负载均衡-加权轮询算法
1. 背景
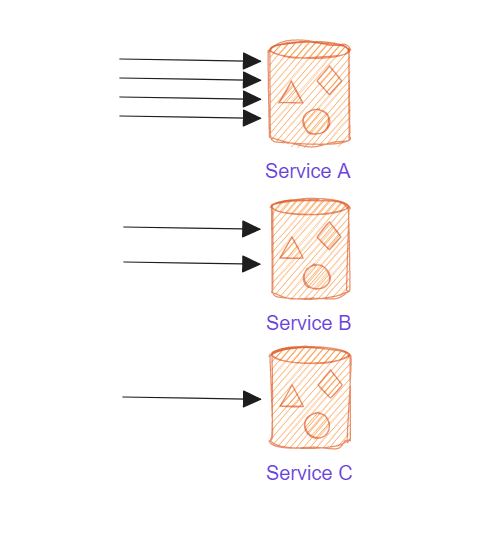
A项目部署在三台机器,A机器(4c2g)、B机器(2c2g)、C机器(1c2g)

如何才让请求聪明地分发在三台机器?
2. 负载均衡分类
- 基于硬件的负载均衡:比如
F5等专门的负载均衡设备,通常具有更强大的性能和功能,能够处理大规模的流量和应用需求。 - 基于软件的负载均衡:比如
Nginx、HAProxy等,这些软件可以通过安装在普通服务器上来实现负载均衡,通常有一定的性能和功能限制,但是适合中小规模的应用负载均衡需求。 DNS负载均衡:通过DNS服务器根据域名解析返回不同的IP地址,从而将请求分发到不同的服务器上,实现负载均衡。LVS(Linux Virtual Server)也可以归类为这一类,它是一种基于Linux内核的负载均衡方案,可以通过网络地址转换(NAT)、直接路由(DR)、IP隧道(TUN)等方式实现负载均衡。
3. 加权轮询算法
3.1 原始加权轮询算法
算法思想
- 轮询所有节点,寻找权重最大节点
- 选中节点,然后将权重减1
- 当所有节点权重都为0时,重置权重

这样的算法存在一个问题:机器A权重为4,那么前2个请求一定会打在机器A上面,造成权重大的机器压力过大,权重小的机器C一直在空闲(我能力小,不代表我一个请求都不能处理),假如权重为{A:10,B:1,C:1}会放大这一现象。
3.2 优化后加权轮询算法
算法思想
- 计算
totalWeight - 开始时计算全部节点的
currentWeight = currentWeight + weight - 选中
currentWeight最大的节点,并设置currentWeight = currentWeight - totalWeight
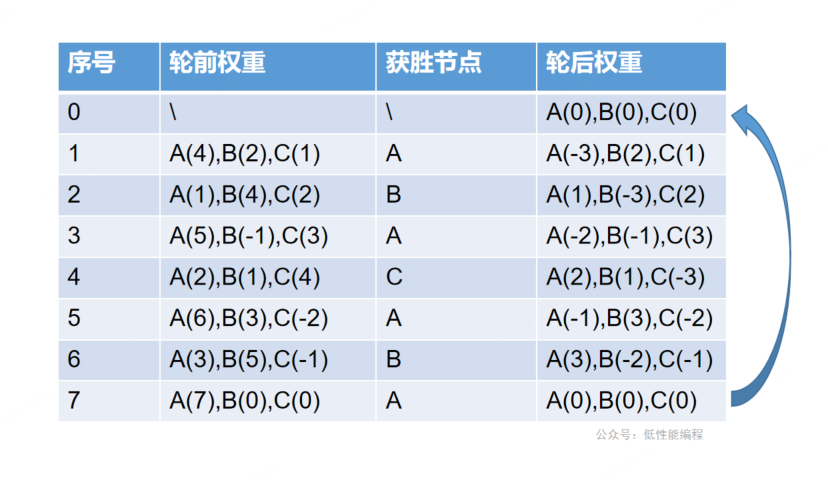
看到这里,你可能疑惑为什么
currentWeight会有一个轮回,应该有一个数学论证,但是我不会。
/**
* @author: handsometaoa
* @description
* @date: 2023/12/19 15:03
*/
@Setter
@Getter
@ToString
public class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
// 服务器IP
private String ip;
// 固定权重
private int weight;
// 当前权重
private int currentWeight;
public Node(String ip, int weight) {
this.ip = ip;
this.weight = weight;
this.currentWeight = 0;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node node) {
return this.getCurrentWeight() - node.getCurrentWeight();
}
}
/**
* @author: handsometaoa
* @description
* @date: 2023/12/19 15:03
*/
public class WeightedRoundRobin {
private static List<Node> serverList;
WeightedRoundRobin(List<Node> serverList) {
WeightedRoundRobin.serverList = serverList;
}
private String select() {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(serverList)) {
throw new RuntimeException("service node is empty");
}
int totalWeight = 0;
for (Node node : serverList) {
totalWeight = totalWeight + node.getWeight();
node.setCurrentWeight(node.getCurrentWeight() + node.getWeight());
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(serverList.toArray()));
Node currentWeightMaxNode = Collections.max(serverList);
currentWeightMaxNode.setCurrentWeight(currentWeightMaxNode.getCurrentWeight() - totalWeight);
return currentWeightMaxNode.getIp();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
Node node1 = new Node("192.168.0.1", 4);
Node node2 = new Node("192.168.0.2", 2);
Node node3 = new Node("192.168.0.3", 1);
List<Node> serverList = Arrays.asList(node1, node2, node3);
WeightedRoundRobin weightedRoundRobin = new WeightedRoundRobin(serverList);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
String select = weightedRoundRobin.select();
map.put(select, map.getOrDefault(select, 0) + 1);
}
System.out.println(map);
}
}
4. Dubbo中的算法

