spring源码阅读(1)-- 容器启动之资源定位
在工作中,基本上所有的项目都需要用到spring,但本人至今一直没有深入研读spring的源码。鉴于此,本人决定对其展开深入研究,并将所思所想记录下来,若理解出现偏差,还望大家不吝赐教。
关于spring的基本使用,这里不便详细展开,关于阅读源码的方式方法,本人认为带着疑问通过debug阅读会更显轻松,亦更为容易达到“知其所以然”的目的。
本文要解决的问题是:spring是如何找到指定的配置文件的?
OK,首先搭建一个maven项目,pom配置如下。本系列文章使用的spring版本是4.3.2.RELEASE

<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.zksite</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-framework-test</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<spring.version>4.3.2.RELEASE </spring.version>
<slf4j.version>1.7.13</slf4j.version>
<logback.version>1.1.3</logback.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId> org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId> spring-context</artifactId>
<version> ${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId> org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId> spring-core</artifactId>
<version> ${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId> org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId> spring-beans</artifactId>
<version> ${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>${slf4j.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>jcl-over-slf4j</artifactId>
<version>${slf4j.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-core</artifactId>
<version>${logback.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>${logback.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
项目结构如下

spring-context-test.xml文件内容:

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="springtest" class="com.zksite.spring.test.SpringBeanTest" scope="singleton"/> </beans>
当项目中使用到了spring之后,我们需要在项目启动时启动spring容器,将需要的bean托管给spring管理。
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-context-test.xml");
SpringBeanTest springBeanTest = applicationContext.getBean(SpringBeanTest.class);
springBeanTest.sayHello();
}
这里使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext启动容器,ClassPathXmlApplicationContext是ApplicationContext其中的一个实现,spring提供了针对不同使用场景ApplicationContext实现如下
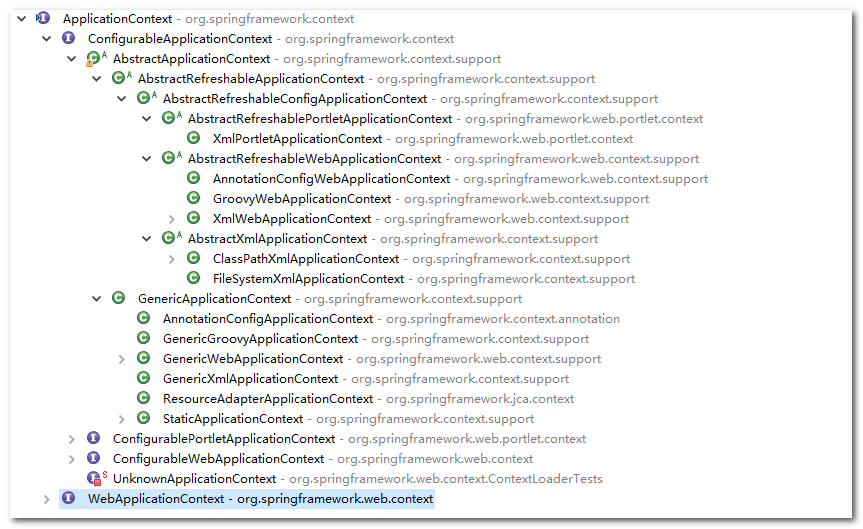
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:从classpath获取指定配置文件,可以使用通配符
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:通过指定文件,可以使用url指定配置文件
XmlWebApplicationContext:web环境时使用,通过web.xml指定配置文件由org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader或org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet启动,关于更多的实现可以参考spring doc
这里选用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext启动spring。本节主要目的深入spring对资源的定位,通过debug进入org.springframework.context.support.AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.refreshBeanFactory()方法。AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext只实现了refreshBeanFactory方法而且还是final的,说明spring规范了BeanFactory的刷新流程。
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();//创建bean工厂
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);//资源定位和加载BeanDefinition
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
这里首先判断当前上下文是否已经存在beanFactory,如果存在,首先销毁所有bean和关闭beanFactory,然后创建beanFactory然后进入loadBeanDefinitions方法。loadBeanDefinitions方法实现了资源的定位和创建BeanDefinition。loadBeanDefinitions方法源码如下
