「号爸十一集训 Day 10.1」 CF 六题题解合集
Codeforces 1272F Two Bracket Sequences
解题报告
一个听他们说好像很“套路”的做法。可惜我不会。
设 f[i][j][k] = {i', j', k'} 表示匹配了 S 的前 i 位,T 的前 j 位,有 k 个多余的左括号没有匹配,需要的括号最少是多少,这个状态下次要往哪里转移(因为要输出方案)
于是跑个 BFS 求出 f[n][m][0] 然后倒推回去就行了。这个过程中每一步都是最优解,因此实际上并不需要记录状态的值。
代码实现
还是要多练习输出方案的题目。
const int MAXN = 200 + 10;
int n, m;
char s[MAXN], t[MAXN]; std::string ans;
struct Node { int i, j, k; };
Node dp[MAXN][MAXN][MAXN * 2];
// 匹配了 s 的前 i 位,t 的前 j 位,多出 k 个左括号
// 上一个状态是从哪转移的
void bfs() {
std::queue<Node> q;
memset(dp, -1, sizeof dp); dp[0][0][0] = {0, 0, 0};
q.push({0, 0, 0});
while (!q.empty()) {
Node now = q.front(); q.pop();
int nxi = now.i + (s[now.i + 1] == '(');
int nxj = now.j + (t[now.j + 1] == '(');
int nxk = now.k + 1;
if (nxk <= n + m && dp[nxi][nxj][nxk].i == -1) {
dp[nxi][nxj][nxk] = now;
q.push({nxi, nxj, nxk});
}
nxi = now.i + (s[now.i + 1] == ')');
nxj = now.j + (t[now.j + 1] == ')');
nxk = now.k - 1;
if (nxk >= 0 && dp[nxi][nxj][nxk].i == -1) {
dp[nxi][nxj][nxk] = now;
q.push({nxi, nxj, nxk});
}
}
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin >> (s + 1) >> (t + 1); n = (int) strlen(s + 1); m = (int) strlen(t + 1);
bfs();
int si = n, sj = m, sk = 0;
while (si || sj || sk) {
Node last = dp[si][sj][sk];
if (last.k < sk) ans = '(' + ans;
else ans = ')' + ans;
si = last.i, sj = last.j, sk = last.k;
} cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
Codeforces 1579F Array Stabilization (AND version)
解题报告
观察到对于每一个 \(a_i\),它将变成 \(a_i \text{ and } a_{i - d} \text{ and } a_{i - 2d} \text{ and } a_{i - 3d} \dots\)
所以这个过程是成了一个环的,按数组下标 \(\bmod m\) 每个剩余系里的下标是一个环。
一个数要几次才能变成 \(0\),就是它在环里走几步才会遇到 \(0\)。如果遇不到 \(0\) 就说明一定会剩下一个 \(1\)。
代码实现
代码是反着写的,也就是先找 \(0\) 然后用 \(0\) 去更新其他的数。
const int MAXN = 1e6 + 10;
int n, d;
int aa[MAXN];
int SolveCircle(int p) {
int ans = 0;
while (true) {
p = (p + d) % n;
if (aa[p] == 0) break;
aa[p] = 0; ++ans;
} return ans;
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int T; cin >> T;
while (T --> 0) {
cin >> n >> d;
rep (i, 0, n - 1) cin >> aa[i];
int ans = 0;
rep (i, 0, n - 1) {
if (aa[i] == 0) ans = std::max(ans, SolveCircle(i)); // 循环模拟
}
bool flg = false; rep (i, 0, n - 1) {
if (aa[i]) flg = true; // 1 环
}
if (flg) cout << "-1" << endl;
else cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Codeforces 1579G Minimal Coverage
解题报告
分享一个非常智慧的做法,从 tutorial 评论区看到的
发现答案长度越大,留给这堆线段施展的空间就越大,也就是答案更容易合法。于是考虑二分答案 \(t\)。
如何 check?
