单链表代码实现和讲解
1、链表的特性
链表分为单链表和多链表,链表相对于数组有什么好处?
- 不是按顺序存储,是链式存储,以节点的形式
-
每个节点都包含date域(节点的内容),next域(下一节点的位置)
- 链表可以没有头节点
- 链表按照节点的next来查找下一个节点,由此当查找时,必须从头开始找,查找麻烦;但是插入和删除时只需要改变前后节点的指定位置就可以,所以插入删除方便
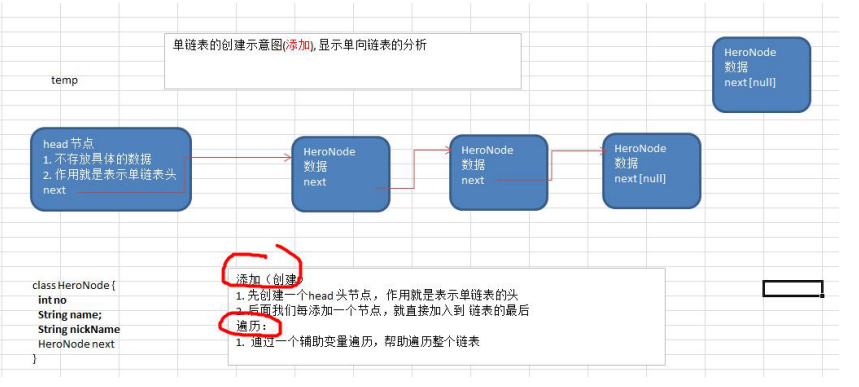
2、代码讲解单链表的应用(代码实现)
//实体类 public class PersonNode { public int no; public String name; public PersonNode next; public PersonNode(int no, String name) { this.no = no; this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "PersonNode{" + "no=" + no + ", name='" + name + '\'' + '}'; } }
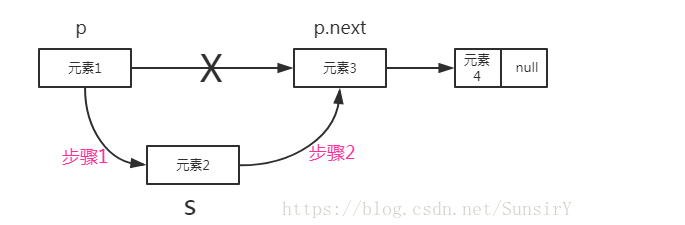
添加节点
1 //添加操作 2 public void add(PersonNode personNode){ 3 //head节点不能动,需要一个节点进行辅助遍历 4 PersonNode temp=head; 5 while (true){ 6 if (temp.next==null){ //遍历链表到结尾,跳出循环执行添加操作 7 break; 8 } 9 temp=temp.next; //辅助节点后移 10 } 11 temp.next=personNode;//将当前节点添加到最后一位 12 }
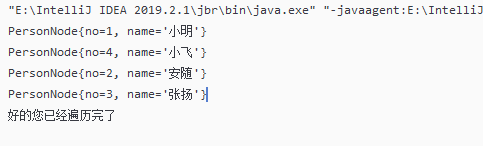
我们测试时发现如果不按顺序添加,如下图,我添加顺序时1423,输出也是按照添加顺序输出,可不可以实现按照大小顺序输出呢?
顺序添加
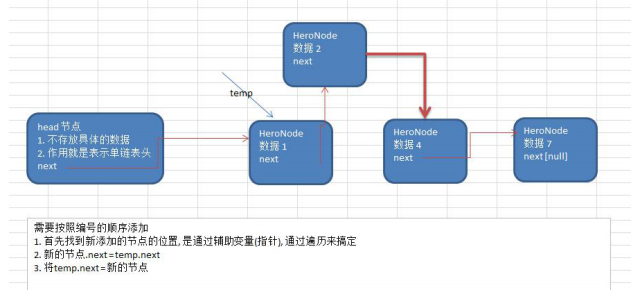
我们只需要在添加的遍历过程中加入判断条件,遍历过程中如果当前节点比下一个节点数值小,就添加在它的前面
pnode.next=temp.next;//当前节点的next指向下一个节点的next,如图,数据2的next指向数据4的next,就插入到数据4的前面
temp.next=pnode;//插入后需要让temp的next指向自己,才能实现添加
1 //顺序添加 2 public void addBySort(PersonNode pnode){ 3 //先顶一个指示 4 PersonNode temp=head; 5 boolean flag=false;//设置一个判断条件,如果遍历过程中发现该no已经存在,就置为true并跳出循环 6 while (true){ 7 if (temp.next==null){ 8 //System.out.println("add遍历已经结束"); 9 break; 10 } 11 if (pnode.no<temp.next.no){ 12 13 break; 14 } 15 else if (pnode.no==temp.next.no){ 16 flag=true; 17 break; 18 } 19 temp=temp.next; 20 } 21 if (flag){ 22 System.out.println("节点已经存在"); //当flag为true时该节点已经存在 23 }else { 24 pnode.next=temp.next; 25 temp.next=pnode; 26 } 27 }
修改
修改和顺序添加类似,就是在遍历过程中找到指定的no进行修改,没有找到就跳出循环
//修改 public void UpdateNode(PersonNode personNode){ if (head.next==null){ System.out.println("别修改了,这是空链表"); return; } PersonNode temp=head.next; boolean flag=false; while (true){ if (temp==null){ break; } if (temp.no==personNode.no){ flag=true; break; } temp=temp.next; } if (flag){ temp.no=personNode.no; temp.name=personNode.name; }else{ System.out.println("没找到,不改了"); } }