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException { // Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory. XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory); // Configure the bean definition reader with this context's // resource loading environment. beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment()); beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this); beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this)); // Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader, // then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions. initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader); loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader); }
因为当前使用的是xml配置spring,所以loadBeanDefinitions的实现由AbstractXmlApplicationContext提供。方法里分别做了以下处理:
1.通过指定的BeanDefinitionRegistry创建XmlBeanDefinitionReader实例
2.设置环境,用于在读取配置文件时使用
3.设置ResourceLoader,为接下来的定位资源做准备(ResourceLoader下面解释)
4.设置SAX解析器
5.加载BeanDefinition
XmlBeanDefinitionReader是BeanDefinitionReader的其中一个实现。BeanDefinitionReader抽象了将配置文件转化为BeanDefinition的过程,分别有:获取bean注册中心、获取资源加载器、获取ClassLoader、获取bean名称生成器、指定资源加载BeanDefinition、指定配置文件加载BeanDefinition

public interface BeanDefinitionReader { /** * 获取BeanDefinition注册中心 * Return the bean factory to register the bean definitions with. * <p>The factory is exposed through the BeanDefinitionRegistry interface, * encapsulating the methods that are relevant for bean definition handling. */ BeanDefinitionRegistry getRegistry(); /** * 获取资源加载器 * Return the resource loader to use for resource locations. * Can be checked for the <b>ResourcePatternResolver</b> interface and cast * accordingly, for loading multiple resources for a given resource pattern. * <p>Null suggests that absolute resource loading is not available * for this bean definition reader. * <p>This is mainly meant to be used for importing further resources * from within a bean definition resource, for example via the "import" * tag in XML bean definitions. It is recommended, however, to apply * such imports relative to the defining resource; only explicit full * resource locations will trigger absolute resource loading. * <p>There is also a {@code loadBeanDefinitions(String)} method available, * for loading bean definitions from a resource location (or location pattern). * This is a convenience to avoid explicit ResourceLoader handling. * @see #loadBeanDefinitions(String) * @see org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePatternResolver */ ResourceLoader getResourceLoader(); /** * 获取ClassLoader * Return the class loader to use for bean classes. * <p>{@code null} suggests to not load bean classes eagerly * but rather to just register bean definitions with class names, * with the corresponding Classes to be resolved later (or never). */ ClassLoader getBeanClassLoader(); /** * 获取bean名字生成器 * Return the BeanNameGenerator to use for anonymous beans * (without explicit bean name specified). */ BeanNameGenerator getBeanNameGenerator(); /** * 指定资源加载BeanDefinition * Load bean definitions from the specified resource. * @param resource the resource descriptor * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors */ int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException; /** * 指定多个资源加载BeanDefinition * Load bean definitions from the specified resources. * @param resources the resource descriptors * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors */ int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException; /** * 指定配置文件加载BeanDefinition * Load bean definitions from the specified resource location. * <p>The location can also be a