shiro身份认证流程
Shiro身份认证流程
身份认证:身份认证主要验证用户的身份,即验证用户操作时是其本人操作的,一般通过验证用户唯一principals和credentials,其中principals代表用户的身份,可以用用户名,邮箱,手机号等标识,唯一即可。credentials代表用户的证明/凭证,我们一般称之为密码。
认证流程源码执行过程
详细代码参考,本示例代码为shiro官网的示例代码
log.info("My First Apache Shiro Application");
Factory<SecurityManager> factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini");
SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
// get the currently executing user:
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// Do some stuff with a Session (no need for a web or EJB container!!!)
Session session = currentUser.getSession();
session.setAttribute("someKey", "aValue");
String value = (String) session.getAttribute("someKey");
if (value.equals("aValue")) {
log.info("Retrieved the correct value! [" + value + "]");
}
// let's login the current user so we can check against roles and permissions:
if (!currentUser.isAuthenticated()) {
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("lonestarr", "vespa");
token.setRememberMe(true);
try {
currentUser.login(token);
} catch (UnknownAccountException uae) {
log.info("There is no user with username of " + token.getPrincipal());
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice) {
log.info("Password for account " + token.getPrincipal() + " was incorrect!");
} catch (LockedAccountException lae) {
log.info("The account for username " + token.getPrincipal() + " is locked. " +
"Please contact your administrator to unlock it.");
}
// ... catch more exceptions here (maybe custom ones specific to your application?
catch (AuthenticationException ae) {
//unexpected condition? error?
}
}
-
首先通过SecurityUtils获取当前的主体,然后通过UsernamePasswordToken封装当前用户的账号和密码,然后通过Subject进行登录认证。
-
Subject.login会调用Subject的唯一实现类DelegatingSubject去进行登录,其会自动委托给Security Manager,调用之前必须通过SecurityUtils. setSecurityManager()设置,详情查看下面代码
public void login(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { //主要为清除session clearRunAsIdentitiesInternal(); //委托给securityManager进行登录 Subject subject = securityManager.login(this, token); PrincipalCollection principals; String host = null; if (subject instanceof DelegatingSubject) { DelegatingSubject delegating = (DelegatingSubject) subject; //we have to do this in case there are assumed identities - we don't want to lose the 'real' principals: principals = delegating.principals; host = delegating.host; } else { principals = subject.getPrincipals(); } if (principals == null || principals.isEmpty()) { String msg = "Principals returned from securityManager.login( token ) returned a null or " + "empty value. This value must be non null and populated with one or more elements."; throw new IllegalStateException(msg); } this.principals = principals; this.authenticated = true; if (token instanceof HostAuthenticationToken) { host = ((HostAuthenticationToken) token).getHost(); } if (host != null) { this.host = host; } Session session = subject.getSession(false); if (session != null) { this.session = decorate(session); } else { this.session = null; } } -
securityManager会交给DefaultSeurityManager去进行登录,登录成功之后返回相应的Subject
public Subject login(Subject subject, AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { AuthenticationInfo info; try { //验证token info = authenticate(token); } catch (AuthenticationException ae) { try { onFailedLogin(token, ae, subject); } catch (Exception e) { if (log.isInfoEnabled()) { log.info("onFailedLogin method threw an " + "exception. Logging and propagating original AuthenticationException.", e); } } throw ae; //propagate } Subject loggedIn = createSubject(token, info, subject); onSuccessfulLogin(token, info, loggedIn); return loggedIn; } -
上面流程中authenticate最终调用Authenticator去验证用户的身份信息,默认调用的是AbstractAuthenticator的authenticate方法
