使用lockbits方法处理图像(转)
锁定比特流
-
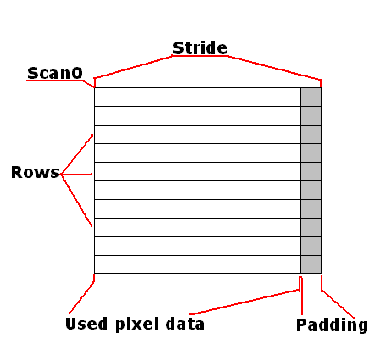
Scan0:数据矩阵在内存中的地址。
-
Stride:数据矩阵中的行宽,以byte为单位。可能会扩展几个Byte,后面会介绍。
-
PixelFormat:像素格式,这对矩阵中字节的定位很重要。
-
Width:位图的宽度。
-
Height:位图的高度。
指针的准确定位
-
32位RGB:假设X、Y为位图中像素的坐标,则其在内存中的地址为scan0+Y*stride+X*4。此时指针指向蓝色,其后分别是绿色、红色,alpha分量。
-
24位RGB:scan0+Y*stride+X*3。此时指针指向蓝色,其后分别是绿色和红色。
-
8位索引:scan0+Y*stride+X。当前指针指向图像的调色盘。
-
4位索引:scan0+Y*stride+(X/2)。当前指针所指的字节包括两个像素,通过高位和低位索引16色调色盘,其中高位表示左边的像素,低位表示右边的像素。
-
1位索引:scan0+Y*stride+X/8。当前指针所指的字节中的每一位都表示一个像素的索引颜色,调色盘为两色,最左边的像素为8,最右边的像素为0。
像素间使用迭代器
BitmapData bmd=bm.LockBits(new Rectangle(0, 0, 10, 10),
System.Drawing.Imaging.ImageLockMode.ReadOnly, bm.PixelFormat);
int PixelSize=4;
for(int y=0; y<bmd.Height; y++)
{
byte* row=(byte *)bmd.Scan0+(y*bmd.Stride);
for(int x=0; x<bmd.Width; x++)
{
row[x*PixelSize]=255;
}
}
int offset = (y * bmd.Stride) + (x >> 1);
bytecurrentByte = ((byte *)bmd.Scan0)[offset];
if((x&1)== 1)
{
currentByte&= 0xF0;
currentByte|= (byte)(colorIndex & 0x0F);
}
else
{
currentByte&= 0x0F;
currentByte|= (byte)(colorIndex << 4);
}
((byte*)bmd.Scan0)[offset]=currentByte;
byte* p=(byte*)bmd.Scan0.ToPointer();
intindex=y*bmd.Stride+(x>>3);
bytemask=(byte)(0x80>>(x&0x7));
if(pixel)
p[index]|=mask;
else
p[index]&=(byte)(mask^0xff);



