Java集合:TreeMap源码剖析
一、概念
TreeMap是基于红黑树结构实现的一种Map,要分析TreeMap的实现首先就要对红黑树有所了解。
1.二叉查询树、红黑树介绍、
1.数组,优点:(1)随机访问效率高(根据下标查询),(2)搜索效率较高(可使用折半方法)。缺点:(1)内存连续且固定,存储效率低。(2)插入和删除效率低(可能会进行数组拷贝或扩容)。
2.链表,优点:(1)不要求连续内存,内存利用率高,(2)插入和删除效率高(只需要改变指针指向)。缺点:(1)不支持随机访问,(2)搜索效率低(需要遍历)。
3.Hash表:优点:(1)搜索效率高,(2)插入和删除效率较高,缺点:(1)内存利用率低(基于数组),(2)存在散列冲突。
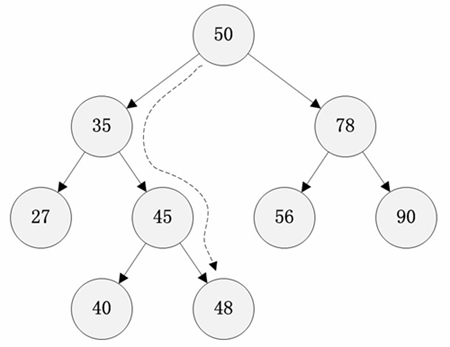
public class BinaryTree { // 二叉树的根节点 public TreeNode rootNode ; // 记录搜索深度 public int count; /** * 利用传入一个数组来建立二叉树 */ public BinaryTree(int[] data) { for (int i = 0; i < data. length; i++) { addNodeToTree(data[i]); } } /** * 将指定的值加入到二叉树中适当的节点 */ private void addNodeToTree(int value) { TreeNode currentNode = rootNode; // 建立树根 if (rootNode == null) { rootNode = new TreeNode(value); return; } // 建立二叉树 while (true) { // 新增的value比节点的value小,则在左子树 if (value < currentNode.value ) { if (currentNode.leftNode == null) { currentNode. leftNode = new TreeNode(value); return; } else { currentNode = currentNode. leftNode; } } else { // 新增的value比节点的value大,在右子树 if (currentNode.rightNode == null) { currentNode. rightNode = new TreeNode(value); return; } else { currentNode = currentNode. rightNode; } } } } /** * 中序遍历(左子树 -树根- 右子树) */ public void inOrder(TreeNode node) { if (node != null) { inOrder(node. leftNode); System. out.print("[" + node.value + "]"); inOrder(node. rightNode); } } /** * 前序遍历(树根 -左子树- 右子树) */ public void preOrder(TreeNode node) { if (node != null) { System. out.print("[" + node.value + "]"); preOrder(node. leftNode); preOrder(node. rightNode); } } /** * 后序遍历(左子树 -右子树- 树根) */ public void postOrder(TreeNode node) { if (node != null) { postOrder(node. leftNode); postOrder(node. rightNode); System. out.print("[" + node.value + "]"); } } /** * 从二叉树中查找指定value */ public boolean findTree(TreeNode node, int value) { if (node == null) { System. out.println("共搜索" + count + "次"); return false; } else if (node.value == value) { System. out.println("共搜索" + count + "次"); return true; } else if (value < node.value) { count++; return findTree(node.leftNode , value); } else { count++; return findTree(node.rightNode , value); } } /** * 