当时想了半天如何贪心,总是想不出正确的策略,遂放弃。
但是贪心 check 的本质还是逐条插入线段,验证每条线段的结尾端点能否落到这个长度为 \(t\) 的区间里。
于是我们考虑直接维护这个东西!!
设 \(01\) 数组 \(b_{j, i}\) 表示考虑前 \(j\) 条线段,第 \(i\) 个位置能(\(1\))否(\(0\))成为第 \(j\) 条线段结尾位置;换句话说,第 \(i\) 个位置能否成为第 \(j + 1\) 条线段开始位置。
考虑新加入一条线段长度为 \(d\),对所有(答案不会越界的)位置 \(i\),它能成为结尾当且仅当位置 \(i \pm d\) 至少有一个能成为开头,也就是:
当前的答案满足条件意味着 \(b_{n}\) 至少有一个位置为 \(1\)。
快速维护这个 \(01\) 数组可以通过 std::bitset 实现。可以直接滚动数组把第一维优化掉。
代码实现
注释写的英文是因为我同时在用 Dev-C++ 和 VSCode,为了防止编码混乱才写成英文的。
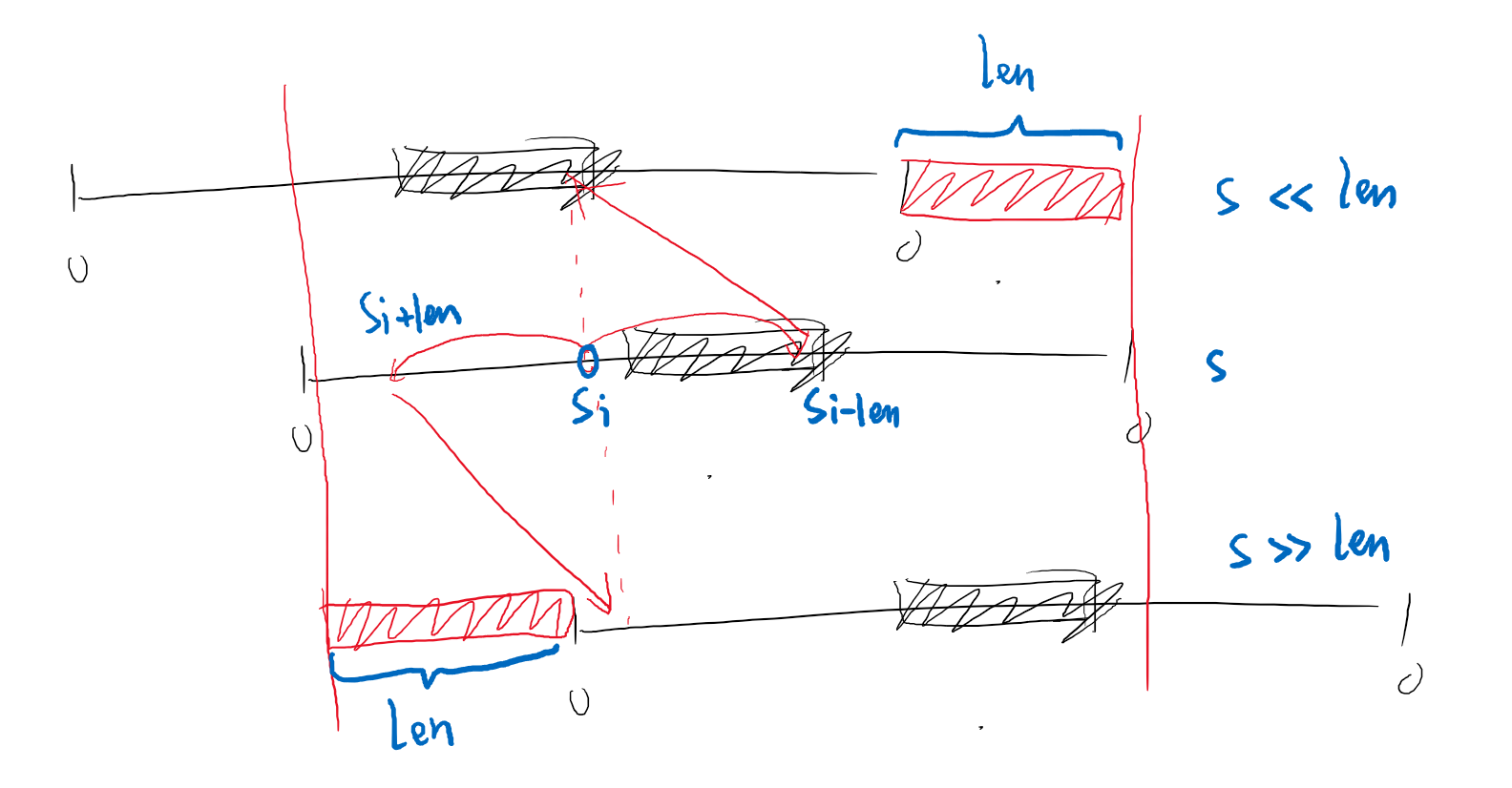
关于那个神奇的式子可以参考下图(线是 1,实心块是 0):
const int MAXN = 10000 + 10;
int n, aa[MAXN];
std::bitset<MAXN> s, t;
// (after j loops) s[i] means (after considering the first j segs)
// whether the jth seg's end can be placed on pos i
// in other words, (before the (j + 1)th loop) s[i] means (after considering the first j segs)
// whether it's possible to place the (j + 1)th seg's start on pos i
// jth seg's end can be placed on pos i if and only if its start can be placed on pos (i - len) or (i + len)
// that is, forall i, new_s[i] = s[i - len] | s[i + len]
bool check(int mid) {
s = 0; t = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= std::min(mid, MAXN - 1); ++i) t.set(i);
s = t;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
s = ((s >> aa[i]) | (s << aa[i])) & t;
// this magic thing equals to:
// for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
// new_s[j] = s[j - aa[i]] | s[j + aa[i]];
// }
} return s.count();
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int T; cin >> T;
while (T --> 0) {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) cin >> aa[i];
int l = 1, r = 2e7, ans = 0;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (check(mid)) r = mid - 1, ans = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
} cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Codeforces 1256F Equalizing Two Strings
解题报告
首先如果字母构成不一样一定 -NO.
发现一个性质:如果一个字符串里有连续相同的字母,那么通过不断交换两个相邻的相同字母,我们可以实现对另一个字符串的任意修改。
接下来考虑字母没有重复的情况。仍然是考虑交换两个相邻字母,此时问题类似于冒泡排序(怎么哪都有你)。
