MyBatis的深入原理-架构设计以及实例分析
MyBatis是目前非常流行的ORM框架,它的功能很强大,然而其实现却比较简单、优雅。本文主要讲述MyBatis的架构设计思路,并且讨论MyBatis的几个核心部件,然后结合一个select查询实例,深入代码,来探究MyBatis的实现。
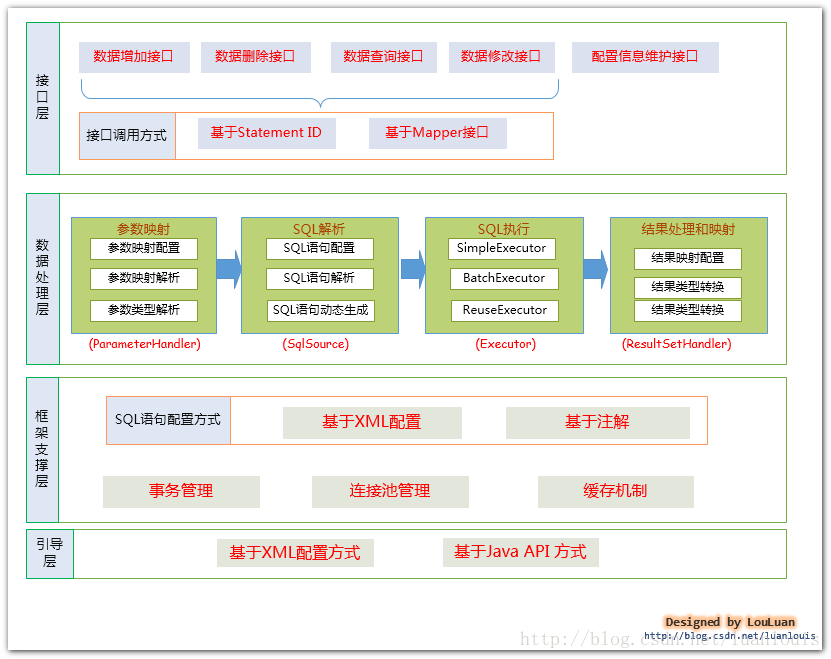
一、MyBatis的框架设计
注:上图很大程度上参考了iteye 上的chenjc_it 所写的博文原理分析之二:框架整体设计 中的MyBatis架构体图,chenjc_it总结的非常好,赞一个!
1.接口层---和数据库交互的方式
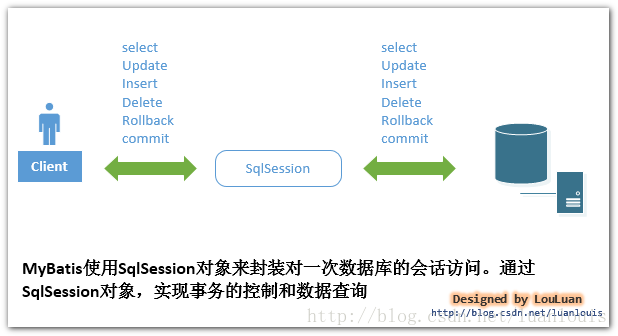
MyBatis和数据库的交互有两种方式:
a.使用传统的MyBatis提供的API;
b. 使用Mapper接口
1.1.使用传统的MyBatis提供的API
这是传统的传递Statement Id 和查询参数给 SqlSession 对象,使用 SqlSession对象完成和数据库的交互;MyBatis 提供了非常方便和简单的API,供用户实现对数据库的增删改查数据操作,以及对数据库连接信息和MyBatis 自身配置信息的维护操作。
上述使用MyBatis 的方法,是创建一个和数据库打交道的SqlSession对象,然后根据Statement Id 和参数来操作数据库,这种方式固然很简单和实用,但是它不符合面向对象语言的概念和面向接口编程的编程习惯。由于面向接口的编程是面向对象的大趋势,MyBatis 为了适应这一趋势,增加了第二种使用MyBatis 支持接口(Interface)调用方式。
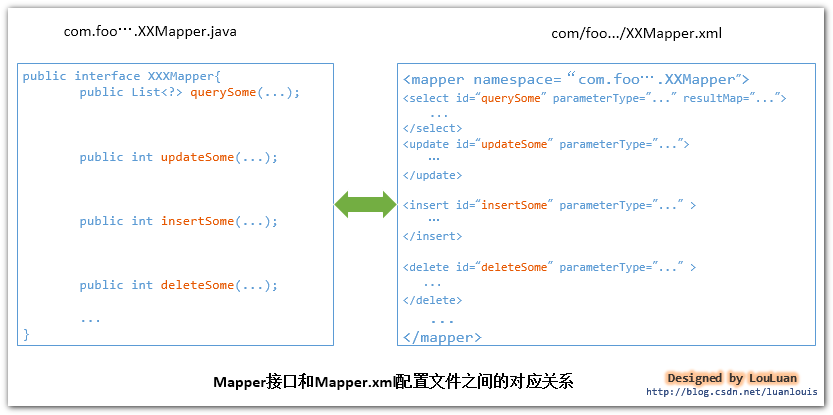
1.2. 使用Mapper接口
MyBatis 将配置文件中的每一个<mapper> 节点抽象为一个 Mapper 接口,而这个接口中声明的方法和跟<mapper> 节点中的<select|update|delete|insert> 节点项对应,即<select|update|delete|insert> 节点的id值为Mapper 接口中的方法名称,parameterType 值表示Mapper 对应方法的入参类型,而resultMap 值则对应了Mapper 接口表示的返回值类型或者返回结果集的元素类型。
根据MyBatis 的配置规范配置好后,通过SqlSession.getMapper(XXXMapper.class) 方法,MyBatis 会根据相应的接口声明的方法信息,通过动态代理机制生成一个Mapper 实例,我们使用Mapper 接口的某一个方法时,MyBatis 会根据这个方法的方法名和参数类型,确定Statement Id,底层还是通过SqlSession.select("statementId",parameterObject);或者SqlSession.update("statementId",parameterObject); 等等来实现对数据库的操作,(至于这里的动态机制是怎样实现的,我将准备专门一片文章来讨论,敬请关注~)
MyBatis 引用Mapper 接口这种调用方式,纯粹是为了满足面向接口编程的需要。(其实还有一个原因是在于,面向接口的编程,使得用户在接口上可以使用注解来配置SQL语句,这样就可以脱离XML配置文件,实现“0配置”)。
2.数据处理层
数据处理层可以说是MyBatis 的核心,从大的方面上讲,它要完成三个功能:
a. 通过传入参数构建动态SQL语句;
b. SQL语句的执行以及封装查询结果集成List<E>2.1.参数映射和动态SQL语句生成
动态语句生成可以说是MyBatis框架非常优雅的一个设计,MyBatis 通过传入的参数值,使用 Ognl 来动态地构造SQL语句,使得MyBatis 有很强的灵活性和扩展性。
参数映射指的是对于java 数据类型和jdbc数据类型之间的转换:这里有包括两个过程:查询阶段,我们要将java类型的数据,转换成jdbc类型的数据,通过 preparedStatement.setXXX() 来设值;另一个就是对resultset查询结果集的jdbcType 数据转换成java 数据类型。
(至于具体的MyBatis是如何动态构建SQL语句的,我将准备专门一篇文章来讨论,敬请关注~)
2.2. SQL语句的执行以及封装查询结果集成List<E>
动态SQL语句生成之后,MyBatis 将执行SQL语句,并将可能返回的结果集转换成List<E> 列表。MyBatis 在对结果集的处理中,支持结果集关系一对多和多对一的转换,并且有两种支持方式,一种为嵌套查询语句的查询,还有一种是嵌套结果集的查询。
3. 框架支撑层
3.1. 事务管理机制
事务管理机制对于ORM框架而言是不可缺少的一部分,事务管理机制的质量也是考量一个ORM框架是否优秀的一个标准,对于数据管理机制我已经在我的博文《深入理解mybatis原理》 MyBatis事务管理机制 中有非常详细的讨论,感兴趣的读者可以点击查看。
3.2. 连接池管理机制
由于创建一个数据库连接所占用的资源比较大, 对于数据吞吐量大和访问量非常大的应用而言,连接池的设计就显得非常重要,对于连接池管理机制我已经在我的博文《深入理解mybatis原理》 Mybatis数据源与连接池 中有非常详细的讨论,感兴趣的读者可以点击查看。
3.3. 缓存机制
为了提高数据利用率和减小服务器和数据库的压力,MyBatis 会对于一些查询提供会话级别的数据缓存,会将对某一次查询,放置到SqlSession中,在允许的时间间隔内,对于完全相同的查询,MyBatis 会直接将缓存结果返回给用户,而不用再到数据库中查找。(至于具体的MyBatis缓存机制,我将准备专门一篇文章来讨论,敬请关注~)
3. 4. SQL语句的配置方式
传统的MyBatis 配置SQL 语句方式就是使用XML文件进行配置的,但是这种方式不能很好地支持面向接口编程的理念,为了支持面向接口的编程,MyBatis 引入了Mapper接口的概念,面向接口的引入,对使用注解来配置SQL 语句成为可能,用户只需要在接口上添加必要的注解即可,不用再去配置XML文件了,但是,目前的MyBatis 只是对注解配置SQL 语句提供了有限的支持,某些高级功能还是要依赖XML配置文件配置SQL 语句。
4 引导层
引导层是配置和启动MyBatis 配置信息的方式。MyBatis 提供两种方式来引导MyBatis :基于XML配置文件的方式和基于Java API 的方式,读者可以参考我的另一片博文:Java Persistence with MyBatis 3(中文版) 第二章 引导MyBatis
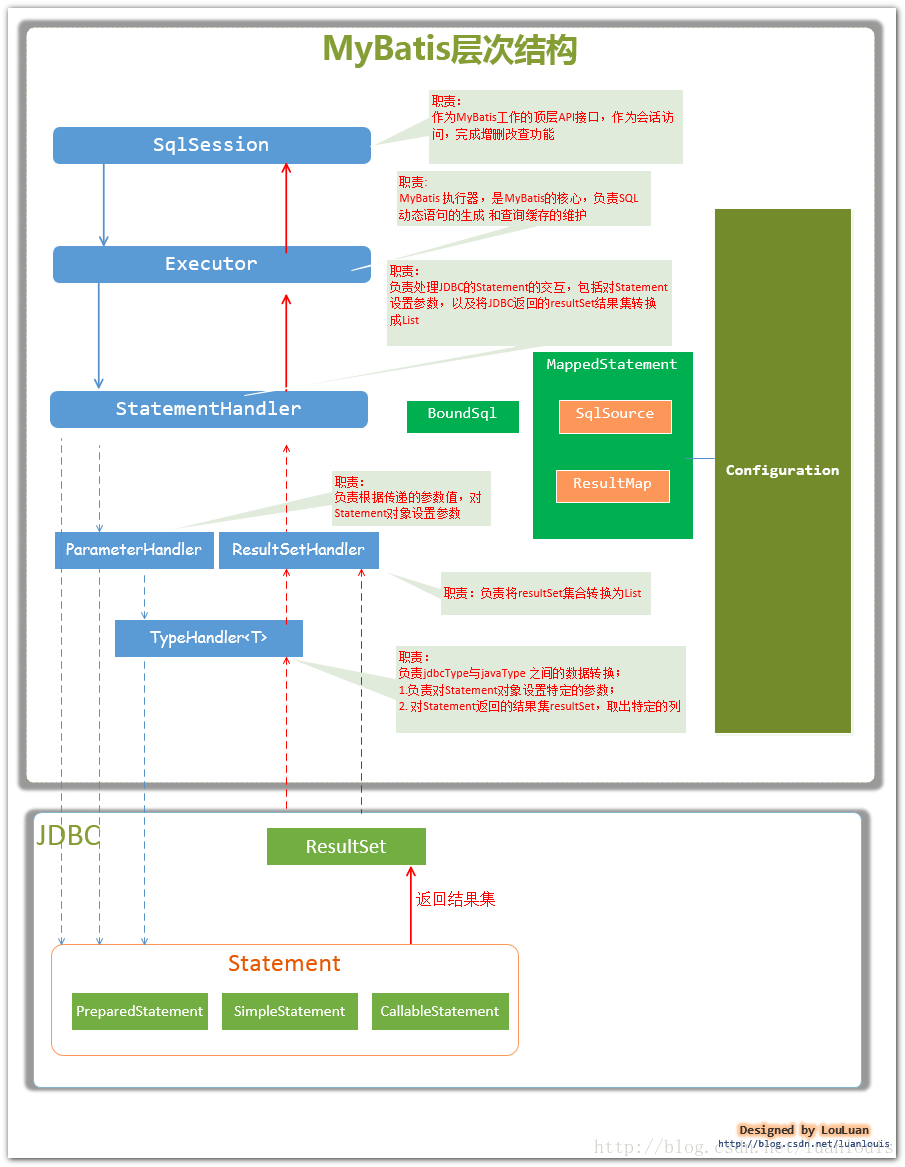
二、MyBatis的主要构件及其相互关系
从MyBatis代码实现的角度来看,MyBatis的主要的核心部件有以下几个:
- SqlSession 作为MyBatis工作的主要顶层API,表示和数据库交互的会话,完成必要数据库增删改查功能
- Executor MyBatis执行器,是MyBatis 调度的核心,负责SQL语句的生成和查询缓存的维护
- StatementHandler 封装了JDBC Statement操作,负责对JDBC statement 的操作,如设置参数、将Statement结果集转换成List集合。
- ParameterHandler 负责对用户传递的参数转换成JDBC Statement 所需要的参数,
- ResultSetHandler 负责将JDBC返回的ResultSet结果集对象转换成List类型的集合;
- TypeHandler 负责java数据类型和jdbc数据类型之间的映射和转换
- MappedStatement MappedStatement维护了一条<select|update|delete|insert>节点的封装,
- SqlSource 负责根据用户传递的parameterObject,动态地生成SQL语句,将信息封装到BoundSql对象中,并返回