利用中序遍历进行排序 */ public void sort() { this.inOrder(rootNode ); } class TreeNode { int value ; TreeNode leftNode; TreeNode rightNode; public TreeNode(int value) { this.value = value; this.leftNode = null; this.rightNode = null; } } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] content = { 50, 35, 27, 45, 40, 48, 78, 56, 90 }; BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(content); System. out.println("前序遍历:" ); tree.preOrder(tree. rootNode); System. out.println("\n中序遍历:" ); tree.inOrder(tree. rootNode); System. out.println("\n后序遍历:" ); tree.postOrder(tree. rootNode); System. out.println("\n\n开始搜索:" ); boolean isFind = tree.findTree(tree.rootNode, 48); System. out.println("是否搜索到" + 48 + ":" + isFind); System. out.println("\n进行排序:" ); tree.sort(); } }
看下运行结果:
前序遍历: [50][35][27][45][40][48][78][56][90] 中序遍历: [27][35][40][45][48][50][56][78][90] 后序遍历: [27][40][48][45][35][56][90][78][50] 开始搜索: 共搜索3次 是否搜索到48:true 进行排序: [27][35][40][45][48][50][56][78][90]

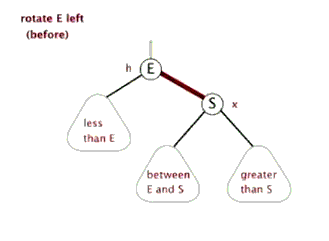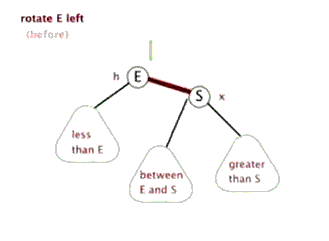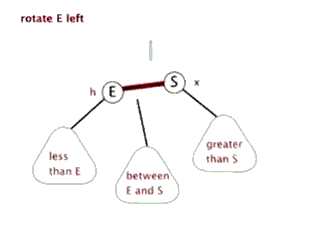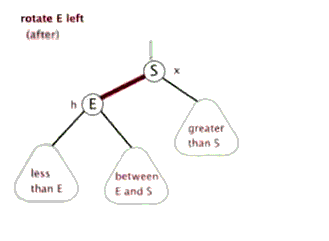
2.TreeMap的底层实现
public class TreeMap<K,V> 2 extends AbstractMap<K,V> 3 implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
可以看到TreeMap继承了AbstractMap抽象类,并实现NavigableMap、Cloneable、Serializable接口。NavigableMap接口扩展了SortedMap,主要是提供了给定搜索目标返回最接近匹配项的导航方法。这个不是我们今天的重点,这里不做分析了。
下面再看下TreeMap的底层存储相关定义:
// 比较器 private final Comparator<? super K> comparator; // 红黑树根节点 private transient Entry<K,V> root = null; // 集合元素数量 private transient int size = 0; // "fail-fast"集合修改记录 private transient int modCount = 0;
这里的Comparator是一个比较器,这里不详细讲解,后面会单独进行分析,这里只要明白,一个类实现了Comparator接口并重写其compare方法,就能进行比较大小。Entry是树的节点类,我们来看一下Entry的定义:
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { K key; V value; // 左孩子节点 Entry<K,V> left = null; // 右孩子节点 Entry<K,V> right = null; // 父节点 Entry<K,V> parent; // 红黑树用来表示节点颜色的属性,默认为黑色 boolean color = BLACK; /** * 用key,value和父节点构造一个Entry,默认为黑色 */ Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> parent) { this.key = key; this.value = value; this.parent = parent; } public K getKey() { return key ; } public V getValue() { return value ; } public V setValue(V value) { V oldValue = this.value ; this.value = value; return oldValue; } public boolean equals(Object o) { if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry)) return false; Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o; return valEquals( key,e.getKey()) && valEquals( value,e.getValue()); } public int hashCode() { int keyHash = (key ==null ? 0 : key.hashCode()); int valueHash = (value ==null ? 0 : value.hashCode()); return keyHash ^ valueHash; } public String toString() { return key + "=" + value; } }
Entry类理解起来比较简单(因为我们前面看过很多的Entry类了),主要是定义了树的孩子和父亲节点引用,和红黑颜色属性,并对equals和hashCode进行重写,以利于比较是否相等。
3.TreeMap的构造方法
接下来看下TreeMap的构造方法:
/** * 默认构造方法,comparator为空,代表使用key的自然顺序来维持TreeMap的顺序,这里要求key必须实现Comparable接口 */ public TreeMap() { comparator = null; } /** * 用指定的比较器构造一个TreeMap */ public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) { this.comparator = comparator; } /** * 构造一个指定map的TreeMap,同样比较器comparator为空,使用key的自然顺序排序 */ public TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { comparator = null; putAll(m); } /** * 构造一个指定SortedMap的TreeMap,根据SortedMap的比较器来来维持TreeMap的顺序 */ public TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) { comparator = m.comparator(); try { buildFromSorted(m.size(), m.entrySet().iterator(), null, null); } catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) { } catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) { } }
从构造方法中可以看出,要创建一个红黑树实现的TreeMap必须要有一个用于比较大小的比较器,因为只有能够比较大小才能实现红黑树的左孩子<树根<右孩子的特点
4.红黑树的添加原理及TreeMap的put实现
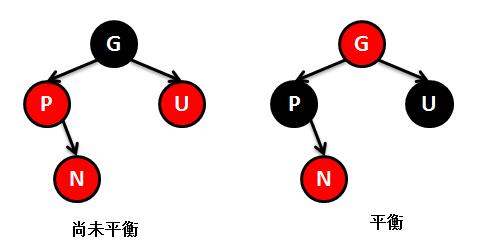
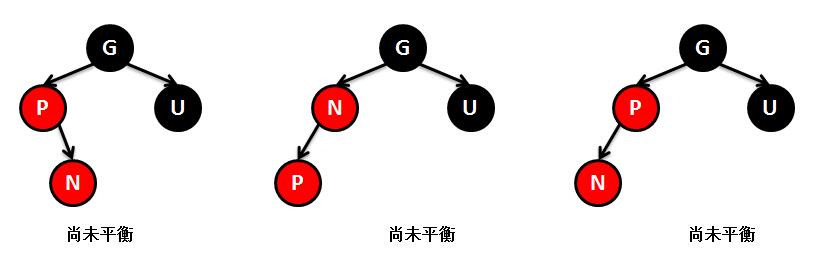
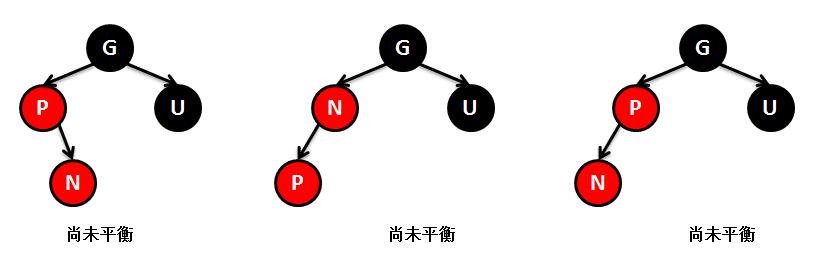
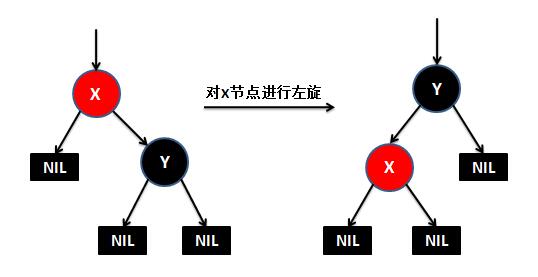
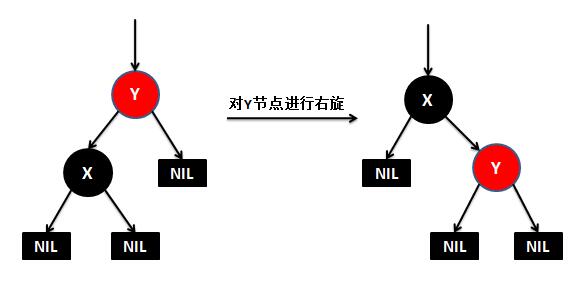