Dubbo 对服务端方法配置负载均衡策略:
<dubbo:service interface="…">
<dubbo:method name="…" loadbalance="roundrobin"/>
</dubbo:service>
Dubbo 用了 Nginx 平滑的加权轮询算法,代码版本:3.2
public class RoundRobinLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
public static final String NAME = "roundrobin";
private static final int RECYCLE_PERIOD = 60000;
// 不同的服务(方法),拥有不同权重,使用map进行存储
private ConcurrentMap<String, ConcurrentMap<String, WeightedRoundRobin>> methodWeightMap = new ConcurrentHashMap();
public RoundRobinLoadBalance() {
}
protected <T> Collection<String> getInvokerAddrList(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, Invocation invocation) {
String key = ((Invoker)invokers.get(0)).getUrl().getServiceKey() + "." + invocation.getMethodName();
Map<String, WeightedRoundRobin> map = (Map)this.methodWeightMap.get(key);
return map != null ? map.keySet() : null;
}
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
// interface路径+方法名称,可达方法级负载均衡
String key = ((Invoker)invokers.get(0)).getUrl().getServiceKey() + "." + invocation.getMethodName();
// 不存在则创建一个 ConcurrentHashMap,map 保存当前key 的所有节点信息
ConcurrentMap<String, WeightedRoundRobin> map = (ConcurrentMap)this.methodWeightMap.computeIfAbsent(key, (k) -> {
return new ConcurrentHashMap();
});
int totalWeight = 0;
long maxCurrent = Long.MIN_VALUE;
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
Invoker<T> selectedInvoker = null;
WeightedRoundRobin selectedWRR = null;
int weight;
for(Iterator var13 = invokers.iterator(); var13.hasNext(); totalWeight += weight) {
Invoker<T> invoker = (Invoker)var13.next();
String identifyString = invoker.getUrl().toIdentityString();
weight = this.getWeight(invoker, invocation);
// 将节点信息,加入map
WeightedRoundRobin weightedRoundRobin = (WeightedRoundRobin)map.computeIfAbsent(identifyString, (k) -> {
WeightedRoundRobin wrr = new WeightedRoundRobin();
wrr.setWeight(weight);
return wrr;
});
// 如果某节点权重更新了,则更新map缓存中权重。
if (weight != weightedRoundRobin.getWeight()) {
weightedRoundRobin.setWeight(weight);
}
// 节点当前权重等于 current + weight
long cur = weightedRoundRobin.increaseCurrent();
weightedRoundRobin.setLastUpdate(now);
if (cur > maxCurrent) {
maxCurrent = cur;
selectedInvoker = invoker;
selectedWRR = weightedRoundRobin;
}
}
// 删除距上次活跃时长 超过60000毫秒的节点
if (invokers.size() != map.size()) {
map.entrySet().removeIf((item) -> {
return now - ((WeightedRoundRobin)item.getValue()).getLastUpdate() > 60000L;
});
}
if (selectedInvoker != null) {
// current = current - totalWeight
selectedWRR.sel(totalWeight);
return selectedInvoker;
} else {
return (Invoker)invokers.get(0);
}
}
protected static class WeightedRoundRobin {
private int weight;
private AtomicLong current = new AtomicLong(0L);
private long lastUpdate;
protected WeightedRoundRobin() {
}
public int getWeight() {
return this.weight;
}
public void setWeight(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
this.current.set(0L);
}
// current + weight
public long increaseCurrent() {
return this.current.addAndGet((long)this.weight);
}
// current - total
public void sel(int total) {
this.current.addAndGet((long)(-1 * total));
}
public long getLastUpdate() {
return this.lastUpdate;
}
public void setLastUpdate(long lastUpdate) {
this.lastUpdate = lastUpdate;
}
}
}
5. 总结
通过上述学习,我们对加权轮询算法有了一个浅略的认识,后续我们便可以应用于实际的开发场景,如客服分配等。
本文来自博客园,作者:帅气的涛啊,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/handsometaoa/p/17919889.html




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 【杭电多校比赛记录】2025“钉耙编程”中国大学生算法设计春季联赛(1)
2022-12-21 3. 无重复字符的最长子串