- BoundSql 表示动态生成的SQL语句以及相应的参数信息
- Configuration MyBatis所有的配置信息都维持在Configuration对象之中。
(注:这里只是列出了我个人认为属于核心的部件,请读者不要先入为主,认为MyBatis就只有这些部件哦!每个人对MyBatis的理解不同,分析出的结果自然会有所不同,欢迎读者提出质疑和不同的意见,我们共同探讨~)
它们的关系如下图所示:
三、从MyBatis一次select 查询语句来分析MyBatis的架构设计
一、数据准备(非常熟悉和应用过MyBatis 的读者可以迅速浏览此节即可)
1. 准备数据库数据,创建EMPLOYEES表,插入数据:
2. 配置Mybatis的配置文件,命名为teaboymybatis.xml:
3. 创建Employee实体Bean 以及配置Mapper配置文件EmployeesMapper.xml
4. 创建eclipse 或者myeclipse 的maven项目,maven配置如下:
5. 客户端代码:
package mybatisTest; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; import com.teaboy.model.Employee; /** * * (查询) * * <p> * 修改历史: <br> * 修改日期 修改人员 版本 修改内容<br> * -------------------------------------------------<br> * 2016年9月26日 下午12:11:15 user 1.0 初始化创建<br> * </p> * * @author Peng.Li * @version 1.0 * @since JDK1.7 */ public class SelectDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //1.加载mybatis配置文件,初始化mybatis,创建SqlSessionFactory的工厂 InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("conf/core/teaboymybatis.xml"); SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(); SqlSessionFactory factory = builder.build(inputStream); //2.从SqlSession工厂SqlSessionFactory中创建一个SqlSession,进行数据库操作 SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession(); //3.使用sqlSession进行查询 Map<String, Object>condMap = new HashMap<String, Object>(); condMap.put("min_salary", 10000); //selectList方法参数 statement == mapper (namespace.id) == Employee.selectByMinSalary List<Employee> elEmployees = sqlSession.selectList("Employee.selectByMinSalary", condMap); System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(elEmployees)); } }
二、SqlSession 的工作过程分析:
1. 开启一个数据库访问会话---创建SqlSession对象:
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
DefaultSqlSessionFactory的openSession方法如下:
public SqlSession openSession() {
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
跟进去看DefaultSqlSessionFactory类中的openSessionFromDataSource方法:
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
//读取配置文件teaboymybatis.xml,通过configuration获取xml配置文件的环境信息
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
//根据环境信息获取环境信息中的TransactionFactory,这里teaboymybatis.xml配置里面transactionManager type="JDBC",所以获取到的TransactionFactory为JdbcTransactionFactory
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
//通过TransactionFactory工厂根据PooledDataSource,隔离级别,创建一个Transaction事务,这里的Transaction为JdbcTransaction
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
//通过Configuration创建Executor
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType, autoCommit);
//创建DefaultSqlSession
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
跟进去看getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment方法:获取TransactionFactory
private TransactionFactory getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(Environment environment) {
//这一步不会走
if (environment == null || environment.getTransactionFactory() == null) {
return new ManagedTransactionFactory();
}
//根据环境配置获取到的TransactionFactory为JdbcTransactionFactory
return environment.getTransactionFactory();
}
跟进去看JdbcTransactionFactory类中的newTransaction方法:
package org.apache.ibatis.transaction.jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.TransactionIsolationLevel;
import org.apache.ibatis.transaction.Transaction;
import org.apache.ibatis.transaction.TransactionFactory;
/**
* Creates {@link JdbcTransaction} instances.
*
* @see JdbcTransaction
*/
public class JdbcTransactionFactory implements TransactionFactory {
public void setProperties(Properties props) {