public V put(K key, V value) { // 根节点 Entry<K,V> t = root; // 如果根节点为空,则直接创建一个根节点,返回 if (t == null) { // TBD: // 5045147: (coll) Adding null to an empty TreeSet should // throw NullPointerException // // compare(key, key); // type check root = new Entry<K,V>(key, value, null); size = 1; modCount++; return null; } // 记录比较结果 int cmp; Entry<K,V> parent; // split comparator and comparable paths // 当前使用的比较器 Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator ; // 如果比较器不为空,就是用指定的比较器来维护TreeMap的元素顺序 if (cpr != null) { // do while循环,查找key要插入的位置(也就是新节点的父节点是谁) do { // 记录上次循环的节点t parent = t; // 比较当前节点的key和新插入的key的大小 cmp = cpr.compare(key, t. key); // 新插入的key小的话,则以当前节点的左孩子节点为新的比较节点 if (cmp < 0) t = t. left; // 新插入的key大的话,则以当前节点的右孩子节点为新的比较节点 else if (cmp > 0) t = t. right; else // 如果当前节点的key和新插入的key想的的话,则覆盖map的value,返回 return t.setValue(value); // 只有当t为null,也就是没有要比较节点的时候,代表已经找到新节点要插入的位置 } while (t != null); } else { // 如果比较器为空,则使用key作为比较器进行比较 // 这里要求key不能为空,并且必须实现Comparable接口 if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException(); Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key; // 和上面一样,喜欢查找新节点要插入的位置 do { parent = t; cmp = k.compareTo(t. key); if (cmp < 0) t = t. left; else if (cmp > 0) t = t. right; else return t.setValue(value); } while (t != null); } // 找到新节点的父节点后,创建节点对象 Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<K,V>(key, value, parent); // 如果新节点key的值小于父节点key的值,则插在父节点的左侧 if (cmp < 0) parent. left = e; // 如果新节点key的值大于父节点key的值,则插在父节点的右侧 else parent. right = e; // 插入新的节点后,为了保持红黑树平衡,对红黑树进行调整 fixAfterInsertion(e); // map元素个数+1 size++; modCount++; return null; } /** 新增节点后对红黑树的调整方法 */ private void fixAfterInsertion(Entry<K,V> x) { // 将新插入节点的颜色设置为红色 x. color = RED; // while循环,保证新插入节点x不是根节点或者新插入节点x的父节点不是红色(这两种情况不需要调整) while (x != null && x != root && x. parent.color == RED) { // 如果新插入节点x的父节点是祖父节点的左孩子 if (parentOf(x) == leftOf(parentOf (parentOf(x)))) { // 取得新插入节点x的叔叔节点 Entry<K,V> y = rightOf(parentOf (parentOf(x))); // 如果新插入x的父节点是红色-------------------① if (colorOf(y) == RED) { // 将x的父节点设置为黑色 setColor(parentOf (x), BLACK); // 将x的叔叔节点设置为黑色 setColor(y, BLACK); // 将x的祖父节点设置为红色 setColor(parentOf (parentOf(x)), RED); // 将x指向祖父节点,如果x的祖父节点的父节点是红色,按照上面的步奏继续循环 x = parentOf(parentOf (x)); } else { // 如果新插入x的叔叔节点是黑色或缺少,且x的父节点是祖父节点的右孩子-------------------② if (x == rightOf( parentOf(x))) { // 左旋父节点 x = parentOf(x); rotateLeft(x); } // 