获取链表列表的内容
//列表 public void list(){ if (head.next==null){ System.out.println("还找列表?这是个空的"); return; } PersonNode temp=head.next; while (true){ if (temp==null){ System.out.println("好的您已经遍历完了"); break; } System.out.println(temp); temp=temp.next; } }
删除操作
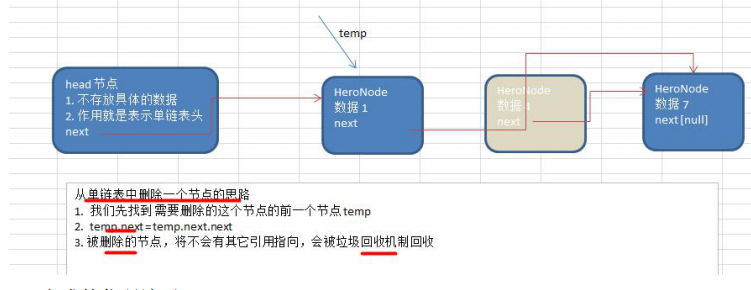
最重要的一句就是遍历过程中的 temp.next=temp.next.next,意思是将当前节点的next直接跳过下一个节点,指向下下个节点,而被删除的节点就相当于野指针,被内存回收
还需要注意temp这里指向的是head不是head.next,就是找到这个需要删除的节点时,temp在这个删除节点之前,为什么这样做?因为单链表和双链表不一样,双链表可以自我删除,单链表不行,必须借助前面的节点进行删除,和双链表记得区分开
//删除 public void removeNode(int num){ PersonNode temp=head; boolean flag=false; while (true){ if (temp.next==null){//遍历结束 break; } if (temp.next.no==num){ flag=true; break; } temp=temp.next; } if (flag){ temp.next=temp.next.next; }else{ System.out.println("抱歉,没有找到"); }
单链表反转(扩展)
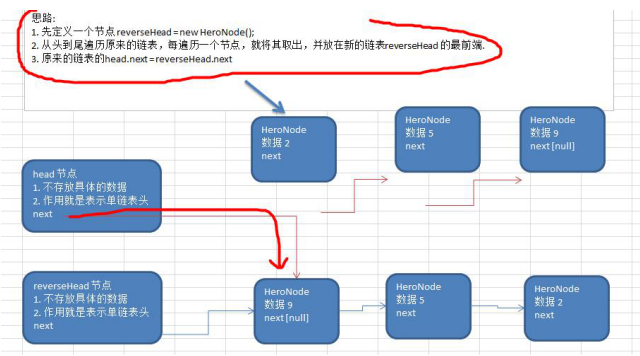
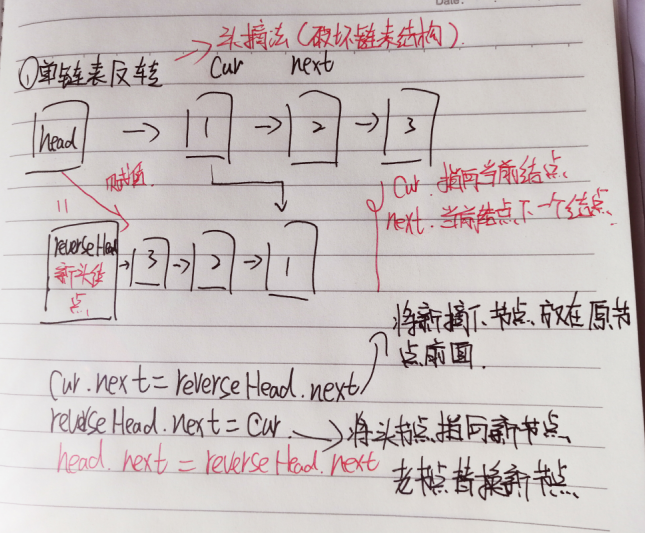
/** * 链表反转(头摘法) * 思路:定义一个新的表头,把原来表的节点逐个取出,每次都放在新头节点的后面 * cur当前节点,next当前节点的下一个节点,reverseHead新的头节点 */ public void reverseList(PersonNode head){ if (head.next==null || head.next.next==null){ return; } PersonNode cur=head.next; PersonNode next=null; PersonNode reverseHead=new PersonNode(0,""); while (cur!=null){ next=cur.next; cur.next=reverseHead.next;//让当前摘下的节点指向新链表头节点后面节点的前面,相当于插队到新的头节点的后面 reverseHead.next=cur;//让头节点指向当前节点 cur=next;//指针后移 } head.next=reverseHead.next;//将原来的头节点指向新的头节点 }
链表逆向输出(不能用上面的头插法,因为会破坏链表结构,这个时候可以用栈的先入后出)
/** * 链表反向输出打印(不能用头摘法,会破坏链表结构),栈先进后出可实现 */ public void reversePrint(PersonNode head){ if (head.next==null || head.next.next==null){ return; } Stack<PersonNode> stackAdd=new Stack<>(); PersonNode cur=head.next; while (cur!=null){ stackAdd.push(cur); cur=cur.next; } //输出打印 while (stackAdd.size()>0){ System.out.println(stackAdd.pop()); } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号