}
public Transaction newTransaction(Connection conn) {
return new JdbcTransaction(conn);
}
//走的是这一步,根据数据源,隔离级别,是否自动提交,得到一个JdbcTransaction,这个地方使用工厂方法设计模式
public Transaction newTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
return new JdbcTransaction(ds, level, autoCommit); } }
跟进去看Configuration里面的newExecutor方法:
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType, boolean autoCommit) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
//1.判断执行器excutor的类型,如果配置里面没有配置的话,默认的是ExecutorType.SIMPLE
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
//返回BatchExecutor的执行器
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
//返回reuseExecutor
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
//返回SimpleExecutor
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
//返回CathingExecutor
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor, autoCommit);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
这里走SimpleExecutor类,通过父类BaseExecutor的构造方法构造一个SimpleExecutor,源码如下:
/*
* Copyright 2009-2012 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.ibatis.executor;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.ibatis.executor.statement.StatementHandler;
import org.apache.ibatis.logging.Log;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.BoundSql;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.ResultHandler;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.RowBounds;
import org.apache.ibatis.transaction.Transaction;
public class SimpleExecutor extends BaseExecutor {
public SimpleExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) {
//父类初始化SimpleExecutor执行器,根据Configuration和Transaction以及prepretualCathe等对象
super(configuration, transaction);
}
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.update(stmt);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
public List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) throws SQLException {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
stmt = handler.prepare(connection);
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
}
然后代码执行executor = new CachingExecutor(executor, autoCommit);方法,通过父类BaseExecutor的构造方法构造一个SimpleExecutor,源码如下:
/*
* Copyright 2009-2012 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.ibatis.executor;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache;
import org.apache.ibatis.cache.CacheKey;
import org.apache.ibatis.cache.TransactionalCacheManager;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.BoundSql;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.ParameterMapping;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.ParameterMode;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.StatementType;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.MetaObject;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.ResultHandler;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.RowBounds;
import org.apache.ibatis.transaction.Transaction;
public class CachingExecutor implements Executor {
private Executor delegate;
private boolean autoCommit; // issue #573. No need to call commit() on autoCommit sessions
private TransactionalCacheManager tcm = new TransactionalCacheManager();
private boolean dirty;
public CachingExecutor(Executor delegate) {
this(delegate, false);
}
//走这一步
public CachingExecutor(Executor delegate, boolean autoCommit) {
this.delegate = delegate;
this.autoCommit = autoCommit;
}
public Transaction getTransaction() {
return delegate.getTransaction();
}