如果新插入x的叔叔节点是黑色或缺少,且x的父节点是祖父节点的左孩子-------------------③ // 将x的父节点设置为黑色 setColor(parentOf (x), BLACK); // 将x的祖父节点设置为红色 setColor(parentOf (parentOf(x)), RED); // 右旋x的祖父节点 rotateRight( parentOf(parentOf (x))); } } else { // 如果新插入节点x的父节点是祖父节点的右孩子,下面的步奏和上面的相似,只不过左旋右旋的区分,不在细讲 Entry<K,V> y = leftOf(parentOf (parentOf(x))); if (colorOf(y) == RED) { setColor(parentOf (x), BLACK); setColor(y, BLACK); setColor(parentOf (parentOf(x)), RED); x = parentOf(parentOf (x)); } else { if (x == leftOf( parentOf(x))) { x = parentOf(x); rotateRight(x); } setColor(parentOf (x), BLACK); setColor(parentOf (parentOf(x)), RED); rotateLeft( parentOf(parentOf (x))); } } } // 最后将根节点设置为黑色,不管当前是不是红色,反正根节点必须是黑色 root.color = BLACK; } /** * 对红黑树的节点(x)进行左旋转 * * 左旋示意图(对节点x进行左旋): * px px * / / * x y * / \ --(左旋)-- / \ * lx y x ry * / \ / \ * ly ry lx ly * */ private void rotateLeft(Entry<K,V> p) { if (p != null) { // 取得要选择节点p的右孩子 Entry<K,V> r = p. right; // "p"和"r的左孩子"的相互指向... // 将"r的左孩子"设为"p的右孩子" p. right = r.left ; // 如果r的左孩子非空,将"p"设为"r的左孩子的父亲" if (r.left != null) r. left.parent = p; // "p的父亲"和"r"的相互指向... // 将"p的父亲"设为"y的父亲" r. parent = p.parent ; // 如果"p的父亲"是空节点,则将r设为根节点 if (p.parent == null) root = r; // 如果p是它父节点的左孩子,则将r设为"p的父节点的左孩子" else if (p.parent. left == p) p. parent.left = r; else // 如果p是它父节点的左孩子,则将r设为"p的父节点的左孩子" p. parent.right = r; // "p"和"r"的相互指向... // 将"p"设为"r的左孩子" r. left = p; // 将"p的父节点"设为"r" p. parent = r; } } /** * 对红黑树的节点进行右旋转 * * 右旋示意图(对节点y进行右旋): * py py * / / * y x * / \ --(右旋)-- / \ * x ry lx y * / \ / \ * lx rx rx ry * */ private void rotateRight(Entry<K,V> p) { if (p != null) { // 取得要选择节点p的左孩子 Entry<K,V> l = p. left; // 将"l的右孩子"设为"p的左孩子" p. left = l.right ; // 如果"l的右孩子"不为空的话,将"p"设为"l的右孩子的父亲" if (l.right != null) l. right.parent = p; // 将"p的父亲"设为"l的父亲" l. parent = p.parent ; // 如果"p的父亲"是空节点,则将l设为根节点 if (p.parent == null) root = l; // 如果p是它父节点的右孩子,则将l设为"p的父节点的右孩子" else if (p.parent. right == p) p. parent.right = l; //如果p是它父节点的左孩子,将l设为"p的父节点的左孩子" else p.parent .left = l; // 将"p"设为"l的右孩子" l. right = p; // 将"l"设为"p父节点" p. parent = l; } }