public final AuthenticationInfo authenticate(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { if (token == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Method argument (authentication token) cannot be null."); } log.trace("Authentication attempt received for token [{}]", token); AuthenticationInfo info; try { info = doAuthenticate(token); if (info == null) { String msg = "No account information found for authentication token [" + token + "] by this " + "Authenticator instance. Please check that it is configured correctly."; throw new AuthenticationException(msg); } } catch (Throwable t) { AuthenticationException ae = null; if (t instanceof AuthenticationException) { ae = (AuthenticationException) t; } if (ae == null) { //Exception thrown was not an expected AuthenticationException. Therefore it is probably a little more //severe or unexpected. So, wrap in an AuthenticationException, log to warn, and propagate: String msg = "Authentication failed for token submission [" + token + "]. Possible unexpected " + "error? (Typical or expected login exceptions should extend from AuthenticationException)."; ae = new AuthenticationException(msg, t); if (log.isWarnEnabled()) log.warn(msg, t); } try { notifyFailure(token, ae); } catch (Throwable t2) { if (log.isWarnEnabled()) { String msg = "Unable to send notification for failed authentication attempt - listener error?. " + "Please check your AuthenticationListener implementation(s). Logging sending exception " + "and propagating original AuthenticationException instead..."; log.warn(msg, t2); } } throw ae; } log.debug("Authentication successful for token [{}]. Returned account [{}]", token, info); notifySuccess(token, info); return info; } -
身份验证的方法最终调用的是ModularRealmAuthenticator的doAuthenticate方法,根据获取到的realms进行真正的身份认证
protected AuthenticationInfo doAuthenticate(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException { //判断是否进行Realms配置,如果没有直接会抛出异常 assertRealmsConfigured(); //获取相关realms集合 Collection<Realm> realms = getRealms(); //根据realms的数量进行响应的操作 if (realms.size() == 1) { //进行身份认证 return doSingleRealmAuthentication(realms.iterator().next(), authenticationToken); } else { return doMultiRealmAuthentication(realms, authenticationToken); } } //Authenticator会把相应的token传入Realm,从Realm获取身份验证信息,如果没有返回/抛出异常表示身份验证失败了。此处可以配置多个Realm,将按照相应的顺序及策略进行访问。 protected AuthenticationInfo doSingleRealmAuthentication(Realm realm, AuthenticationToken token) { //判断该realm是否支持该token的验证 if (!realm.supports(token)) { String msg = "Realm [" + realm + "] does not support authentication token [" + token + "]. Please ensure that the appropriate Realm implementation is " + "configured correctly or that the realm accepts AuthenticationTokens of this type."; throw new UnsupportedTokenException(msg); } //根据主体的唯一查询出该用户 AuthenticationInfo info = realm.getAuthenticationInfo(token); if (info == null) { String msg = "Realm [" + realm + "] was unable to find account data for the " + "submitted AuthenticationToken [" + token + "]."; throw new UnknownAccountException(msg); } return info; } -
realm进行身份认证,默认调用的是AuthenticatingRealm的getAuthenticationInfo进行身份与凭证的验证
public final AuthenticationInfo getAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { //如果配置了缓存,则从缓存中获取AuthenticationInfo,即AuthenticationInfo中封装了用户的身份和凭证信息 AuthenticationInfo info = getCachedAuthenticationInfo(token); if (info == null) { //otherwise not cached, perform the lookup: //缓存中没有,则调用该方法获取AuthenticationInfo info = doGetAuthenticationInfo(token); log.debug("Looked up AuthenticationInfo [{}] from doGetAuthenticationInfo", info); if (token != null && info != null) { cacheAuthenticationInfoIfPossible(token, info); } } else { log.debug("Using cached authentication info [{}] to perform credentials matching.", info); } if (info != null) { //对用户的凭证进行校验,即密码 assertCredentialsMatch(token, info); } else { log.debug("No AuthenticationInfo found for submitted AuthenticationToken [{}]. Returning null.", token); } return info; }
身份认证流程总结
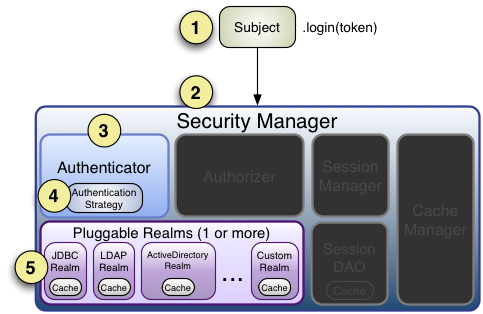
1、首先调用Subject.login(token)进行登录,其会自动委托给Security Manager,调用之前必须通过SecurityUtils. setSecurityManager()设置;
2、SecurityManager负责真正的身份验证逻辑;它会委托给Authenticator进行身份验证;
3、Authenticator才是真正的身份验证者,Shiro API中核心的身份认证入口点,此处可以自定义插入自己的实现;
4、Authenticator可能会委托给相应的AuthenticationStrategy进行多Realm身份验证,默认ModularRealmAuthenticator会调用AuthenticationStrategy进行多Realm身份验证;
5、Authenticator会把相应的token传入Realm,从Realm获取身份验证信息,如果没有返回/抛出异常表示身份验证失败了。此处可以配置多个Realm,将按照相应的顺序及策略进行访问
参考:
跟我学shiro### Shiro身份认证流程
身份认证:身份认证主要验证用户的身份,即验证用户操作时是其本人操作的,一般通过验证用户唯一principals和credentials,其中principals代表用户的身份,可以用用户名,邮箱,手机号等标识,唯一即可。credentials代表用户的证明/凭证,我们一般称之为密码。
认证流程源码执行过程
详细代码参考,本示例代码为shiro官网的示例代码
log.info("My First Apache Shiro Application");
Factory<SecurityManager> factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini");
SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
// get the currently executing user:
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// Do some stuff with a Session (no need for a web or EJB container!!!)
