洛谷P1886《滑动窗口》
原更新时间:2018-10-04 19:00:47
单调队列的应用
题目描述
现在有一堆数字共N个数字(N<=10^6),以及一个大小为k的窗口。现在这个从左边开始向右滑动,每次滑动一个单位,求出每次滑动后窗口中的最大值和最小值。
例如:
The array is [1 3 -1 -3 5 3 6 7], and k = 3.
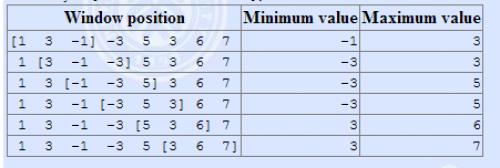
第二行为n个数(\(n<2^{31}-1\)).
输出格式
输出共两行,第一行为每次窗口滑动的最小值
第二行为每次窗口滑动的最大值
输入样例
8 3
1 3 -1 -3 5 3 6 7
输出样例
-1 -3 -3 -3 3 3
3 3 5 5 6 7
数据范围
50%的数据,n<=10^5
100%的数据,n<=10^6
解题思路
最经典的单调队列题目
暴力妥妥的T,不用多说(不过居然有70pts)
我们先研究最大值怎么求
每次往单调队列里面扔一个数,显然不管队列里发生了什么改变,单调性并不变。
我们开一个id数组,记录当前的数被push进去的时间
接着扫描id数组,将所有过期的数全都pop出去
最后当循环了至少k次时,输出答案。
最小值同理,把单调队列改一下即可。
(《单调队列学习笔记》将不久后更新)
代码实现
/* -- Basic Headers -- */
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cctype>
#include <algorithm>
/* -- STL Iterator -- */
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
/* -- Defined Functions -- */
#define For(a,x,y) for (int a = x; a <= y; ++a)
#define Bak(a,y,x) for (int a = y; a >= x; --a)
using namespace std;
namespace FastIO {
void DEBUG(char comment[], int x) {
cerr << comment << x << endl;
}
inline int getint() {
int s = 0, x = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while (!isdigit(ch)) {
if (ch == '-') x = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(ch)) {
s = s * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return s * x;
}
inline void __basic_putint(int x) {
if (x < 0) {
x = -x;
putchar('-');
}
if (x >= 10) __basic_putint(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
inline void putint(int x, char external) {
__basic_putint(x);
putchar(external);
}
}
namespace Solution {
const int MAXN = 1000000 + 10;
struct Queue {
int q[MAXN];
int head, tail;
Queue() {
memset(q, 0, sizeof(q));
head = 1;
tail = 0;
}
void push(int s) {
// 维护单调递增的队列
while (s >= q[tail] && head <= tail) --tail;
q[++tail] = s;
}
void push_back(int s) {
// 维护单调递减的序列
while (s <= q[tail] && head <= tail) --tail;
q[++tail] = s;
}
void pop() {
++head;
}
int front() {
return q[head];
}
int size() {
return tail - head + 1;
}
bool empty() {
return tail - head + 1;
}
void clear() {
Queue();
}
int __tail_location() {
return tail;
}
int __head_location() {
return head;
}
} q1, q2;
int n, k;
int seq[MAXN];
int id[MAXN];
void GetMax() {
For (i, 1, n) {
q1.push(seq[i]);
id[q1.__tail_location()] = i;
while (id[q1.__head_location()] <= i - k) q1.pop(); // 清理过期的数
if (i >= k) FastIO::putint(q1.front(), ' '); // 输出
}
}
void GetMin() {
For (i, 1, n) {
q2.push_back(seq[i]);
id[q2.__tail_location()] = i;
while (id[q2.__head_location()] <= i - k) q2.pop();
if (i >= k) FastIO::putint(q2.front(), ' ');
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char *const argv[]) {
#ifdef HANDWER_FILE
freopen("testdata.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("testdata.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
using namespace Solution;
using namespace FastIO;
n = getint();
k = getint();
For (i, 1, n) {
seq[i] = getint();
}
GetMin();
puts("");
GetMax();
return 0;
}


