[北航软工]第一次结对作业-最长单词链
BUAA软件工程 第一次结对作业
| 项目 | 内容 |
|---|---|
| 这个作业属于哪个课程? | 北航软工 |
| 这个作业的要求在哪里? | 第一次结对作业 |
| 我在这个课程的目标是? | 学习高效严谨的软件工程开发过程,建立团队意识 |
| 这个作业在哪个具体方面帮助我实现目标 | 熟悉并了解软件工程的基本知识,建立兴趣 |
1. 项目的Github地址
项目有两个分支,master分支是命令行形式,UI分支是带GUI的程序。
2. 14. PEP表格
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 30 | 30 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 30 | 30 |
| Development | 开发 | 815 | 1200 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 30 | 120 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 30 | 90 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) | 15 | 30 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 30 | 15 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 50 | 30 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 300 | 600 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 60 | 90 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 300 | 500 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 240 | 195 |
| · Test Report | · 测试报告 | 120 | 120 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 15 | 15 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 105 | 60 |
| 合计 | 1085 | 1700 |
3.看教科书和其它资料中关于Information Hiding, Interface Design, Loose Coupling的章节,说明你们在结对编程中是如何利用这些方法对接口进行设计的
信息隐藏
信息隐藏是指在设计和确定模块时,使得一个模块内包含的特定信息(过程或数据),对于不需要这些信息的其他模块来说,是不可访问的。 在我们的设计过程中,模块除了被调用的两个接口或者说成员函数以外,其他的成员都是private属性的,它如何实现算法,如何存储数据,过程中某个变量的值如何,都与外部无关,从外部不可访问和修改,保证编程的安全性。
接口设计
对调用者和使用者而言,不需要知道函数内部的实现,只需要掌握接口的信息。接口设计主要是作用和副作用的明确性,如果接口应该一开始就设计的比较成熟,这样我们修改实现接口的程序时,调用接口的程序就不用修改。我们设计的两个接口,约定了函数的具体作用即以不同的方式寻找最长单词链,约定了传入参数的具体意义,并且规定了只能修改char * result变量作为结果的输出,其他的参数应该不改变。
松耦合
松耦合和接口设计是相辅相成的。只有在规定好接口规范以后,才能实现进一步的解耦合。我们只规定接口的作用,而不规定接口的内容。这样不同组件之间可以轻易地做到互相独立。
附加题:换GUI体现松耦合
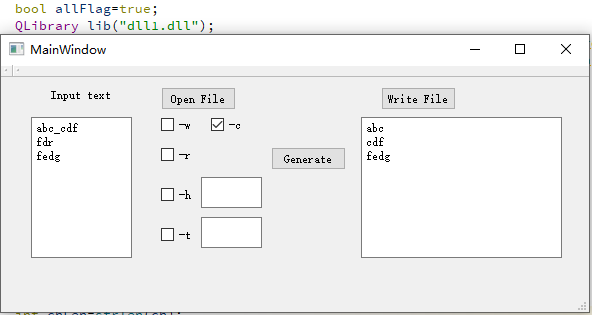
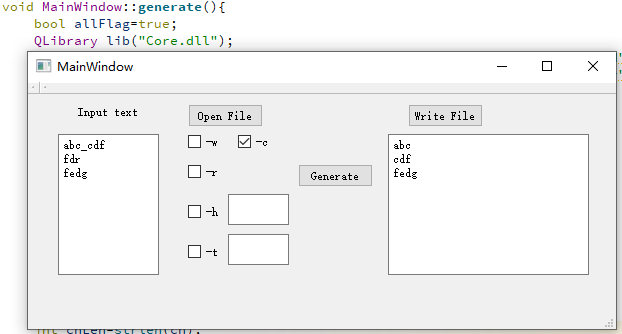
我们在完成代码编写后,与其他组同学互换了GUI和DLL,另一个组是周二的白世豪(16061167),宋卓洋(16061170)组。由于生成dll的教程类似,并没有出现什么问题,对于无异常情况可以正常运行,如下图所示:
其中Core.dll是我们生成的dll,DLL1.dll是另外一个组的dll,经过测试,加载两个dll时GUI的行为一致。
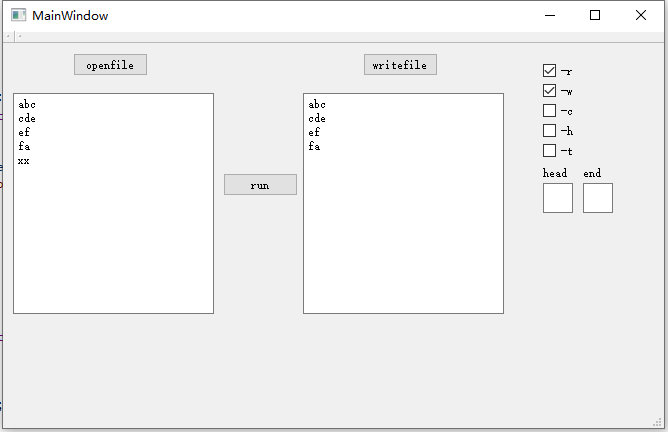
4. 计算模块接口的设计与实现过程
整个程序的逻辑大致如下图所示:
因为GUI程序是不会涉及到普通的参数正确性的(只有关于指定头尾的字母是否正确),所以 出于解耦合的需要,我们并没有将处理参数的程序集成在Core类之中,而是独立出来,在main函数中判断参数的正确性。Core类中确保接受到的是正确的单词组char *words[]和其他合适的参数。我们暴露在外的只有两个接口。
int gen_chain_word(char* words[], int len, char* result[], char head, char tail, bool enable_loop);
int gen_chain_char(char* words[], int len, char* result[], char head, char tail, bool enable_loop);
其他的部分以private成员的形式,供内部使用。
然后每个接口中对单词的处理也需要分成两种。
\\没有-r选项,检测有环时直接报错,无环时以宽度优先搜索的形式(不会陷入死循环)找到最长单词链;
\\有-r选项,不需要检测是否有环,直接以深度优先搜索的形式搜索最长单词链;
\\伪代码如下
if(!enable_loop)
{
roundtest();//有环时抛出错误
createMap();//建立bfs的地图
BFS();//宽度优先搜索
getBFSResult();//处于节省时间和空间的考虑,上一步宽度优先搜索并没有保存路径,而是得出了最长的长度,然后根据长度倒推出路径。
}
else
{
createMap();//建立dfs的地图
DFS();//深度优先搜素
getDFSResult();//推导最终路径,原因同上
}
基础的函数大致就是这些,两种类型chain_word和chain_char的各有一套。然后我们还引入了get_tails()就是在扫描边的时候,排除不可能的首尾选项。大致原理就是当不成环的时候,出度为0的点才可能是尾字母,否则不可能是最长链。这样我们可以剪枝,减少搜索时的复杂度。
5.画出UML图显示计算模块部分各个实体之间的关系 [u]
使用了自动化工具生成类图与调用关系,参考工具Github,生成的调用关系如下:
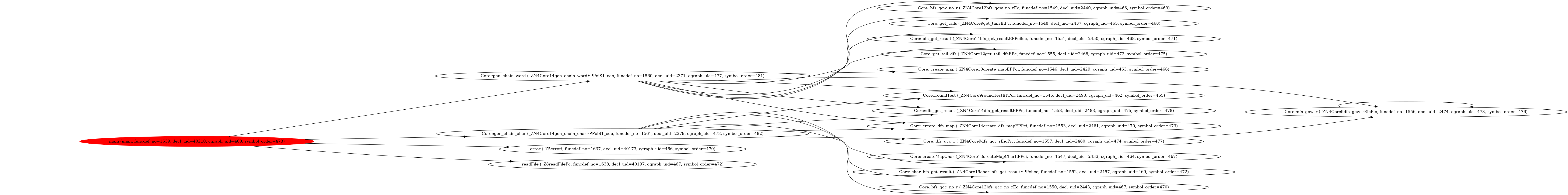
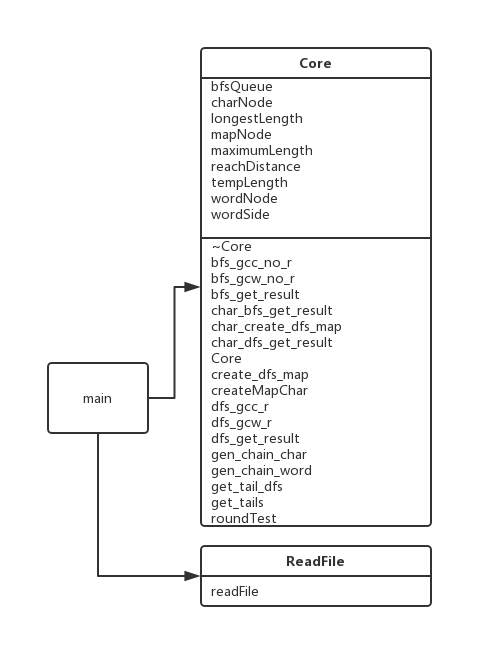
手画类图如下,我们的类关系相当简单。
6.计算模块接口部分的性能改进
整体上说,我们采取了BFS解决没有-r的情况,使用DFS解决有-r的情况。
首先是没有-r的部分。由于算法在设计之初就已经考虑到了一些优化,我们重复执行同一条指令50次,取得更好的采样效果。如图所示,整个算法的耗时最长是在建图与删重边。程序在输入8000个单词时运算时间在1s以内。因此没有做进一步改进,这里介绍一下完成的优化。
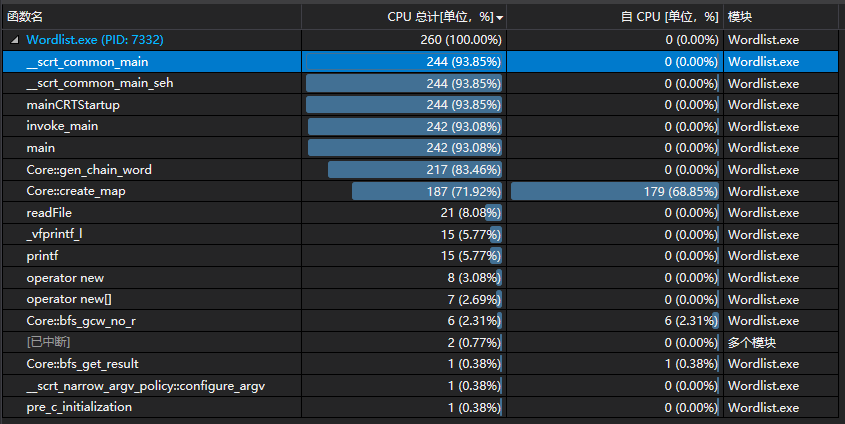
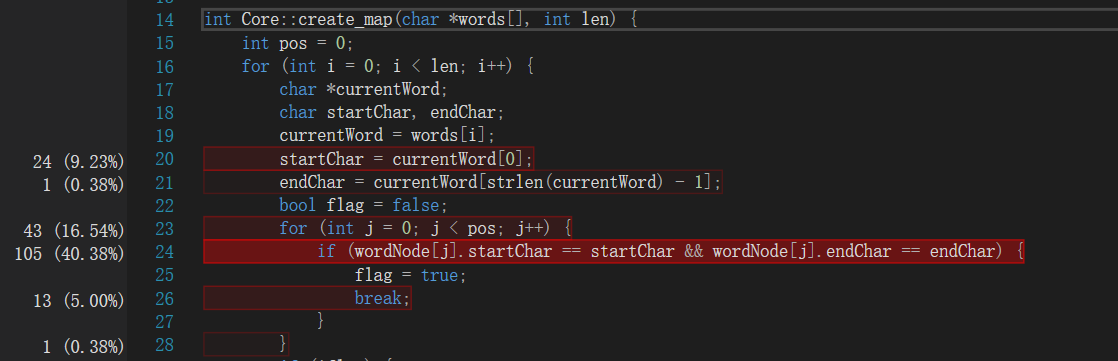
我们主要完成了以下几个优化:
- 建图时有重边的只保留一条。这样可以避免BFS重复搜索节点。
- BFS节点记忆化。在访问BFS节点后记录当前距离,在下一次另一条边访问时判断,如果小于当前记忆的距离则剪枝。
- 减少起始搜索节点。考虑到没有环,因此不考虑自环时起始节点的入度为0,末尾节点的出度为0。在没有指定开始/结束字符时,通过这种方法减少可能的起始节点,降低搜索次数。
在含有-r的部分,考虑到这是一个NP问题,而且要求的是准确解,不是近似解,我们采用回溯法进行深度搜索。程序输入90个单词,摘自Wikipedia的一个随机网页,运行时间3分04秒。
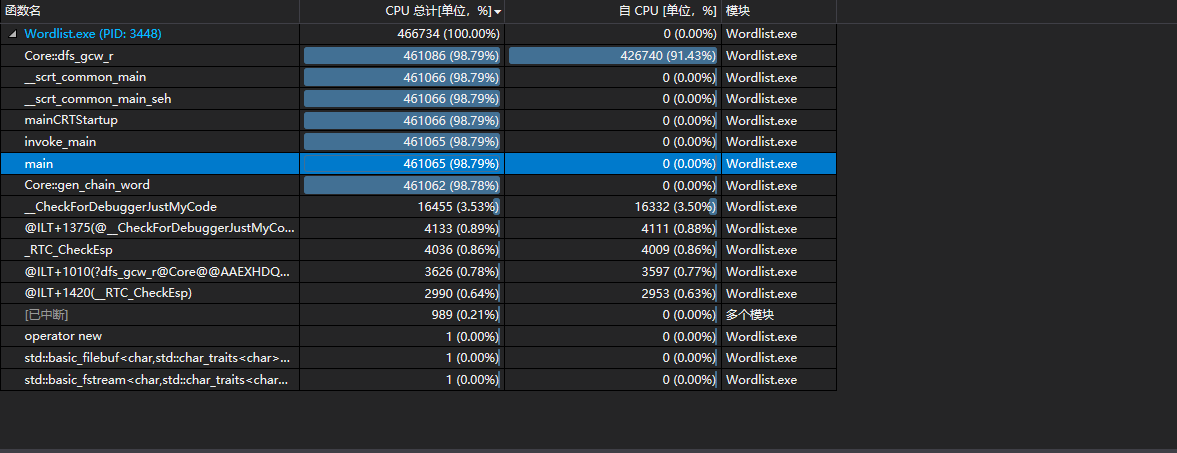
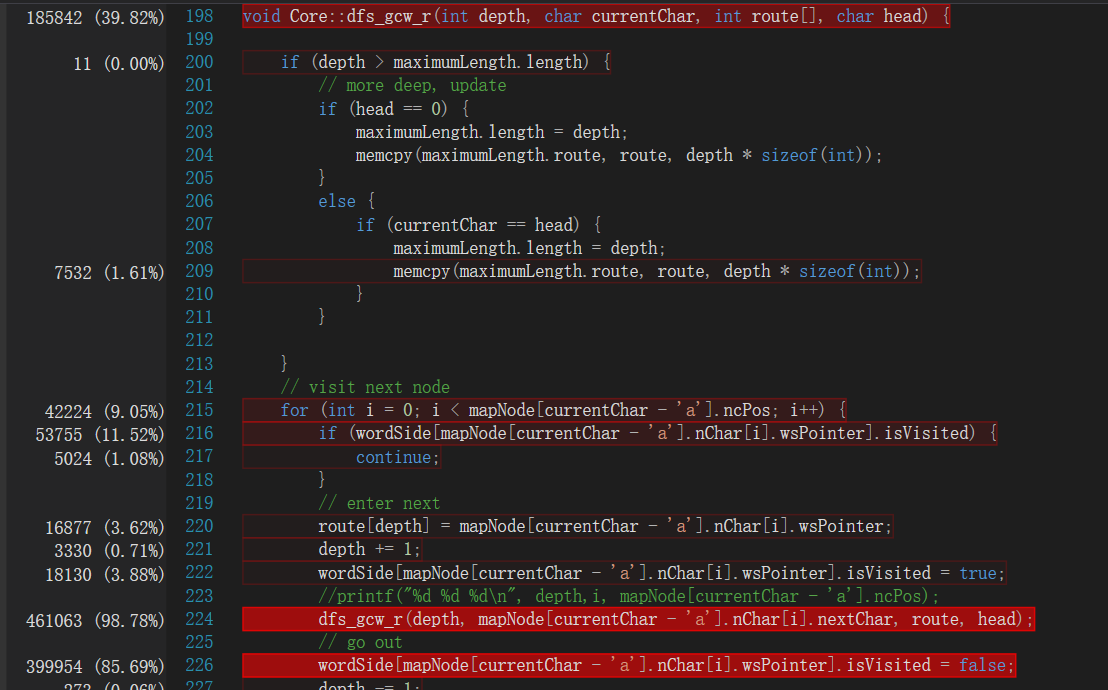
可以发现,程序在DFS上耗费了大量的时间。我们对于这种模式依然做了一些优化,我们同BFS一样减少了可能的起点,因为起点的出度>=入度,终点的入度>=出度,也有一定效果。
此外,我们还在整体上对程序进行了优化。考虑到处理器支持AVX指令集,我们在编译选项中选择了支持生成AVX2指令的编译选项,取得了不错的效果,对于一组较复杂的测试用例,运行时间从2分58秒减少到2分03秒,提升接近1/3。
7.看Design by Contract, Code Contract的内容:描述这些做法的优缺点, 说明你是如何把它们融入结对作业中的
契约式设计要求软件设计者为软件组件定义正式的,精确的并且可验证的接口,接受一个合规的输入,并保证合规的输出。根据百科的定义来看,这种设计模式重在精确二字。
- 优点
- 减少了防御式编程的一部分工作量
- 提高了程序的可维护性
- 使程序员的之间的合作变得有序
- 缺点
- 制定契约,维护契约,使程序满足契约的代价(时间和人力)比较大
- 必须强制要求整个项目内的代码都符合契约,否则部分的无效影响整个工程的质量