Session session = currentUser.getSession();
session.setAttribute("someKey", "aValue");
String value = (String) session.getAttribute("someKey");
if (value.equals("aValue")) {
log.info("Retrieved the correct value! [" + value + "]");
}
// let's login the current user so we can check against roles and permissions:
if (!currentUser.isAuthenticated()) {
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("lonestarr", "vespa");
token.setRememberMe(true);
try {
currentUser.login(token);
} catch (UnknownAccountException uae) {
log.info("There is no user with username of " + token.getPrincipal());
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice) {
log.info("Password for account " + token.getPrincipal() + " was incorrect!");
} catch (LockedAccountException lae) {
log.info("The account for username " + token.getPrincipal() + " is locked. " +
"Please contact your administrator to unlock it.");
}
// ... catch more exceptions here (maybe custom ones specific to your application?
catch (AuthenticationException ae) {
//unexpected condition? error?
}
}
-
首先通过SecurityUtils获取当前的主体,然后通过UsernamePasswordToken封装当前用户的账号和密码,然后通过Subject进行登录认证。
-
Subject.login会调用Subject的唯一实现类DelegatingSubject去进行登录,其会自动委托给Security Manager,调用之前必须通过SecurityUtils. setSecurityManager()设置,详情查看下面代码
public void login(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { //主要为清除session clearRunAsIdentitiesInternal(); //委托给securityManager进行登录 Subject subject = securityManager.login(this, token); PrincipalCollection principals; String host = null; if (subject instanceof DelegatingSubject) { DelegatingSubject delegating = (DelegatingSubject) subject; //we have to do this in case there are assumed identities - we don't want to lose the 'real' principals: principals = delegating.principals; host = delegating.host; } else { principals = subject.getPrincipals(); } if (principals == null || principals.isEmpty()) { String msg = "Principals returned from securityManager.login( token ) returned a null or " + "empty value. This value must be non null and populated with one or more elements."; throw new IllegalStateException(msg); } this.principals = principals; this.authenticated = true; if (token instanceof HostAuthenticationToken) { host = ((HostAuthenticationToken) token).getHost(); } if (host != null) { this.host = host; } Session session = subject.getSession(false); if (session != null) { this.session = decorate(session); } else { this.session = null; } } -
securityManager会交给DefaultSeurityManager去进行登录,登录成功之后返回相应的Subject
public Subject login(Subject subject, AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { AuthenticationInfo info; try { //验证token info = authenticate(token); } catch (AuthenticationException ae) { try { onFailedLogin(token, ae, subject); } catch (Exception e) { if (log.isInfoEnabled()) { log.info("onFailedLogin method threw an " + "exception. Logging and propagating original AuthenticationException.", e); } } throw ae; //propagate } Subject loggedIn = createSubject(token, info, subject); onSuccessfulLogin(token, info, loggedIn); return loggedIn; } -
上面流程中authenticate最终调用Authenticator去验证用户的身份信息,默认调用的是AbstractAuthenticator的authenticate方法
public final AuthenticationInfo authenticate(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { if (token == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Method argument (authentication token) cannot be null."); } log.trace("Authentication attempt received for token [{}]", token); AuthenticationInfo info; try { info = doAuthenticate(token); if (info == null) { String msg = "No account information found for authentication token [" + token + "] by this " + "Authenticator instance. Please check that it is configured correctly."; throw new AuthenticationException(msg); } } catch (Throwable t) { AuthenticationException