public void close(boolean forceRollback) {
try {
//issue #499. Unresolved session handling
//issue #573. Autocommit sessions should commit
if (dirty && !autoCommit) {
tcm.rollback();
} else {
tcm.commit();
}
} finally {
delegate.close(forceRollback);
}
}
public boolean isClosed() {
return delegate.isClosed();
}
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject) throws SQLException {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
return delegate.update(ms, parameterObject);
}
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, parameterObject, boundSql);
if (!dirty) {
//获取读写锁的读锁,ReadWriteLock的使用
cache.getReadWriteLock().readLock().lock();
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> cachedList = (List<E>) cache.getObject(key);
if (cachedList != null) return cachedList;
} finally {
cache.getReadWriteLock().readLock().unlock();
}
}
List<E> list = delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578. Query must be not synchronized to prevent deadlocks
return list;
}
}
return delegate.<E>query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
public List<BatchResult> flushStatements() throws SQLException {
return delegate.flushStatements();
}
public void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException {
delegate.commit(required);
tcm.commit();
dirty = false;
}
public void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException {
try {
delegate.rollback(required);
dirty = false;
} finally {
if (required) {
tcm.rollback();
}
}
}
private void ensureNoOutParams(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, BoundSql boundSql) {
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
for (ParameterMapping parameterMapping : boundSql.getParameterMappings()) {
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.IN) {
throw new ExecutorException("Caching stored procedures with OUT params is not supported. Please configure useCache=false in " + ms.getId() + " statement.");
}
}
}
}
public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) {
return delegate.createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
}
public boolean isCached(MappedStatement ms, CacheKey key) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("The CachingExecutor should not be used by result loaders and thus isCached() should never be called.");
}
public void deferLoad(MappedStatement ms, MetaObject resultObject, String property, CacheKey key, Class<?> targetType) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("The CachingExecutor should not be used by result loaders and thus deferLoad() should never be called.");
}
public void clearLocalCache() {
delegate.clearLocalCache();
}
private void flushCacheIfRequired(MappedStatement ms) {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
dirty = true; // issue #524. Disable using cached data for this session
tcm.clear(cache);
}
}
}
从上面的代码可以看出,创建Transaction事务,一次配置加载有且对应一个数据源。最后通过下面构造方法拿到DefaultSqlSession,sqlSession
public DefaultSqlSession(Configuration configuration, Executor executor) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.executor = executor;
this.dirty = false;
}
在看看DefaultSqlSession到底干了什么事情? MyBatis封装了对数据库的访问,把对数据库的会话和事务控制放到了SqlSession对象中。
2. 为SqlSession传递一个配置的Sql语句 的Statement Id和参数,然后返回结果:
//3.使用sqlSession进行查询 Map<String, Object>condMap = new HashMap<String, Object>(); condMap.put("min_salary", 6000); //selectList方法参数 statement == mapper (namespace.id) == Employee.selectByMinSalary List<Employee> elEmployees = sqlSession.selectList("Employee.selectByMinSalary", condMap);上述的"Employee.selectByMinSalary",是配置在EmployeesMapper.xml 的Statement ID,params 是传递的查询参数。