location pattern, provided that the * ResourceLoader of this bean definition reader is a ResourcePatternResolver. * @param location the resource location, to be loaded with the ResourceLoader * (or ResourcePatternResolver) of this bean definition reader * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors * @see #getResourceLoader() * @see #loadBeanDefinitions(org.springframework.core.io.Resource) * @see #loadBeanDefinitions(org.springframework.core.io.Resource[]) */ int loadBeanDefinitions(String location) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException; /** * 指定多个配置文件加载BeanDefinition * Load bean definitions from the specified resource locations. * @param locations the resource locations, to be loaded with the ResourceLoader * (or ResourcePatternResolver) of this bean definition reader * @return the number of bean definitions found * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors */ int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException; }
通过BeanDefinitionReader里的方法定义看出接口依赖Resource和ResourceLoader这两个组件。spring将配置抽象为Resource,并针对不同使用场景提供了不同实现,Resource的实现如下
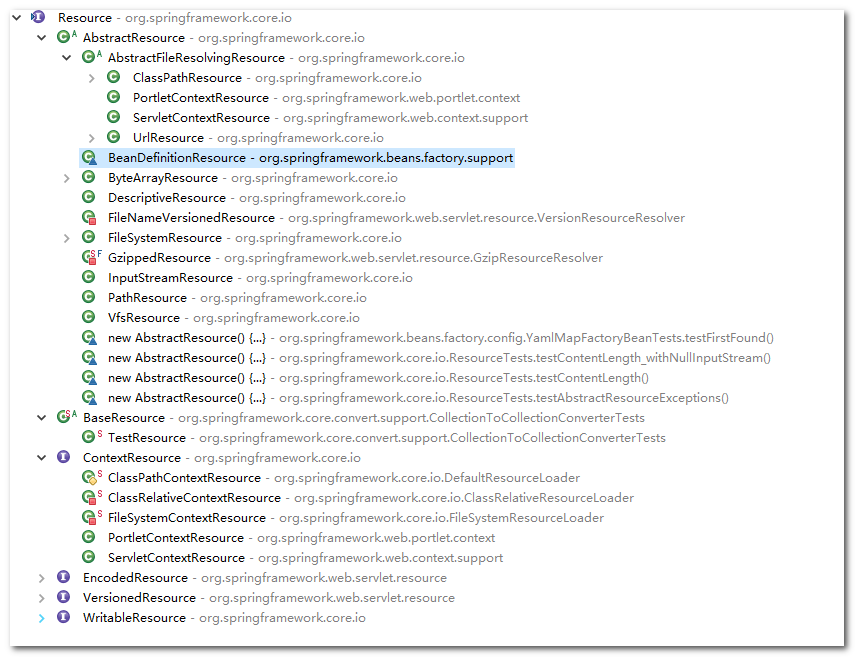
ClassPathResource:classpath路径资源,通过指定的ClassLoader加载资源
FileSystemResource:文件系统资源
UrlResource:URL资源
而另一个组件ResourceLoader负责资源的加载,ResourceLoader的实现如下

从结构可以发现,ClassPathXmlApplicationContext是ResourceLoader的其中一个实现,但ClassPathXmlApplicationContext并没有真正实现了怎么去加载一个资源,而是通过持有PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver实例,通过委派给PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver去加载资源,具体后面会介绍到,接着进入的loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader)方法
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException { Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources(); if (configResources != null) { reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources); } String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations(); if (configLocations != null) { reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations); } }
方法里首先调用getConfigResources(),这是一个预留给子类扩展的一个方法这方法,在ClassPathXmlApplicationContext是一个空实现(估计是因为ClassPathXmlApplicationContext不需要加载自定以的配置)。然后调用getConfigLocations()方法获取用户配置或默认配置,然后调用XmlBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions()方法进行BeanDefinition加载
然后一直debug执行到AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(String location, Set<Resource> actualResources)
1 public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, Set<Resource> actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 2 ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader(); 3 if (resourceLoader == null) { 4 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( 5 "Cannot import bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available"); 6 } 7 8 if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) { 9 // Resource pattern matching available. 10 try { 11 Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location); 12 int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resources); 13 if (actualResources != null) { 14 for (Resource resource : resources) { 15 actualResources.add(resource); 16 } 17 } 18 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 19 logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]"); 20 } 21 return loadCount; 22 } 23 catch (IOException ex) { 24 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( 