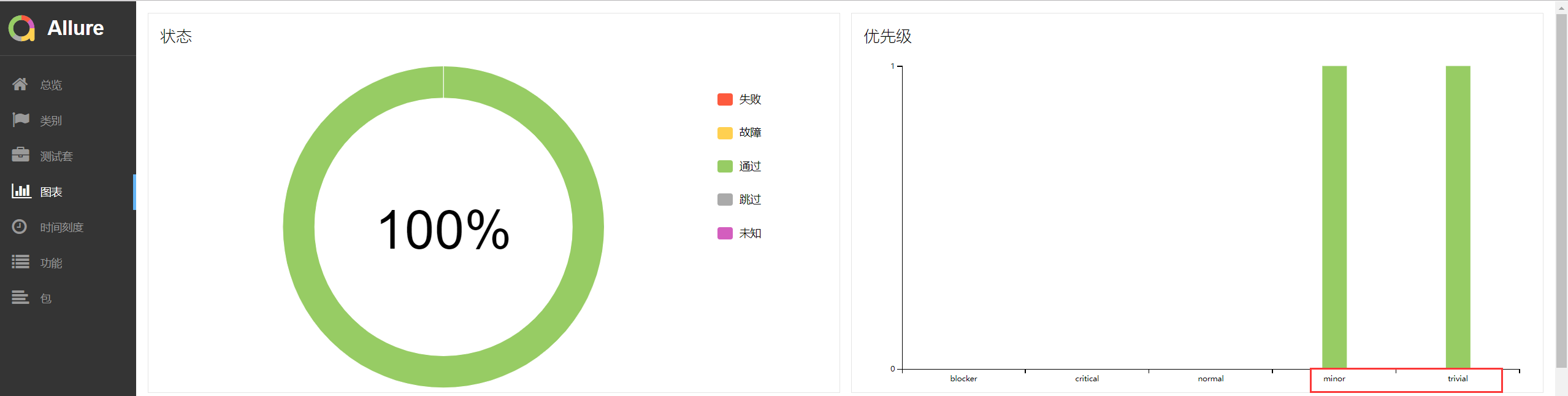
setp方法的演示:
1.总的步骤备注
代码:
1 import pytest,allure 2 @allure.feature("测试") 3 class Test_Demo(): 4 5 #@allure.story("test_demo_1") 6 #@allure.severity("trivial") 7 @allure.step("这是两个负数的比较") #标记代码 8 def test_demo_1(self): 9 # """ 10 # 用例描述:22222222222222 11 # """ 12 #allure.MASTER_HELPER.description("11111111111111") 13 assert -1 == -1 14 #@allure.story("test_demo_4") 15 #@allure.severity("minor") 16 @allure.step("这是两个整数的比较") #标记代码 17 def test_demo_4(self): 18 assert 3 == 3
报告展示:
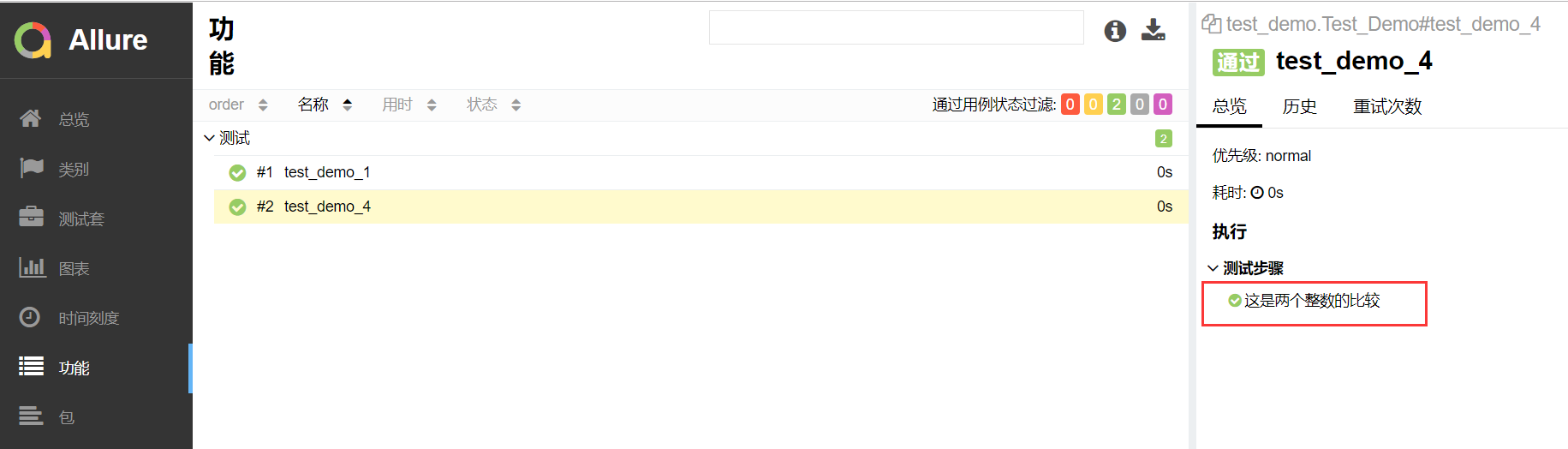
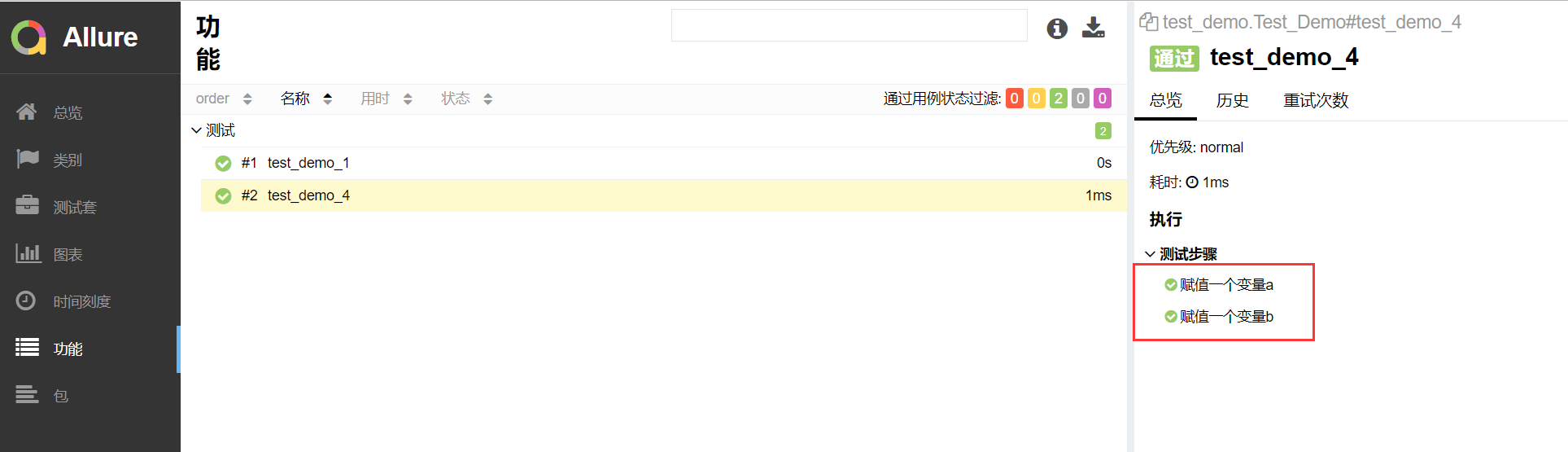
2.分步骤备注
代码:
1 import pytest,allure 2 @allure.feature("测试") 3 class Test_Demo(): 4 5 #@allure.story("test_demo_1") 6 #@allure.severity("trivial") 7 #@allure.step("这是两个负数的比较") 8 def test_demo_1(self): 9 # """ 10 # 用例描述:22222222222222 11 # """ 12 #allure.MASTER_HELPER.description("11111111111111") 13 assert -1 == -1 14 #@allure.story("test_demo_4") 15 #@allure.severity("minor") 16 #@allure.step("这是两个整数的比较") 17 def test_demo_4(self): 18 with allure.step("赋值一个变量a"): #标记代码 19 a=1 20 with allure.step("赋值一个变量b"): #标记代码 21 b=1 22 assert a == b
报表展示:
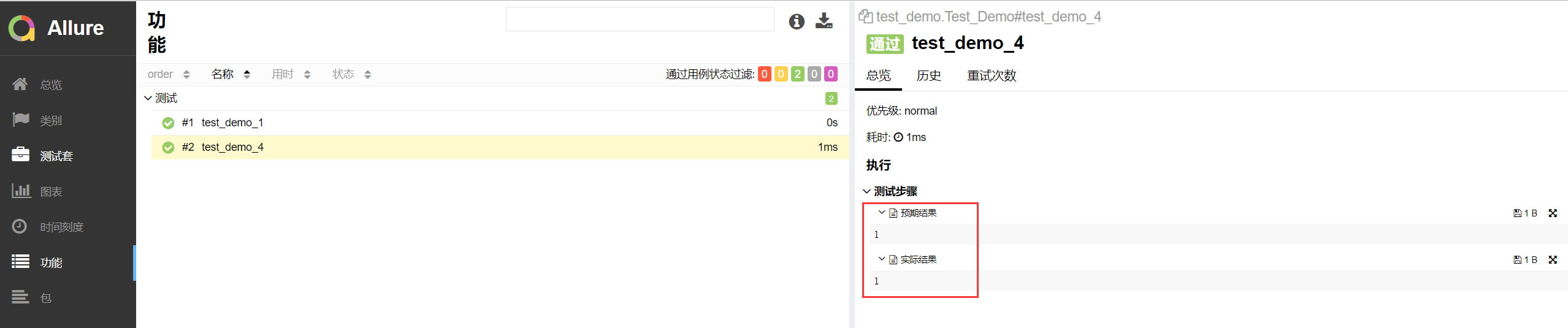
attach方法的演示:
代码:
1 import pytest,allure 2 @allure.feature("测试") 3 class Test_Demo(): 4 5 #@allure.story("test_demo_1") 6 #@allure.severity("trivial") 7 #@allure.step("这是两个负数的比较") 8 def test_demo_1(self): 9 # """ 10 # 用例描述:22222222222222 11 # """ 12 #allure.MASTER_HELPER.description("11111111111111") 13 assert -1 == -1 14 #@allure.story("test_demo_4") 15 #@allure.severity("minor") 16 #@allure.step("这是两个整数的比较") 17 def test_demo_4(self): 18 a = 1 19 allure.attach("{0}".format(a),"预期结果") #标记代码 第一个参数是body,第二个参数是name 20 b=1 21 allure.attach("{0}".format(b),"实际结果") #标记代码 22 assert a == b
报告展示:
图片附件形式:
代码:
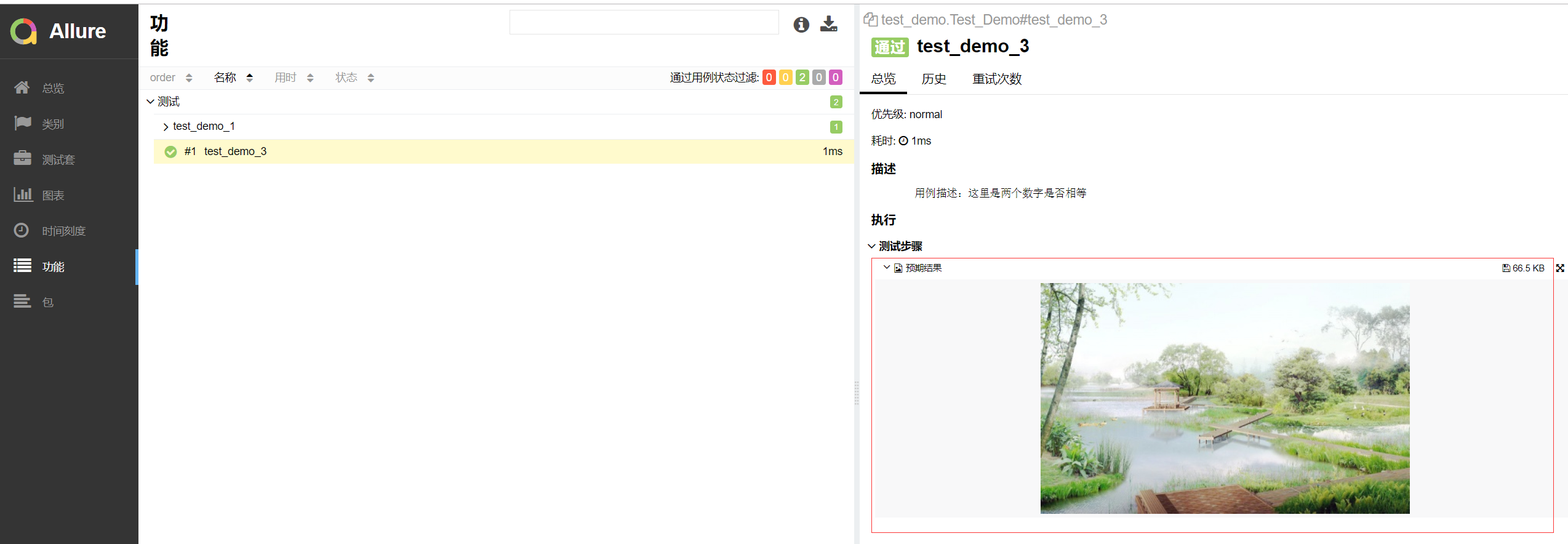
1 import pytest,allure 2 @allure.feature("测试") 3 class Test_Demo(): 4 5 @allure.story("test_demo_1") 6 @allure.severity("trivial") 7 def test_demo_1(self): 8 assert 1 == 1 9 10 def test_demo_3(self): 11 """ 12 用例描述:这里是两个数字是否相等 13 """ 14 a = 3 15 b = 3 16 with open(r"G:\Web_automation\Learn_pytest\test_cases\img\2.jpg","rb") as file: #标记代码,需要先打开图片 17 file=file.read() #标记代码,读取图片 18 allure.attach(file,"预期结果",attachment_type=allure.attachment_type.JPG) #标记代码 19 assert a == b
报告展示:
issue和testcase方法的演示:
代码:
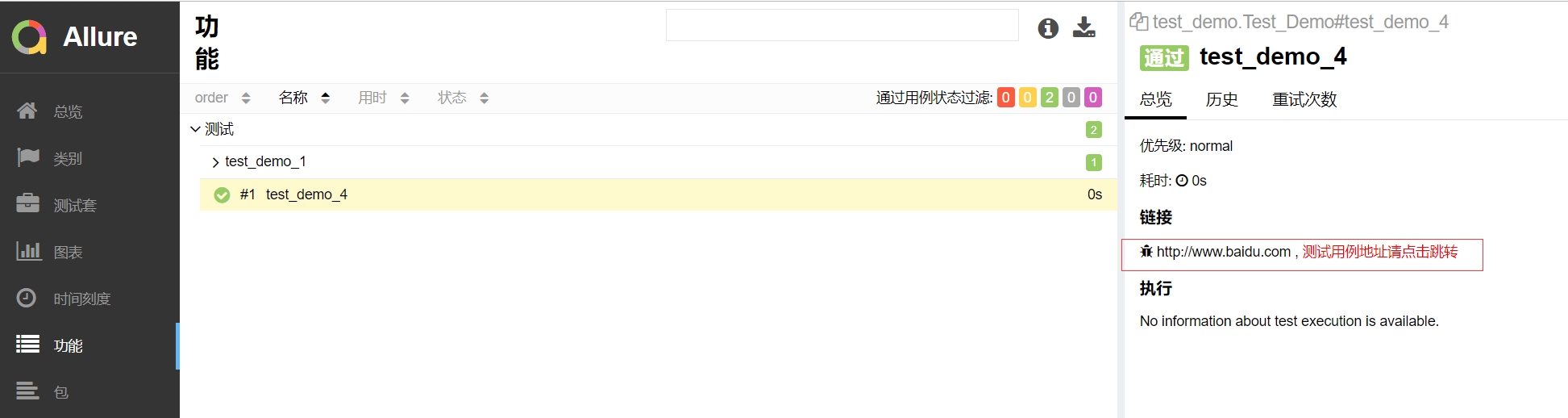
1 import pytest,allure 2 @allure.feature("测试") 3 class Test_Demo(): 4 5 @allure.story("test_demo_1") 6 @allure.testcase("https://home.cnblogs.com/") 7 def test_demo_1(self): 8 assert 1 == 1 9 10 @allure.testcase("https://home.cnblogs.com/","测试用例地址请点击跳转") #标记代码,你可以指定连接的名字,报告里面就会现在这个名字的连接 11 @allure.issue("http://www.baidu.com") #标记代码,哪个写在后,在报告里面就会显示在前面 12 def test_demo_4(self): 13 assert 3 == 3
报表展示:
description方法的演示:
代码:(这两种备注方式不能同时是存在,如果同时存在他会先使用description的,而不取3引号的)
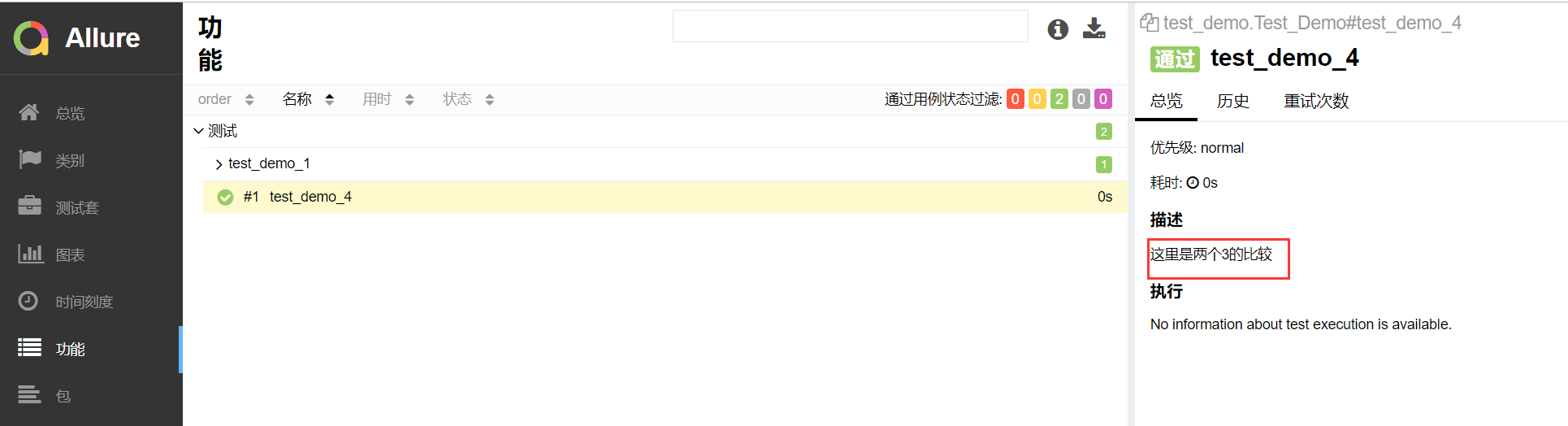
1 import pytest,allure 2 @allure.feature("测试") 3 class Test_Demo(): 4 5 6 @allure.story("test_demo_1") 7 @allure.testcase("https://home.cnblogs.com/") 8 def test_demo_1(self): 9 assert 1 == 1 10 11 @allure.description("这里是两个3的比较") #标记代码,优先取这个 12 def test_demo_4(self): 13 """ 14 用例描述:这里是两个数字是否相等 #如果没有description,那么就取3引号的 15 """ 16 assert 3 == 3