本次结对作业中,首要契约是作业要求中规定的接口,这个降低了沟通的一部分任务。实际编程中我们制定的契约主要是双方完成的函数方法部分对于类成员的行为,以及对于异常情况的处理。在如此契约之下,我们才完成了从Core类到GUI的低耦合。
8.计算模块部分单元测试展示
单元测试整体覆盖率91%。未覆盖到的部分主要是抛出异常的if语句。

计算模块暴露的接口共有两个,分别为
- int gen_chain_word(char* words[], int len, char* result[], char head, char tail, bool enable_loop)
- int gen_chain_char(char* words[], int len, char* result[], char head, char tail, bool enable_loop)
我们对其进行了单元测试。测试的流程是测试程序加载一组测试数据,放入char * words[]中,与一些参数一起传入函数,得到返回的result后加载标答并逐个比较,如下面的代码片段所示:
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod1)
{
Core * core = new Core();
// do sth to update words
core->gen_chain_word(words1, len, result1, 0, 0, false);
// get true value into realAnswer
Assert::AreEqual(51, length_of_result1);
for (int i = 0; i < length_of_result1; i++) {
Assert::AreEqual(strcmp(result1[i], realAnswer[i]), 0);
}
}
对于正常数据,我们使用随机生成+对拍的方式检验。
对于异常数据,我们构造了以下几个特殊情况:
- words 为空,模拟文件异常或不存在
- words 有环,但是没有-r
- tail 或 head 指定的单词链找不到
- 没有单词链
其中对于有环的情况,我们还分了以下几种情况:
- 有自环
- 有多个自环
- 有多条边组成的环
以下为单元测试展示,由于太长默认收起。
注意,请依次运行每个单元测试,不要一起运行,防止出错。
正确数据测试 -w
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod1)
{
Core * core = new Core();
int len = readFile1("../WordChainUnitTesr/words1.txt");
core->gen_chain_word(words1, len, result1, 0, 0, false);
int len2 = readFile1("../WordChainUnitTesr/solution1.txt");
Assert::AreEqual(51, len2);
for (int i = 0; i < len2; i++) {
Assert::AreEqual(strcmp(result1[i], words1[i]), 0);
}
}
正确数据测试 -c
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod2)
{
Core * core = new Core();
int len = readFile1("../WordChainUnitTesr/words1_1.txt");
core->gen_chain_char(words1, len, result1, 0, 0, false);
int len2 = readFile1("../WordChainUnitTesr/solution1_1.txt");
Assert::AreEqual(51, len2);
for (int i = 0; i < len2; i++) {
Assert::AreEqual(strcmp(result1[i], words1[i]), 0);
}
}
正确数据测试 -w -r
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod3)
{
Core * core = new Core();
int len = readFile1("../WordChainUnitTesr/words2.txt");
core->gen_chain_word(words1, len, result1, 0, 0, true);
int len2 = readFile1("../WordChainUnitTesr/solution2.txt");