让我们来看一下sqlSession.selectList()方法的定义:
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter) { return this.selectList(statement, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT); } public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) { try { MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement); List<E> result = executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER); return result; } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
MyBatis在初始化的时候,会将MyBatis的配置信息全部加载到内存中,使用org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration实例来维护。使用者可以使用sqlSession.getConfiguration()方法来获取。MyBatis的配置文件中配置信息的组织格式和内存中对象的组织格式几乎完全对应的。上述例子中的
<!-- 查询工资低于 min_salary的员工 --> <select id="selectByMinSalary" resultMap="BaseResultMap" parameterType="java.util.Map"> select <include refid='BASE_COLUMN_LIST' /> from <include refid='TABLE_NAME' /> t <where> <if test="min_salary != null"> t.SALARY < #{min_salary,jdbcType=VARCHAR} </if> </where> </select>加载到内存中会生成一个对应的MappedStatement对象,然后会以key="Employee.selectByMinSalary",
value为MappedStatement对象的形式维护到Configuration的一个Map中。当以后需要使用的时候,只需要通过Id值来获取就可以了。从上述的代码中我们可以看到SqlSession的职能是:
SqlSession根据Statement ID, 在mybatis配置对象Configuration中获取到对应的MappedStatement对象,然后调用mybatis执行器来执行具体的操作。
3.MyBatis执行器Executor根据SqlSession传递的参数执行query()方法(由于代码过长,读者只需阅读我注释的地方即可):
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException { //1.根据具体传入的参数,动态的生成执行的SQL语句,用BoundSql对象表示
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
//2.为当前查询创建一个缓存key CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId()); if (closed) throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed."); if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) { clearLocalCache(); } List<E> list; try { queryStack++; list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null; if (list != null) { handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql); } else {
//3.查询缓存中没有值,直接从数据库中读取数据 list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); } } finally { queryStack--; } if (queryStack == 0) { for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) { deferredLoad.load(); } deferredLoads.clear(); // issue #601 if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) { clearLocalCache(); // issue #482 } } return list; }进入BaseExecutor 的queryFromDatabase方法:
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { List<E> list; localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER); try {
//4.执行查询,返回List查询结果 list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); } finally { localCache.removeObject(key); }
//5将查询结果放入缓存中 localCache.putObject(key, list); if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) { localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter); } return list; }然后进入SimpleExecutor的doQuery方法:
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; try {
//5.获取Configuration配置信息 Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
//6.通过配置对象获取一个新的StatementHandler,该类主要用来处理一次sql操作 StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); //7.预处理StatementHandler对象,得到Statement对象
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
//8.调用StatementHandler.query()方法,返回List结果 return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler); } finally { closeStatement(stmt); } }进入 StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);看下newStatementHandler到底干了些什么事情?