ae = null; if (t instanceof AuthenticationException) { ae = (AuthenticationException) t; } if (ae == null) { //Exception thrown was not an expected AuthenticationException. Therefore it is probably a little more //severe or unexpected. So, wrap in an AuthenticationException, log to warn, and propagate: String msg = "Authentication failed for token submission [" + token + "]. Possible unexpected " + "error? (Typical or expected login exceptions should extend from AuthenticationException)."; ae = new AuthenticationException(msg, t); if (log.isWarnEnabled()) log.warn(msg, t); } try { notifyFailure(token, ae); } catch (Throwable t2) { if (log.isWarnEnabled()) { String msg = "Unable to send notification for failed authentication attempt - listener error?. " + "Please check your AuthenticationListener implementation(s). Logging sending exception " + "and propagating original AuthenticationException instead..."; log.warn(msg, t2); } } throw ae; } log.debug("Authentication successful for token [{}]. Returned account [{}]", token, info); notifySuccess(token, info); return info; } -
身份验证的方法最终调用的是ModularRealmAuthenticator的doAuthenticate方法,根据获取到的realms进行真正的身份认证
protected AuthenticationInfo doAuthenticate(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException { //判断是否进行Realms配置,如果没有直接会抛出异常 assertRealmsConfigured(); //获取相关realms集合 Collection<Realm> realms = getRealms(); //根据realms的数量进行响应的操作 if (realms.size() == 1) { //进行身份认证 return doSingleRealmAuthentication(realms.iterator().next(), authenticationToken); } else { return doMultiRealmAuthentication(realms, authenticationToken); } } //Authenticator会把相应的token传入Realm,从Realm获取身份验证信息,如果没有返回/抛出异常表示身份验证失败了。此处可以配置多个Realm,将按照相应的顺序及策略进行访问。 protected AuthenticationInfo doSingleRealmAuthentication(Realm realm, AuthenticationToken token) { //判断该realm是否支持该token的验证 if (!realm.supports(token)) { String msg = "Realm [" + realm + "] does not support authentication token [" + token + "]. Please ensure that the appropriate Realm implementation is " + "configured correctly or that the realm accepts AuthenticationTokens of this type."; throw new UnsupportedTokenException(msg); } //根据主体的唯一查询出该用户 AuthenticationInfo info = realm.getAuthenticationInfo(token); if (info == null) { String msg = "Realm [" + realm + "] was unable to find account data for the " + "submitted AuthenticationToken [" + token + "]."; throw new UnknownAccountException(msg); } return info; } -
realm进行身份认证,默认调用的是AuthenticatingRealm的getAuthenticationInfo进行身份与凭证的验证
public final AuthenticationInfo getAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { //如果配置了缓存,则从缓存中获取AuthenticationInfo,即AuthenticationInfo中封装了用户的身份和凭证信息 AuthenticationInfo info = getCachedAuthenticationInfo(token); if (info == null) { //otherwise not cached, perform the lookup: //缓存中没有,则调用该方法获取AuthenticationInfo info = doGetAuthenticationInfo(token); log.debug("Looked up AuthenticationInfo [{}] from doGetAuthenticationInfo", info); if (token != null && info != null) { cacheAuthenticationInfoIfPossible(token, info); } } else { log.debug("Using cached authentication info [{}] to perform credentials matching.", info); } if (info != null) { //对用户的凭证进行校验,即密码 assertCredentialsMatch(token, info); } else { log.debug("No AuthenticationInfo found for submitted AuthenticationToken [{}]. Returning null.", token); } return info; }
身份认证流程总结

1、首先调用Subject.login(token)进行登录,其会自动委托给Security Manager,调用之前必须通过SecurityUtils. setSecurityManager()设置;
2、SecurityManager负责真正的身份验证逻辑;它会委托给Authenticator进行身份验证;
3、Authenticator才是真正的身份验证者,Shiro API中核心的身份认证入口点,此处可以自定义插入自己的实现;
4、Authenticator可能会委托给相应的AuthenticationStrategy进行多Realm身份验证,默认ModularRealmAuthenticator会调用AuthenticationStrategy进行多Realm身份验证;
5、Authenticator会把相应的token传入Realm,从Realm获取身份验证信息,如果没有返回/抛出异常表示身份验证失败了。此处可以配置多个Realm,将按照相应的顺序及策略进行访问