报告演示:
四.报告显示
报告显示方法一:
第1步:以上运行之后,可以在CMD中运行命令
allure generate report -o html --clean
report是alluredir生成的xml目录,html是最终生成html的目录
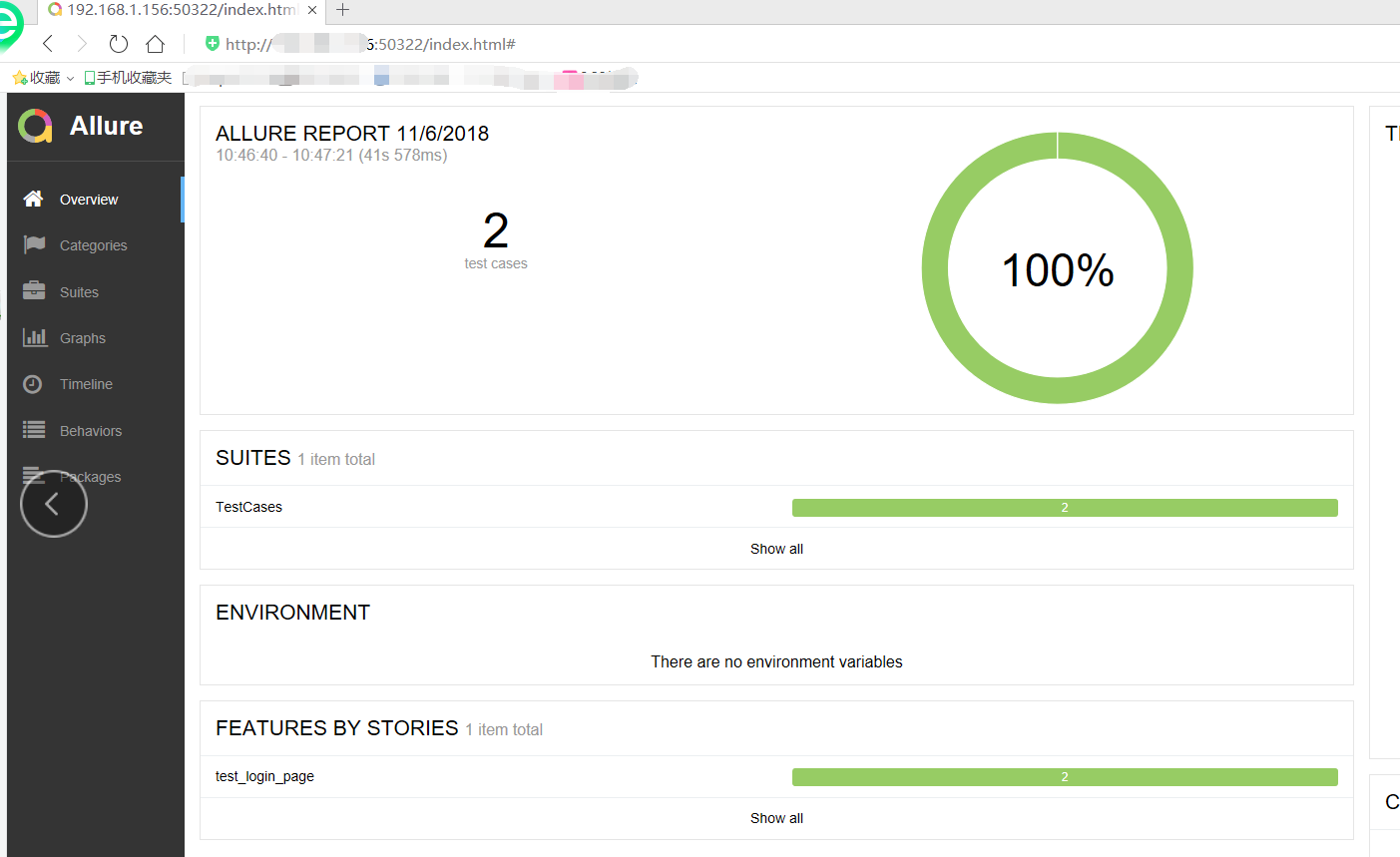
第2步:运行命令后,可以在html路径下看到生成的数据,其中index.html就是我们要的allure报告,你可以在pycharm里面打开,报告展示如下

报告显示方法二(这种相当于是调试):
第1步:以上运行之后,可以在CMD中运行命令
allure serve report (report是alluredir生成的xml目录)
运行后,浏览器会自动跳转到allure report界面
四.pytest+allure+jenkins集成
参考我另外的一个博客文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/hao2018/p/11135180.html
注意:在本地运行的时候需要手动把代码拷贝到jenkins目录下面的workspace文件夹里面;如果在git或svn上运行,jekins会直接把代码拷贝到workspace目录 ,如果jenkins是指定工作目录就不用管了


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号