Assert::AreEqual(4, len2);
for (int i = 0; i < len2; i++) {
Assert::AreEqual(strcmp(result1[i], words1[i]), 0);
}
}
正确数据测试 -c -r
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod4)
{
Core * core = new Core();
int len = readFile1("../WordChainUnitTesr/words2_1.txt");
core->gen_chain_char(words1, len, result1, 0, 0, true);
int len2 = readFile1("../WordChainUnitTesr/solution2_1.txt");
Assert::AreEqual(3, len2);
for (int i = 0; i < len2; i++) {
Assert::AreEqual(strcmp(result1[i], words1[i]), 0);
}
}
正确数据测试 -w -r -h e
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod5)
{
Core * core = new Core();
int len = readFile1("../WordChainUnitTesr/words3.txt");
core->gen_chain_word(words1, len, result1, 'e', 0, false);
int len2 = readFile1("../WordChainUnitTesr/solution3.txt");
Assert::AreEqual(4, len2);
for (int i = 0; i < len2; i++) {
Assert::AreEqual(strcmp(result1[i], words1[i]), 0);
}
}
正确数据测试 -w-r -t e
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod6)
{
Core * core = new Core();
int len = readFile1("../WordChainUnitTesr/words4.txt");
core->gen_chain_word(words1, len, result1, 0, 'e', false);
int len2 = readFile1("../WordChainUnitTesr/solution4.txt");
Assert::AreEqual(4, len2);
for (int i = 0; i < len2; i++) {
Assert::AreEqual(strcmp(result1[i], words1[i]), 0);
}
}
正确数据测试 -w -h c -t e
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod7)
{
Core * core = new Core();
int len = readFile1("../WordChainUnitTesr/words5.txt");
core->gen_chain_word(words1, len, result1, 'c', 'e', false);
int len2 = readFile1("../WordChainUnitTesr/solution5.txt");
Assert::AreEqual(2, len2);
for (int i = 0; i < len2; i++) {
Assert::AreEqual(strcmp(result1[i], words1[i]), 0);
}
}
正确数据测试 -c -r -h e -t e
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod8)
{
Core * core = new Core();
int len = readFile1("../WordChainUnitTesr/words6.txt");
core->gen_chain_char(words1, len, result1, 'e', 'e', true);
int len2 = readFile1("../WordChainUnitTesr/solution6.txt");
Assert::AreEqual(3, len2);
for (int i = 0; i < len2; i++) {
Assert::AreEqual(strcmp(result1[i], words1[i]), 0);
}
}
正确数据测试 -w 大数据