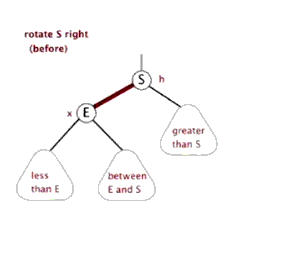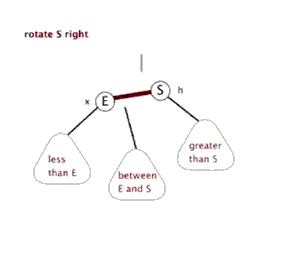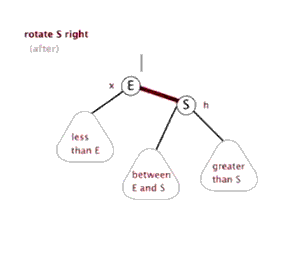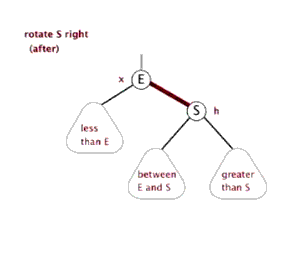
单纯的看代码和注释,绝对会发出,cha这是什么乱七八糟的,任谁也看不懂,所以一定要结合上面的图解,不懂了就看看图,然后动手画一下。如果你告诉我,还是没有懂,没问题可以理解,这里有一位大神录制的红黑树增加元素视频动画,来吧,http://v.youku.com/v_show/id_XNjI4NzgxMjA4.html(视频不是我录得,尊重版权,向大神致敬)。
5.红黑树的删除原理及TreeMap的remove实现
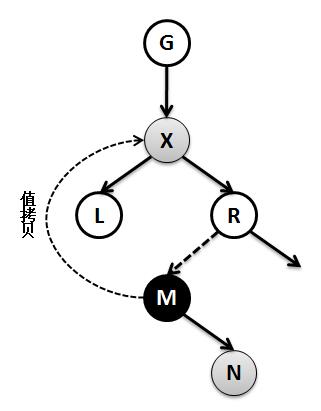
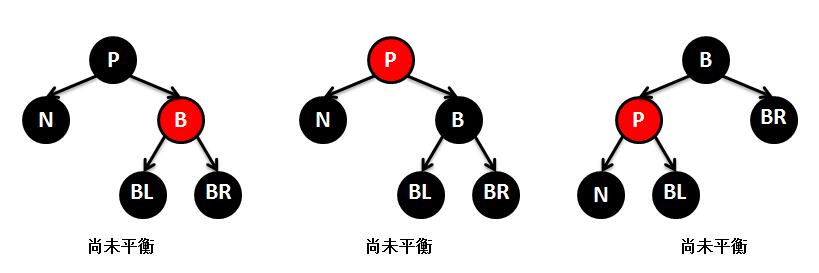

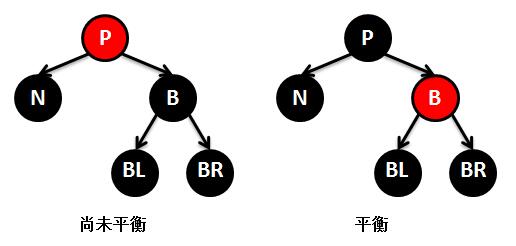
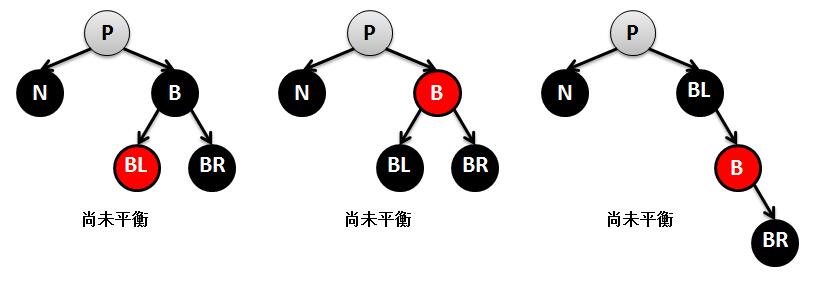
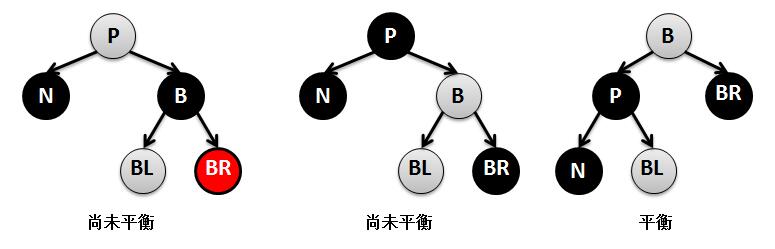
public V remove(Object key) { // 根据key查找到对应的节点对象 Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key); if (p == null) return null; // 记录key对应的value,供返回使用 V oldValue = p. value; // 删除节点 deleteEntry(p); return oldValue; } private void deleteEntry(Entry<K,V> p) { modCount++; // map容器的元素个数减一 size--; // If strictly internal, copy successor's element to p and then make p // point to successor. // 如果被删除的节点p的左孩子和右孩子都不为空,则查找其替代节点-----------这里表示要删除的节点有两个孩子(3) if (p.left != null && p. right != null) { // 查找p的替代节点 Entry<K,V> s = successor (p); p. key = s.key ; p. value = s.value ; // 将p指向替代节点,※※※※※※从此之后的p不再是原先要删除的节点p,而是替代者p(就是图解里面讲到的M) ※※※※※※ p = s; } // p has 2 children // Start fixup at replacement node, if it exists. // replacement为替代节点p的继承者(就是图解里面讲到的N),p的左孩子存在则用p的左孩子替代,否则用p的右孩子 Entry<K,V> replacement = (p. left != null ? p.left : p. right); if (replacement != null) { // 如果上面的if有两个孩子不通过--------------这里表示要删除的节点只有一个孩子(2) // Link replacement to parent // 将p的父节点拷贝给替代节点 replacement. parent = p.parent ; // 如果替代节点p的父节点为空,也就是p为跟节点,则将replacement设置为根节点 if (p.parent == null) root = replacement; // 如果替代节点p是其父节点的左孩子,则将replacement设置为其父节点的左孩子 else if (p == p.parent. left) p. parent.left = replacement; // 如果替代节点p是其父节点的左孩子,则将replacement设置为其父节点的右孩子 else p. parent.right = replacement; // Null out links so they are OK to use by fixAfterDeletion. // 将替代节点p的left、right、parent的指针都指向空,即解除前后引用关系(相当于将p从树种摘除),使得gc可以回收 p. left = p.right = p.parent = null; // Fix replacement // 如果替代节点p的颜色是黑色,则需要调整红黑树以保持其平衡 if (p.color == BLACK) fixAfterDeletion(replacement); } else if (p.parent == null) { // return if we are the only