CF708E Student's Camp
Student's Camp
题面翻译
有一个
除了第一行和最后一行,其他每一行每一天最左边和最右边的格子都有
求
题目描述
Alex studied well and won the trip to student camp Alushta, located on the seashore.
Unfortunately, it's the period of the strong winds now and there is a chance the camp will be destroyed! Camp building can be represented as the rectangle of
Every day there is a breeze blowing from the sea. Each block, except for the blocks of the upper and lower levers, such that there is no block to the left of it is destroyed with the probability 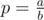 . Similarly, each night the breeze blows in the direction to the sea. Thus, each block (again, except for the blocks of the upper and lower levers) such that there is no block to the right of it is destroyed with the same probability
. Similarly, each night the breeze blows in the direction to the sea. Thus, each block (again, except for the blocks of the upper and lower levers) such that there is no block to the right of it is destroyed with the same probability
The period of the strong winds will last for
Find the probability that Alex won't have to look for other opportunities and will be able to spend the summer in this camp.
输入格式
The first line of the input contains two integers
The second line of the input contains two integers
The third line contains a single integer
输出格式
Consider the answer as an irreducible fraction is equal to  . Print one integer equal to
. Print one integer equal to 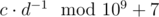 . It's guaranteed that within the given constraints
. It's guaranteed that within the given constraints 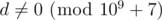 .
.
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
2 2
1 2
1
样例输出 #1
937500007
样例 #2
样例输入 #2
5 1
3 10
1
样例输出 #2
95964640
样例 #3
样例输入 #3
3 3
1 10
5
样例输出 #3
927188454
提示
In the first sample, each of the four blocks is destroyed with the probability  . There are
. There are 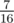 , so you should print
, so you should print 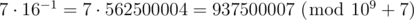
Solution
一道神仙前缀和优化概率
先定义
显然
因为我们要求的东西是与每一层的区间相关的,所以不如再定义一个
那么由此引出设计的状态:定义
这样求解的话不难发现转移是
考虑容斥,与
将三个带有求和号的部分重新定义一下:
那么可以改写一下
现在来看怎么转移
其实可以发现:
考虑怎么计算
发现此时的
总时间复杂度为
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
constexpr int _SIZE = 1.5e3, mod = 1e9 + 7, _MAXN = 1e5;
int Qpow(int x, int y) {
int res = 1, base = x % mod;
while (y) {
if (y & 1) res = res * base % mod;
y >>= 1, base = base * base % mod;
}
return res;
}
int F[2], D[_MAXN + 5], R[2][_SIZE + 5], L[2][_SIZE + 5], S[2][_SIZE + 5];
int sum1[_SIZE + 5], sum2[_SIZE + 5];
int p, fac[_MAXN + 5], inv[_MAXN + 5];
int n, k, m, a, b;
int cur = 1, last = 0;
void init() {
fac[0] = 1; inv[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) fac[i] = fac[i - 1] * i % mod, inv[i] = Qpow(fac[i], mod - 2);
}
int C(int x, int y) {
return fac[x] * inv[y] % mod * inv[x - y] % mod;
}
void initD() {
for (int i = 0; i <= k; i++)
D[i] = C(k, i) * Qpow(p, i) % mod * Qpow(mod + 1 - p, k - i) % mod;
sum1[0] = D[0];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) sum1[i] = (sum1[i - 1] + D[i]) % mod;
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
cin >> a >> b; p = a * Qpow(b, mod - 2) % mod;
cin >> k;
init(); initD();
S[cur][m] = 1; F[cur] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
swap(cur, last);
sum2[0] = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= m + 1; j++) (sum2[j] = sum2[j - 1] + D[j - 1] * L[last][j] % mod) %= mod;
for (int r = 1; r <= m; r++) {
S[cur][r] = D[m - r] * (((F[last] - R[last][r] + mod) % mod * sum1[r - 1] % mod - sum2[r] + mod) % mod) % mod;
}
for (int j = 1; j <= m + 1; j++) (L[cur][j] = L[cur][j - 1] + S[cur][j - 1]) %= mod, R[cur][m - j + 1] = L[cur][j];
F[cur] = L[cur][m + 1];
}
cout << F[cur] << '\n';
return 0;
}





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步