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod9)
{
Core * core = new Core();
int len = readFile1("../WordChainUnitTesr/words7.txt");
core->gen_chain_word(words1, len, result1, 0, 0, false);
int len2 = readFile1("../WordChainUnitTesr/solution7.txt");
Assert::AreEqual(13, len2);
for (int i = 0; i < len2; i++) {
Assert::AreEqual(strcmp(result1[i], words1[i]), 0);
}
delete core;
}
异常数据测试 没有-r却有环 多个自环
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod10)
{
try {
Core * core = new Core();
int len = readFile1("../WordChainUnitTesr/words8.txt");
core->gen_chain_word(words1, len, result1, 0, 0, false);
//RAISE EXCEPTION "Find a loop but no -r"
}
catch (const char* msg) {
Assert::AreEqual(strcmp(msg, "Find a loop but no -r"), 0);
}
}
异常数据测试 没有-r却有环 多条边组成的环
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod11)
{
try {
Core * core = new Core();
int len = readFile1("../WordChainUnitTesr/words9.txt");
core->gen_chain_word(words1, len, result1, 0, 0, false);
//RAISE EXCEPTION "Find a loop but no -r"
}
catch (const char* msg) {
Assert::AreEqual(strcmp(msg, "Find a loop but no -r"), 0);
}
}
异常数据测试 没有找到链 所有单词没有形成链
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod12)
{
try {
Core * core = new Core();
int len = readFile1("../WordChainUnitTesr/words10.txt");
core->gen_chain_word(words1, len, result1, 0, 0, false);
//RAISE EXCEPTION "Find a loop but no -r"
}
catch (const char* msg) {
Assert::AreEqual(strcmp(msg, "No chains found"), 0);
}
}
异常数据测试 没有找到链 指定的头不存在链
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod13)
{
try {
Core * core = new Core();
int len = readFile1("../WordChainUnitTesr/words11.txt");
core->gen_chain_word(words1, len, result1, 'e', 0, false);
//RAISE EXCEPTION "Find a loop but no -r"
}
catch (const char* msg) {
Assert::AreEqual(strcmp(msg, "No chains found"), 0);
}
}
异常数据测试 没有找到链 指定的尾不存在链
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod14)
{
try {
Core * core = new Core();
int len = readFile1("../WordChainUnitTesr/words12.txt");
core->gen_chain_word(words1, len, result1, 0,'e', false);
//RAISE EXCEPTION "Find a loop but no -r"
}