node. // 如果要替代节点p没有父节点,代表p为根节点,直接删除即可 root = null; } else { // No children. Use self as phantom replacement and unlink. // 判断进入这里说明替代节点p没有孩子--------------这里表示没有孩子则直接删除(1) // 如果p的颜色是黑色,则调整红黑树 if (p.color == BLACK) fixAfterDeletion(p); // 下面删除替代节点p if (p.parent != null) { // 解除p的父节点对p的引用 if (p == p.parent .left) p. parent.left = null; else if (p == p.parent. right) p. parent.right = null; // 解除p对p父节点的引用 p. parent = null; } } } /** * 查找要删除节点的替代节点 */ static <K,V> TreeMap.Entry<K,V> successor(Entry<K,V> t) { if (t == null) return null; // 查找右子树的最左孩子 else if (t.right != null) { Entry<K,V> p = t. right; while (p.left != null) p = p. left; return p; } else { // 查找左子树的最右孩子 Entry<K,V> p = t. parent; Entry<K,V> ch = t; while (p != null && ch == p. right) { ch = p; p = p. parent; } return p; } } /** From CLR */ private void fixAfterDeletion(Entry<K,V> x) { // while循环,保证要删除节点x不是跟节点,并且是黑色(根节点和红色不需要调整) while (x != root && colorOf (x) == BLACK) { // 如果要删除节点x是其父亲的左孩子 if (x == leftOf( parentOf(x))) { // 取出要删除节点x的兄弟节点 Entry<K,V> sib = rightOf(parentOf (x)); // 如果删除节点x的兄弟节点是红色---------------------------① if (colorOf(sib) == RED) { // 将x的兄弟节点颜色设置为黑色 setColor(sib, BLACK); // 将x的父节点颜色设置为红色 setColor(parentOf (x), RED); // 左旋x的父节点 rotateLeft( parentOf(x)); // 将sib重新指向旋转后x的兄弟节点 ,进入else的步奏③ sib = rightOf(parentOf (x)); } // 如果x的兄弟节点的两个孩子都是黑色-------------------------③ if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK && colorOf(rightOf (sib)) == BLACK) { // 将兄弟节点的颜色设置为红色 setColor(sib, RED); // 将x的父节点指向x,如果x的父节点是黑色,需要将x的父节点整天看做一个节点继续调整-------------------------② x = parentOf(x); } else { // 如果x的兄弟节点右孩子是黑色,左孩子是红色-------------------------④ if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) { // 将x的兄弟节点的左孩子设置为黑色 setColor(leftOf (sib), BLACK); // 将x的兄弟节点设置为红色 setColor(sib, RED); // 右旋x的兄弟节点 rotateRight(sib); // 将sib重新指向旋转后x的兄弟节点,进入步奏⑤ sib = rightOf(parentOf (x)); } // 如果x的兄弟节点右孩子是红色-------------------------⑤ setColor(sib, colorOf (parentOf(x))); // 将x的父节点设置为黑色 setColor(parentOf (x), BLACK); // 将x的兄弟节点的右孩子设置为黑色 setColor(rightOf (sib), BLACK); // 左旋x的父节点 rotateLeft( parentOf(x)); // 达到平衡,将x指向root,退出循环 