这两个字符串能变换成相同字符串的充要条件是:逆序对奇偶性相同。
考虑都把它们排成递增,需要的次数就是逆序对数。如果一个多一个少,那么少的那个可以通过不断地交换最后两个字母来平衡一下。
根据鸽巢原理字符串长度一定不超过 \(26\)。直接暴力求逆序对即可。
代码实现
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10;
std::string ss, tt;
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int T; cin >> T;
while (T --> 0) {
int n; cin >> n;
cin >> ss >> tt;
int cnt[26], cnt2[26];
memset(cnt, 0, sizeof cnt);
memset(cnt2, 0, sizeof cnt2);
int flg = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
++cnt[ss[i] - 'a']; ++cnt2[tt[i] - 'a'];
}
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) {
if (cnt[i] != cnt2[i]) { flg = 1; break; }
if (cnt[i] >= 2 || cnt2[i] >= 2) { flg = 2; }
}
if (flg == 1) { cout << "NO" << endl; continue; }
else if (flg == 2) { cout << "YES" << endl; continue; }
int invp[2] = {0, 0};
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
invp[0] += (ss[i] > ss[j]);
invp[1] += (tt[i] > tt[j]);
}
}
if ((invp[0] & 1) != (invp[1] & 1)) cout << "NO" << endl;
else cout << "YES" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Codeforces 1077F2 Pictures with Kittens (hard version)
解题报告
设状态 f[i][j] 表示前 \(i\) 张图选了 \(j\) 张的最大美观度。
转移是三维的,需要枚举上一次选的哪张图片,取最大的美观度,还要保证两张图距离不超过 \(k\)。
那这实际上就是一个滑动窗口求最大值,搞个单调队列优化一下就可以了。
代码实现
各种 DP 优化都要熟练掌握。
const int MAXN = 5000 + 10;
#define int lli
int n, k, x;
int aa[MAXN];
int dp[MAXN][MAXN];
std::deque<int> mq[MAXN];
signed main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> k >> x;
rep (i, 1, n) cin >> aa[i];
memset(dp, -0x3f, sizeof dp);
dp[0][0] = 0; mq[0].push_back(0);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = x; j >= 1; --j) {
while (!mq[j - 1].empty() && mq[j - 1].front() < i - k) mq[j - 1].pop_front();
if (!mq[j - 1].empty()) {
dp[i][j] = std::max(dp[i][j], dp[mq[j - 1].front()][j - 1] + aa[i]);
while (!mq[j].empty() && dp[mq[j].back()][j] <= dp[i][j]) mq[j].pop_back();
mq[j].push_back(i);
}
}
} int ans = -1;
for (int i = n - k + 1; i <= n; ++i) ans = std::max(ans, dp[i][x]);