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { //9.根据相关参数获取对应的StatementHandler对象
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); //10.为StatementHandler对象绑定拦截器插件,可以自定义拦截器实现Interceptor拦截器,比如实现分页拦截器,在prepare执行前,通过动态代理的方式
//在执行invoke方法的时候,调用intercept方法对BoundSql进行处理,设置分页信息,从而实现分页查询。
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);return statementHandler; }进入RoutingStatementHandler类看下构造方法:
public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { switch (ms.getStatementType()) { case STATEMENT: delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); break; case PREPARED: delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); break; case CALLABLE: delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); break; default: throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType()); } }根据MappedStatement对象的StatementType来创建不同的StatementHandler,这个跟前面的执行器类似。StatementType有STATEMENT、PREPARED和CALLABLE三种类型,跟JDBC里面的Statement类型一一对应。
进入InterceptorChain类的pluginAll类看下方法:
public Object pluginAll(Object target) { for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
//调用拦截器接口的Plugin方法 target = interceptor.plugin(target); } return target; }下面是自己实现了一个分页拦截器如下:
package com.teaboy.dao.pagination; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Properties; import org.apache.ibatis.executor.ErrorContext; import org.apache.ibatis.executor.ExecutorException; import org.apache.ibatis.executor.statement.BaseStatementHandler; import org.apache.ibatis.executor.statement.RoutingStatementHandler; import org.apache.ibatis.executor.statement.StatementHandler; import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.BoundSql; import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement; import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.ParameterMapping; import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.ParameterMode; import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Interceptor; import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Intercepts; import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Invocation; import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Plugin; import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Signature; import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.MetaObject; import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.property.PropertyTokenizer; import org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.ForEachSqlNode; import org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration; import org.apache.ibatis.type.TypeHandler; import org.apache.ibatis.type.TypeHandlerRegistry; import com.teaboy.dao.pagination.dialect.Dialect; import com.teaboy.util.ReflectHelper; /** * Mybatis分页拦截器 * * @Title:PaginationInterceptor.java * * @Description:MyBatis分页拦截器 * * @author zhaoyang * @date Jan 17, 2014 10:05:02 AM * @version V1.0 */ @Intercepts({ @Signature(type = StatementHandler.class, method = "prepare", args = { Connection.class }) }) public class PaginationInterceptor implements Interceptor { //dialect private Dialect dialect = null; //分页查询拦截 private String paginationSqlRegEx = ".*ByCond"; /** * 连接 * override intercept * <p>Title: intercept</p> * <p>Description: </p> * @param invocation * @return * @throws Throwable */ public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable { //statement handler if (invocation.getTarget() instanceof RoutingStatementHandler) { RoutingStatementHandler statementHandler = (RoutingStatementHandler) invocation.getTarget(); BaseStatementHandler delegate = (BaseStatementHandler) ReflectHelper.getValueByFieldName(statementHandler, "delegate"); MappedStatement mappedStatement = (MappedStatement) ReflectHelper.getValueByFieldName(delegate, "mappedStatement"); //statement是否符合模式,检查是符合正则表达式以ByCond结尾 if (mappedStatement.getId().matches(paginationSqlRegEx)) { //获取sql BoundSql boundSql = delegate.getBoundSql(); String sql = boundSql.getSql(); sql = sql.replaceAll("\\s{1,}", " "); Object parameterObject = boundSql.getParameterObject(); if (parameterObject != null) { PaginationInfo paginationInfo = null; if (parameterObject instanceof Map<?, ?>) { paginationInfo = (PaginationInfo) ((Map<?, ?>) parameterObject).get("paginationInfo"); } else { Field pageField = ReflectHelper.getFieldByFieldName(parameterObject, "paginationInfo"); if (pageField != null) { paginationInfo = (PaginationInfo) ReflectHelper.getValueByFieldName(parameterObject, "paginationInfo"); } } if (paginationInfo != null) { int count = 0; Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement countStmt = null; ResultSet rs = null; try { connection = (Connection) invocation.getArgs()[0]; String countSql = this.dialect.getCountString(sql); countStmt = connection.prepareStatement(countSql); setParameters(countStmt, mappedStatement, boundSql, parameterObject); rs = countStmt.executeQuery(); if (rs.next()) { count = rs.getInt(1); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { rs.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { countStmt.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (parameterObject instanceof Map<?, ?>) { paginationInfo = (PaginationInfo) ((Map<?, ?