x = root; } } else { // symmetric // 如果要删除节点x是其父亲的右孩子,和上面情况一样,这里不再细讲 Entry<K,V> sib = leftOf(parentOf (x)); if (colorOf(sib) == RED) { setColor(sib, BLACK); setColor(parentOf (x), RED); rotateRight( parentOf(x)); sib = leftOf(parentOf (x)); } if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK && colorOf(leftOf (sib)) == BLACK) { setColor(sib, RED); x = parentOf(x); } else { if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) { setColor(rightOf (sib), BLACK); setColor(sib, RED); rotateLeft(sib); sib = leftOf(parentOf (x)); } setColor(sib, colorOf (parentOf(x))); setColor(parentOf (x), BLACK); setColor(leftOf (sib), BLACK); rotateRight( parentOf(x)); x = root; } } } setColor(x, BLACK); }
6.红黑树的查询
public V get(Object key) { Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key); return (p==null ? null : p. value); } final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) { // Offload comparator-based version for sake of performance if (comparator != null) // 如果比较器为空,只是用key作为比较器查询 return getEntryUsingComparator(key); if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException(); Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key; // 取得root节点 Entry<K,V> p = root; // 从root节点开始查找,根据比较器判断是在左子树还是右子树 while (p != null) { int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key ); if (cmp < 0) p = p. left; else if (cmp > 0) p = p. right; else return p; } return null; } final Entry<K,V> getEntryUsingComparator(Object key) { K k = (K) key; Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator ; if (cpr != null) { Entry<K,V> p = root; while (p != null) { int cmp = cpr.compare(k, p.key ); if (cmp < 0) p = p. left; else if (cmp > 0) p = p. right; else return p; } } return null; }
查询看起来真的是so easy。。。





【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发中对象命名的一点思考
· .NET Core内存结构体系(Windows环境)底层原理浅谈
· C# 深度学习:对抗生成网络(GAN)训练头像生成模型
· .NET 适配 HarmonyOS 进展
· .NET 进程 stackoverflow异常后,还可以接收 TCP 连接请求吗?
· 本地部署 DeepSeek:小白也能轻松搞定!
· 基于DeepSeek R1 满血版大模型的个人知识库,回答都源自对你专属文件的深度学习。
· 在缓慢中沉淀,在挑战中重生!2024个人总结!
· 大人,时代变了! 赶快把自有业务的本地AI“模型”训练起来!
· Tinyfox 简易教程-1:Hello World!