catch (const char* msg) {
Assert::AreEqual(strcmp(msg, "No chains found"), 0);
}
}
异常数据测试 文件为空
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod15)
{
try {
Core * core = new Core();
words1[0] = "";
core->gen_chain_word(words1, 0, result1, 0, 'e', false);
//RAISE EXCEPTION "Find a loop but no -r"
}
catch (const char* msg) {
Assert::AreEqual(strcmp(msg, "Input file is empty"), 0);
}
}
异常数据测试 命令行参数有错
Wordlist.exe -w in.txt -c in.txt "duplicated read file"
Wordlist.exe -w -r "missing arguments"
Wordlist.exe -w aaa.xyz(does not exist) "file not exist"
Wordlist.exe -w in.txt -h a -h b "duplicated -h"
Wordlist.exe -w in.txt -h ab "wrong -h"
Wordlist.exe -w in.txt -t a -t b "duplicated -t"
Wordlist.exe -w in.txt -t ab "wrong -t"
Wordlist.exe -w in.txt -r -r "duplicated -r"
Wordlist.exe -r "no input file";
Wordlist.exe -x "undefined error"
Wordlist.exe -w in.doc "wrong format, not *.txt"
9.计算模块部分异常处理说明
计算模块共计有三种异常,异常分别是:
- 有环却没有-r
- words为空
- 不存在需求的单词链(包括没有以规定字母为首尾的链和只有长度为1的链)
测试数据见上一节
计算模块通过抛出异常的方式处理异常,向上一级抛出一个字符串,内容是具体的异常信息。
10.界面模块的详细设计过程
我们使用QT绘制界面,通过加载DLL调用接口。在网上查询了教程后,我们发现设计界面模块不是很难,主要流程如下:
- 画出界面上按钮,文本框等的位置
- 针对按钮编写不同的运行逻辑
- 针对报错弹出报错窗口
在实现过程中,我们参考了这篇教程。
由于时间等原因,我们并没有对界面进行过多的美化,以体现功能为主。界面主要代码如下:
code
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include "ui_mainwindow.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
typedef int(*gen_chain_word)(char * words[], int len, char * result[], char head, char tail, bool enable_loop);
typedef int(*gen_chain_char)(char * words[], int len, char * result[], char head, char tail, bool enable_loop);
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent) :
QMainWindow(parent),
ui(new Ui::MainWindow)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
drawUI(this);
connect(this->pushButton,SIGNAL(clicked()),this,SLOT(fileOpen()));
connect(this->pushButton_2,SIGNAL(clicked()),this,SLOT(generate()));
connect(this->pushButton_3,SIGNAL(clicked()),this,SLOT(fileSave()));
}
void MainWindow::fileOpen(){
QString filePath= QFileDialog::getOpenFileName(this,tr("file"),"",tr("TXT(.txt)"));
if (filePath.isEmpty()){
return;
}else{
