一间大屋子有两个功能 : 睡觉、学习、互不相干
现在小南要学习,小女要睡觉,但如果只用一间屋子(一个对象锁)的话,那么并发度很低
解决方法时准备多个房间(多个对象锁)
死锁
有这样的情况 : 一个线程需要同时获取多把锁,这时就容易发生死锁
t1 线程获得A对象锁,接下来想获取B对象的锁
t2 线程获取B对象锁,接下来想获取A对象的锁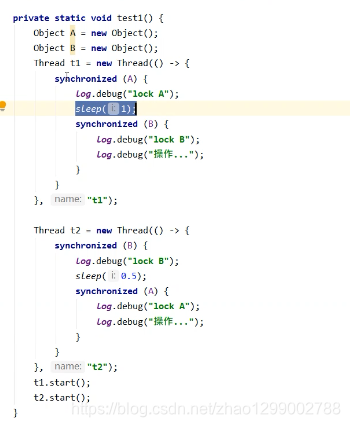
定位死锁
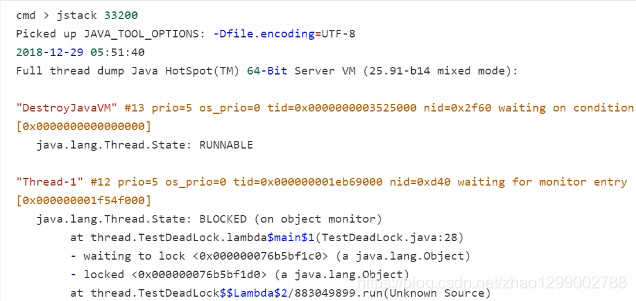
- 检测死锁可以使用jconsole工具,或者使用jps定位进程id,再用jstack定位死锁 :

先来看看一个线程饥饿的例子,使用顺序加锁的方式解决之前的死锁问题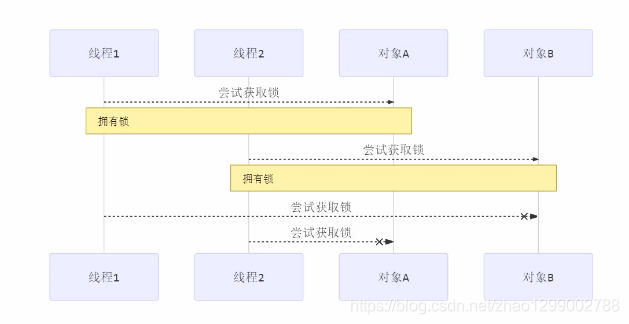
顺序加锁的解决方案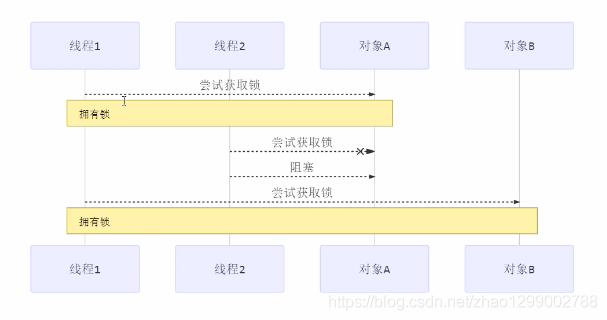
相对于synchronized它具备如下特点
- 可中断
- 可设置超时时间
- 可以设置为公平锁
- 支持多个条件变量
与synch一样,都支持可重入
可重入
可重入是指用一个线程如果首次获得了这把锁,那么因为它是这把锁的拥有者,因此有权利再次获取这把锁
如果是不可重入锁,那么第二次获得锁时,自己也会被锁挡住
基本语法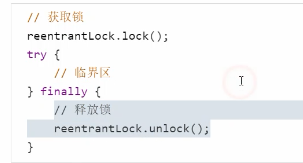
固定运行顺序
比如,必须先2后1打印
wait notify版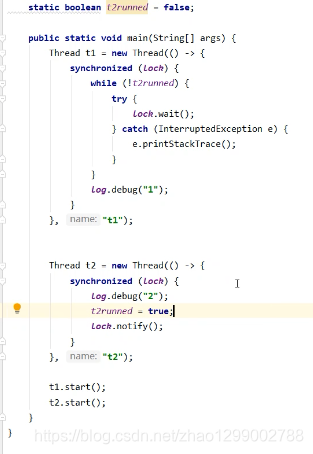
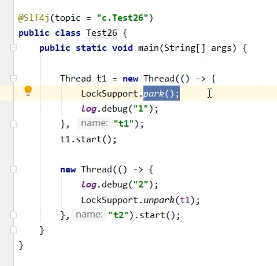
线程1输出a5次,线程2输出b5次,线程3输出c5次。现在要去输出abcabcabcabcabc怎么实现
package com.example.demo;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j
public class Test27 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
WaitNotify waitNotify = new WaitNotify(1, 5);
new Thread(() -> {
waitNotify.print("a", 1, 2);
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
waitNotify.print("b", 2, 3);
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
waitNotify.print("c", 3, 1);
}).start();
}
}
/**
* 输出内容 等待标记 下一个标记
* a 1 2
* b 2 3
* c 3 1
*/
class WaitNotify {
/**
* 打印
* @param str
* @param waitFlag
* @param nextFLag
*/
public void print(String str, int waitFlag, int nextFLag) {
for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++) {
synchronized (this) {
while (flag != waitFlag) {
try {
this.wait();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(str);
flag = nextFLag;
this.notifyAll();
}
}
}
/**
* 等待标记
*/
private int flag;
/**
* 循环次数
*/
private int loopNumber;
public WaitNotify(int flag, int loopNumber) {
this.flag = flag;
this.loopNumber = loopNumber;
}
}
package com.example.demo;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
AwaitSignal awaitSignal = new AwaitSignal(5);
Condition a = awaitSignal.newCondition();
Condition b = awaitSignal.newCondition();
Condition c = awaitSignal.newCondition();
new Thread(() -> {
awaitSignal.print("a", a, b);
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
awaitSignal.print("b", b, c);
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
awaitSignal.print("c", c, a);
}).start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
awaitSignal.lock();
try {
System.out.println("开始。。。。");
a.signal();
} finally {
awaitSignal.unlock();
}
}
}
class AwaitSignal extends ReentrantLock {
private int loopNumber;
public AwaitSignal(int loopNumber) {
this.loopNumber = loopNumber;
}
/**
* 参数1 打印内容,参数2 进入那一间休息室,参数3 下一间休息室
* @param str
* @param current
* @param next
*/
public void print(String str, Condition current, Condition next) {
for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++) {
lock();
try {
current.await();
System.out.println(str);
next.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
unlock();
}
}
}
}