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
Codeforces 1256E Yet Another Division Into Teams
解题报告
首先显然是按从小到大顺序选最优。于是先排个序。
设 f[i] 表示前 \(i\) 个学生组队完的最小极差和。
转移需要从 \(1\) 开始枚举上一组是在哪截止的,取最小的那一个记录方案。
于是直接套一个前缀最小值优化。
代码实现
写的有亿点点长。主要还是输出方案不熟练。
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10;
struct T { lli val, id; } ts[MAXN];
bool cmp1(T x, T y) { return x.val < y.val; }
bool cmp2(T x, T y) { return x.id < y.id; }
int n; lli aa[MAXN];
lli dp[MAXN], prefdp[MAXN];
int last[MAXN], last_pref[MAXN];
// last[i] 记录的是 f[i] 从哪转移过来
// last_pref[i] 记录的是 prefdp[i] 在 dp 数组中的下标
void getDetail() {
/* DEBUG */
int r = n;
int now = n;
std::vector<std::pair<int, int> > ans;
while (now) {
now = last[now];
ans.push_back({now + 1, r});
r = now;
}
std::reverse(ALL(ans)); int teams = 0;
for (auto v : ans) {
++teams;
for (int i = v.first; i <= v.second; ++i) ts[i].val = teams;
} cout << ' ' << teams << endl;
std::sort(ts + 1, ts + 1 + n, cmp2);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) cout << ts[i].val << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { cin >> ts[i].val; ts[i].id = i; }
std::sort(ts + 1, ts + 1 + n, cmp1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
aa[i] = ts[i].val;
}
memset(dp, 0x3f, sizeof dp); memset(prefdp, 0x3f, sizeof prefdp);
dp[3] = aa[3] - aa[1]; prefdp[3] = dp[3] - aa[4];
last[3] = 0; last_pref[3] = 3;
for (int i = 4; i <= n; ++i) {
// dp[i] = std::min(dp[i - 1] - aa[i - 1], prefdp[i - 3]) + aa[i];
// prefdp[i] = std::min(prefdp[i - 1], dp[i] - aa[i + 1]);
if (dp[i - 1] - aa[i - 1] < prefdp[i - 3]) {
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] - aa[i - 1];
last[i] = last[i - 1];
} else {
dp[i] = prefdp[i - 3];
last[i] = last_pref[i - 3];
} dp[i] += aa[i];
if (prefdp[i - 1] < dp[i] - aa[i + 1]) {
prefdp[i] = prefdp[i - 1];
last_pref[i] = last_pref[i - 1];
} else {
prefdp[i] = dp[i] - aa[i + 1];
last_pref[i] = i;
}
} cout << dp[n];
getDetail();
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号