>) parameterObject).get("paginationInfo"); if (paginationInfo == null) { paginationInfo = new PaginationInfo(1, count); } } else { Field pageField = ReflectHelper.getFieldByFieldName(parameterObject, "paginationInfo"); if (pageField != null) { paginationInfo = (PaginationInfo) ReflectHelper.getValueByFieldName(parameterObject, "paginationInfo"); if (paginationInfo == null) { paginationInfo = new PaginationInfo(); } ReflectHelper.setValueByFieldName(parameterObject, "paginationInfo", paginationInfo); } else { throw new NoSuchFieldException(parameterObject.getClass().getName() + "不存在 PaginationInfo 属性"); } } paginationInfo.setTotalRecord(count); paginationInfo.setTotalPage(((count - 1) / paginationInfo.getRecordPerPage()) + 1); String paginationSql = this.dialect.getLimitString(sql, paginationInfo.getOffset(), paginationInfo.getLimit()); //System.out.println("pagination sql : " + paginationSql); ReflectHelper.setValueByFieldName(boundSql, "sql", paginationSql); } } } } return invocation.proceed(); } /** * 设置查询param * setParameters * @Title: setParameters * @Description: TODO * @param ps * @param mappedStatement * @param boundSql * @param parameterObject * @throws SQLException */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps, MappedStatement mappedStatement, BoundSql boundSql, Object parameterObject) throws SQLException { ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId()); List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings(); if (parameterMappings != null) { Configuration configuration = mappedStatement.getConfiguration(); TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry(); MetaObject metaObject = parameterObject == null ? null : configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject); for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) { ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i); if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) { Object value; String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty(); PropertyTokenizer prop = new PropertyTokenizer(propertyName); if (parameterObject == null) { value = null; } else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) { value = parameterObject; } else if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName); } else if (propertyName.startsWith(ForEachSqlNode.ITEM_PREFIX) && boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(prop.getName())) { value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(prop.getName()); if (value != null) { value = configuration.newMetaObject(value).getValue( propertyName.substring(prop.getName().length())); } } else { value = metaObject == null ? null : metaObject.getValue(propertyName); } @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler(); if (typeHandler == null) { throw new ExecutorException("There was no TypeHandler found for parameter " + propertyName + " of statement " + mappedStatement.getId()); } typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, parameterMapping.getJdbcType()); } } } } /** * 设置plugin * override plugin * <p>Title: plugin</p> * <p>Description: </p> * @param arg0 * @return */ public Object plugin(Object arg0) { return Plugin.wrap(arg0, this); } /** * 设置属性 * override setProperties * <p>Title: setProperties</p> * <p>Description: </p> * @param p */ public void setProperties(Properties p) { } /** * 获得dialect * getDialect * @Title: getDialect * @Description: TODO * @return */ public Dialect getDialect() { return dialect; } /** * * setDialect * @Title: setDialect * @Description: TODO * @param dialect */ public void setDialect(Dialect dialect) { this.dialect = dialect; } /** * * getPaginationSqlRegEx * @Title: getPaginationSqlRegEx * @Description: TODO * @return */ public String getPaginationSqlRegEx() { return paginationSqlRegEx; } /** * * setPaginationSqlRegEx * @Title: setPaginationSqlRegEx * @Description: TODO * @param paginationSqlRegEx */ public void setPaginationSqlRegEx(String paginationSqlRegEx) { this.paginationSqlRegEx = paginationSqlRegEx; } }接着上面的plugin方法,然后进入Plugin类,可以看到是JDK动态代理实现的类,里面的wrap方式生成一个代理对象的方法,通过目标对象taget=PreparedStatementHandler以及上面黄色部分的注解StatementHandler 接口动态的生成代理对象。然后在执行invoke方法的时候,再次检测
黄色部分注解信息中的method = "prepare"方法,如果存在要拦截的方法,则执行PaginationInterceptor中的intercept方法做拦截处理,加上分页条件等。然后才执行prepare方法。
/* * Copyright 2009-2012 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.apache.ibatis.plugin; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ExceptionUtil; public class Plugin implements InvocationHandler { private Object target; private Interceptor interceptor; private Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap; private Plugin(Object target, Interceptor interceptor, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) { this.target = target; this.interceptor = interceptor; this.signatureMap = signatureMap; } //动态的生成代理对象,通过目标对象 public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) { Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor); Class<?> type = target.getClass(); Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap); if (interfaces.length > 0) { return Proxy.newProxyInstance( type.getClassLoader(), interfaces, new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap)); } return target; } //每次调用目标类中的方法,必须要经过的invoke方法 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { try { Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass()); if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) { return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args)); } return method.invoke(target, args); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e); } } private static Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> getSignatureMap(Interceptor interceptor) { Intercepts interceptsAnnotation = interceptor.getClass().getAnnotation(Intercepts.class); if (interceptsAnnotation == null) { // issue #251 throw new PluginException("No @Intercepts annotation was found in interceptor " + interceptor.getClass().getName()); } Signature[] sigs = interceptsAnnotation.value(); Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = new HashMap<Class<?>, Set<Method>>(); for (Signature sig : sigs) { Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(sig.type()); if (methods == null) { methods = new HashSet<Method>(); signatureMap.put(sig.type(), methods); } try { Method method = sig.type().getMethod(sig.method(), sig.args()); methods.add(method); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { throw new PluginException("Could not find method on " + sig.type() + " named " + sig.method() + ". Cause: " + e, e); } } return signatureMap; } private static Class<?>[] getAllInterfaces(Class<?> type, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) { Set<Class<?>> interfaces = new HashSet<Class<?>>(); while (type != null) { for (Class<?> c : type.getInterfaces()) { if (signatureMap.containsKey(c)) { interfaces.add(c); } } type = type.getSuperclass(); } return interfaces.toArray(new Class<?>[interfaces.size()]); } }