25 "Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", ex); 26 } 27 } 28 else { 29 // Can only load single resources by absolute URL. 30 Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location); 31 int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resource); 32 if (actualResources != null) { 33 actualResources.add(resource); 34 } 35 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 36 logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location [" + location + "]"); 37 } 38 return loadCount; 39 } 40 }
方法里首先获取ResourceLoader,获取到的是刚才在new XmlBeanDefinitionReader时设置的ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(ClassPathXmlApplicationContext实现了ResourceLoader)。然后判断是否是一个ResourcePatternResolver实例(我们在使用spring时,当有多个配置文件时,是可以通过模糊匹配配置,例如当有如下配置文件时:spring-context-db.xml、spring-context-cache.xml,在设置配置文件路径时可以写成spring-context-*.xml),ApplicationContext接口继承了ResourcePatternResolver,所以这里直接进入到if里面,然后通过resourceLoader.getResources()方法,执行到这里,才开始资源的定位。代码如下:
1 public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException { 2 return this.resourcePatternResolver.getResources(locationPattern); 3 }
可以看到,最终获取资源是通过ClassPathXmlApplicationContex里的resourcePatternResolver去实现。resourcePatternResolver是PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver的一个实例,resourcePatternResolver的初始化是在创建ClassPathXmlApplicationContex是发生。进入PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver.getResources()方法:
1 public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException { 2 Assert.notNull(locationPattern, "Location pattern must not be null"); 3 if (locationPattern.startsWith(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX)) { 4 // a class path resource (multiple resources for same name possible) 5 if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()))) { 6 // a class path resource pattern 7 return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern); 8 } 9 else { 10 // all class path resources with the given name 11 return findAllClassPathResources(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length())); 12 } 13 } 14 else { 15 // Only look for a pattern after a prefix here 16 // (to not get fooled by a pattern symbol in a strange prefix). 17 int prefixEnd = locationPattern.indexOf(":") + 1; 18 if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(prefixEnd))) { 19 // a file pattern 20 return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern); 21 } 22 else { 23 // a single resource with the given name 24 return new Resource[] {getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)}; 25 } 26 } 27 }
方法里首先判断一下指定的配置文件路径是否是以“classpath*:”开头,如果不是再判断一下是否已“:”开头,如果这两者都不是,则调用DefaultResourceLoader提供的getResource()方法返回单个资源,里面的实现会根据指定的配置确定返回的是UrlResource或ClassPathContextResource。
如果指定的配置文件路径是以“classpath*:”或“:”开头,将使用 ant path匹配规则去匹配(Ant path匹配规则)。当配置文件路径为“classpath*:spring-context-*.xml”时,进去findPathMatchingResources(),在classpath模糊匹配多个资源。当配置文件为“classpath*:spring-context.xml”时,在classpath路径下获取单个文件。其实当配置文件是“classpath*:spring-context-*.xml”时,也会调用doFindAllClassPathResources方法,因为需要会找出classpath的所有文件包括jar,如果是jar包也会在jar包里面查找。
至此,已经加载完指定的所有资源,下面给出加载资源的时序图,从时序图可以看得出,资源的最终定位是由PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver实现。
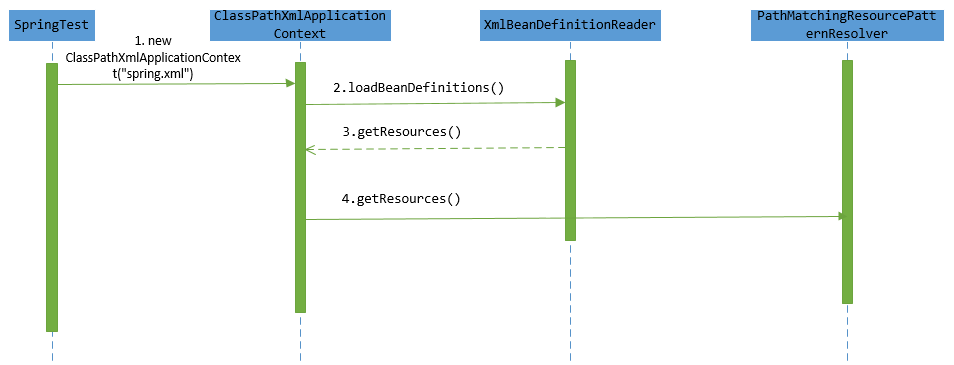
最后总结一下,spring容器启动时资源定位涉及到的组件:
Application:spring应用上下文
BeanDefinitionReader:负责从配置文件加载BeanDefinition
ResourceLoader:负责资源的加载



