八. 双向链表的增,删,改,查
由于单向链表只能从头遍历,那么在做增删改查操作时,必须从头结点开始遍历。特别是在尾节点做追加操作时,需要将所有节点全部遍历一遍。在时间上花费较多。但是双向链表就不存在这个问题,在对双向链表做追加操作时只需要对头结点的先序节点进行一次遍历就到达了链表的尾部。这样就大大的减少了时间上的开销。
以下是双向链表的结构示意图:
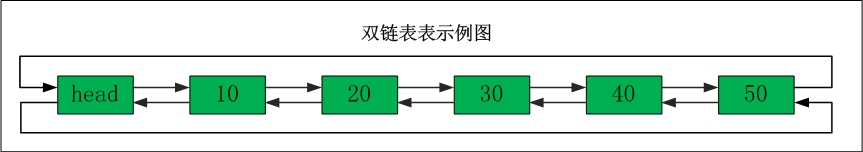
可以看出,每个节点都有两个指针,一个指向前面,一个指向后面。指向前面的叫先序节点,指向后面的叫后继结点。
我们通过这两个指针来访问所有节点,并通过他们来对链表进行操作。
双链表删除节点
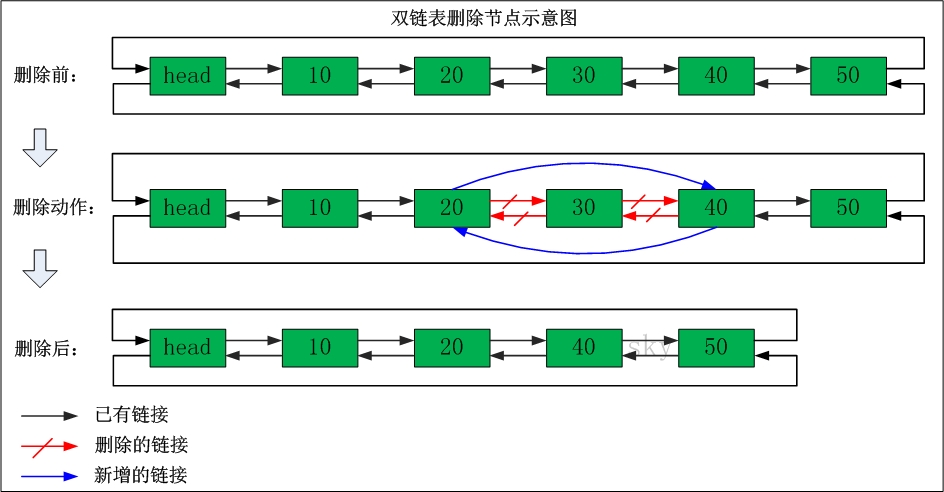
以下是对应代码:
void DeleteNode(Node *head,int num) //删除一个节点
{
int i = 0;
Node *temp = NULL;
for(i=0;i<num;i++)
{
head = head->next;
}
temp = head; //先暂存被删除节点
head->prior->next = head->next;
head->next->prior = head->prior;
free(temp);
printf("删除完毕\n");
}
双链表增加节点
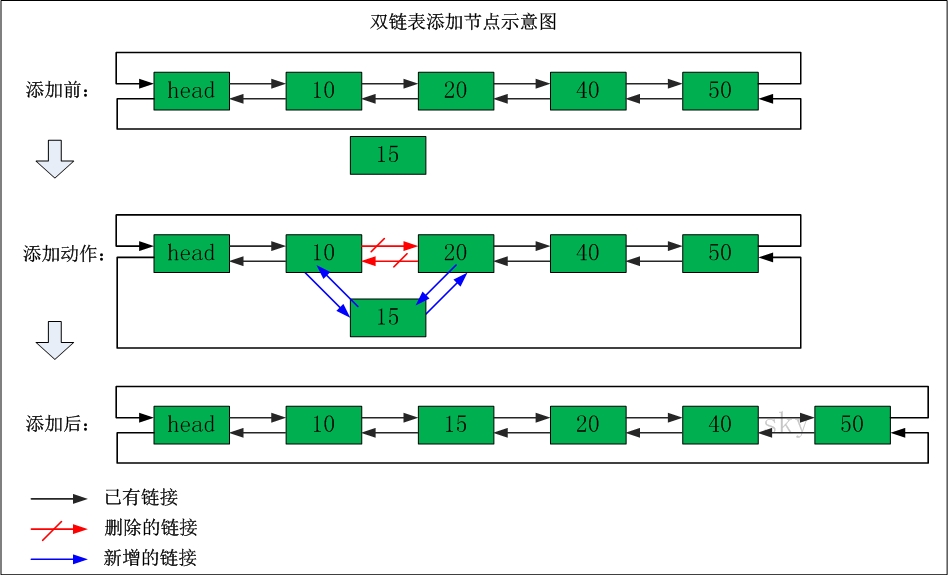
对应代码:
void InsertNode(Node *head,int num,int data) //在第num个数后面插入一个节点
{
int i= 0;
Node *temp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
Node *tp = head;
temp->data = data;
for(i=0;i<num&&(head->next!=tp);i++)
{
head = head->next;
}
temp->next = head->next;
temp->prior = head;
head->next->prior = temp;
head->next = temp;
printf("插入成功\n");
}
为便于测试,我在这里贴上所有代码,如下:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct ListNode
{
int data;
struct ListNode *prior; //前驱节点
struct ListNode *next; //后驱节点
}Node;
int AddNode(Node *head,int data) //在链表尾部增加一个节点
{
Node *temp = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
temp->data = data;
temp->next = head;
temp->prior = head->prior;
head->prior->next = temp;
head->prior = temp;
}
void PrintList(Node *head) //打印所有节点
{
Node *temp = head;
while (head->next!=temp) //判断链表是否到了尾部
{
head = head->next;
printf("%d ",head->data);
}
printf("\n");
}
void Reverse_PrintList(Node *head) //倒序打印所有节点
{
Node *temp = head;
while (head->prior!=temp) //判断链表是否到了头部
{
head = head->prior;
printf("%d ",head->data);
}
printf("\n");
}
void DeleteNode(Node *head,int num) //删除一个节点
{
int i = 0;
Node *temp = NULL;
for(i=0;i<num;i++)
{
head = head->next;
}
temp = head; //先暂存被删除节点
head->prior->next = head->next;
head->next->prior = head->prior;
free(temp);
printf("删除完毕\n");
}
void InsertNode(Node *head,int num,int data) //在第num个数后面插入一个节点
{
int i= 0;
Node *temp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
Node *tp = head;
temp->data = data;
for(i=0;i<num&&(head->next!=tp);i++)
{
head = head->next;
}
temp->next = head->next;
temp->prior = head;
head->next->prior = temp;
head->next = temp;
printf("插入成功\n");
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
int i = 0;
Node *head = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
head->prior = head;
head->next = head;
for (i=0;i<5;i++)
{
AddNode(head,i);
}
PrintList(head);
AddNode(head,99);
PrintList(head);
InsertNode(head,6,66);
PrintList(head);
InsertNode(head,3,33);
PrintList(head);
Reverse_PrintList(head);
//printf("Hello World!\r\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}