拦截器接口如下:
package org.apache.ibatis.plugin; import java.util.Properties; public interface Interceptor { Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable; Object plugin(Object target); void setProperties(Properties properties); }上述的Executor.query()方法几经转折,最后会创建一个StatementHandler对象,然后将必要的参数传递给StatementHandler,使用StatementHandler来完成对数据库的查询,最终返回List结果集。
从上面的代码中我们可以看出,Executor的功能和作用是:
(1、根据传递的参数,完成SQL语句的动态解析,生成BoundSql对象,供StatementHandler使用;
(2、为查询创建缓存,以提高性能;
(3、创建JDBC的Statement连接对象,传递给StatementHandler对象,返回List查询结果。
4. StatementHandler对象负责设置Statement对象中的查询参数、处理JDBC返回的resultSet,将resultSet加工为List 集合返回:
接着上面的Executor第六步,看一下:prepareStatement() 方法的实现:
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException { Statement stmt; Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog); stmt = handler.prepare(connection); handler.parameterize(stmt); return stmt; }
以上我们可以总结StatementHandler对象主要完成两个工作:
(1. 对于JDBC的PreparedStatement类型的对象,创建的过程中,我们使用的是SQL语句字符串会包含 若干个? 占位符,我们其后再对占位符进行设值。
StatementHandler通过parameterize(statement)方法对Statement进行设值;
(2.StatementHandler通过List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler)方法来完成执行Statement,和将Statement对象返回的resultSet封装成List;
5. PreparedStatementHandler的parameterize(statement) 方法的实现:
public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
//使用ParameterHandler对象来完成对Statement的?占位符的赋值
parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement);} public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException { ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId()); List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings(); if (parameterMappings != null) { MetaObject metaObject = parameterObject == null ? null : configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject); for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) { ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i); if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) { Object value; String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty(); if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { // issue #448 ask first for additional params value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName); } else if (parameterObject == null) { value = null; } else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) { value = parameterObject; } else { value = metaObject == null ? null : metaObject.getValue(propertyName); }
//每个mapping都有一个typeHandler TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler(); JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType(); if (value == null && jdbcType == null) jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull(); typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType); } } } }从上述的代码可以看到,StatementHandler 的parameterize(Statement) 方法调用了 ParameterHandler的setParameters(statement) 方法,
ParameterHandler的setParameters(Statement)方法负责 根据我们输入的参数,对statement对象的 ? 占位符处进行赋值。
6. StatementHandler 的List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler)方法的实现:
//PreparedStatementHandler中的query方法实现public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
//1.调用preparedStatemnt excute方法,然后将resultSet交给ResultSetHandler处理 PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement; ps.execute();
//2.使用ResultHandler来处理ResultSet return resultSetHandler.<E> handleResultSets(ps); }
//ResultSetHandler类的HandleResultSets方法实现
public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException { final List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList<Object>(); int resultSetCount = 0; ResultSetWrapper rsw = getFirstResultSet(stmt); List<ResultMap> resultMaps = mappedStatement.getResultMaps(); int resultMapCount = resultMaps.size(); validateResultMapsCount(rsw, resultMapCount); while (rsw != null && resultMapCount > resultSetCount) { ResultMap resultMap = resultMaps.get(resultSetCount); handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, null); rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt); cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet(); resultSetCount++; } while (rsw != null && resultSetCount < mappedStatement.getResulSets().length) { ResultMapping parentMapping = nextResultMaps.get(mappedStatement.getResulSets()[resultSetCount]); if (parentMapping != null) { String nestedResultMapId = parentMapping.getNestedResultMapId(); ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(nestedResultMapId); handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, null, parentMapping); } rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt); cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet(); resultSetCount++; } return collapseSingleResultList(multipleResults); }从上述代码我们可以看出,StatementHandler 的List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler)方法的实现,是调用了ResultSetHandler的handleResultSets(Statement) 方法。ResultSetHandler的handleResultSets(Statement) 方法会将Statement语句执行后生成的resultSet 结果集转换成List<E> 结果集。

 注:上图很大程度上参考了iteye 上的
注:上图很大程度上参考了iteye 上的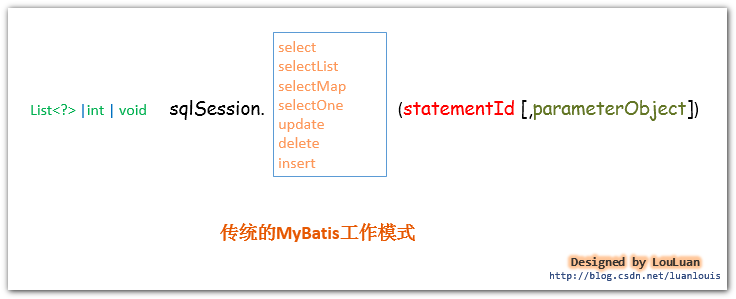


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号