QFile fin(filePath);
if (fin.open(QIODevice::ReadOnly | QIODevice::Text)){
while (!fin.atEnd()){
QByteArray line = fin.readLine();
QString strin(line);
this->textEdit->insertPlainText(strin);
}
}
fin.close();
}
}
void MainWindow::generate(){
bool allFlag=true;
QLibrary lib("dll1.dll");
gen_chain_word get_chain_word=(gen_chain_word)lib.resolve("gen_chain_word");
gen_chain_word get_chain_char=(gen_chain_char)lib.resolve("gen_chain_char");
bool A_w,A_c,A_r,A_h,A_t;
A_w=this->checkBox->isChecked()?true:false;
A_c=this->checkBox_2->isChecked()?true:false;
A_r=this->checkBox_3->isChecked()?true:false;
A_h=this->checkBox_4->isChecked()?true:false;
A_t=this->checkBox_5->isChecked()?true:false;
QString textin=this->textEdit->toPlainText();
qDebug() << textin;
char ch;
QByteArray ba = textin.toLatin1();
ch=ba.data();
char ** words=new char[10000];
char ** result=new char[10000];
int len=0;
int chLen=strlen(ch);
int currPos=0;
while (currPos<chLen){
if (isalpha(ch[currPos]) != 0) {
char * wordBuff = new char[1000];
int wordBuffPos = 0;
//printf("%c",currentChar);
while (isalpha(ch[currPos]) != 0) {
wordBuff[wordBuffPos] = tolower(ch[currPos]);
wordBuffPos++;
currPos++;
}
wordBuff[wordBuffPos] = '\0';
words[len] = wordBuff;
len++;
}
else {
currPos++;
}
}
qDebug()<<ch;
qDebug()<<len;
qDebug()<<words[len-1];
char head=0,tail=0;
if (A_t){
QString tmp=this->plainTextEdit_2->toPlainText();
char* tt;
QByteArray ba = tmp.toLatin1();
tt=ba.data();
if (strlen(tt)!=1){
allFlag=false;
QMessageBox::critical(0 , "ERROR" , "More than one char or no char got in -h or -t", QMessageBox::Ok | QMessageBox::Default ,0 , 0 );
}else{
tail=tt[0];
}
}
if (A_h){
QString tmp=this->plainTextEdit->toPlainText();
char* tt;
QByteArray ba = tmp.toLatin1();
tt=ba.data();
if (strlen(tt)!=1){
allFlag=false;
QMessageBox::critical(0 , "ERROR" , "More than one char or no char got in -h or -t", QMessageBox::Ok | QMessageBox::Default ,0 , 0 );
}else{
head=tt[0];
}
}
if (A_w && A_c){
allFlag=false;
QMessageBox::critical(0 , "ERROR" , "Cannot choose both -w and -c", QMessageBox::Ok | QMessageBox::Default ,0 , 0 );
}
if ((!A_w)&&(!A_c)){
allFlag=false;
QMessageBox::critical(0 , "ERROR" , "Must choose -w or -c", QMessageBox::Ok | QMessageBox::Default ,0 , 0 );
}
qDebug()<<"!!!!!!";
qDebug()<<(int)tail;
qDebug()<<(int)head;
if (allFlag){
try {
if (A_c) get_chain_char(words,len,result,head,tail,A_r);
if (A_w) get_chain_word(words,len,result,head,tail,A_r);
} catch (const char* msg) {
QMessageBox::critical(0 , "ERROR" , msg, QMessageBox::Ok | QMessageBox::Default ,0 , 0 );
}catch(...){
QMessageBox::critical(0 , "ERROR" , "ERROR", QMessageBox::Ok | QMessageBox::Default ,0 , 0 );
}
qDebug()<<"!!!!!!";
int pp=0;
while (result[pp]!=NULL){
qDebug(result[pp]);
this->textEdit_2->insertPlainText(result[pp]);
this->textEdit_2->insertPlainText("\n");
pp++;
}
}
}
void MainWindow::fileSave(){
QString filePath= QFileDialog::getSaveFileName(this,tr("file"),"",tr("TXT(*.txt)"));
if (filePath.isEmpty()){
return;
}else{
QFile fout(filePath);
if (fout.open(QIODevice::WriteOnly | QIODevice::Text)){
QString textin=this->textEdit_2->toPlainText();
QTextStream out(&fout);
out << textin << endl;
}
fout.close();
}
}
MainWindow::~MainWindow()
{
delete ui;
}
界面模块可以在GitHub上的UI分支里看到
11.界面模块与计算模块的对接
界面模块通过加载DLL的方式与计算模块对接,关键代码为:
typedef int(*gen_chain_word)(char * words[], int len, char * result[], char head, char tail, bool enable_loop);
typedef int(*gen_chain_char)(char * words[], int len, char * result[], char head, char tail, bool enable_loop);
QLibrary lib("dll1.dll");
gen_chain_word get_chain_word=(gen_chain_word)lib.resolve("gen_chain_word");
gen_chain_word get_chain_char=(gen_chain_char)lib.resolve("gen_chain_char");
通过上面的代码即实现了功能对接。
12.描述结对的过程



13.看教科书和其它参考书,网站中关于结对编程的章节,例如:说明结对编程的优点和缺点。结对的每一个人的优点和缺点在哪里 (要列出至少三个优点和一个缺点)。
结对编程的优点是如果两个人配合的好的话,当然比一个人干活进行更加轻松速度。缺点就是为了好好地合作往往要付出一定的代价,制定规范,分配任务,推进进度,对于社交恐惧症患者来说还是有一定难度的。然后如果两个人合作开发,比如同一个类的方法实现,那么可能对这个类的公共资源可能会造成浪费。比如为了实现不同的函数两个人分别在类里面定义了一个成员数组,但其实一个数组可以分别用在两个函数中。当然,这种浪费可以通过事先的规范和事后的重构来避免和消除,总归是不便利的。
结对同学的优点
- 不咕,该完成的任务没有拖延过;
- 代码质量还是比较高的;
- 交流顺畅,回消息会的很快,而且约定的当面交流也没有迟到过。
缺点是第一次提交的部分代码没有注释,可读性比较差。后来交流过之后趁晚上补上了注释,点赞!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号