深入剖析 instanceof 运算符
一、instanceof
1、引入 instanceof
在JS中,判断一个变量的类型,常常会用到 typeof 运算符,但当用 typeof 来判断引用类型变量时,无论是什么类型的变量,它都会返回 Object
// 基本类型 console.log(typeof 100) // number console.log(typeof 'dylan') // string console.log(typeof true) // boolean console.log(typeof undefined) // undefined console.log(typeof null) // object,这里注意 null 的结果是 object // 引用类型 console.log(typeof {}) // object console.log(typeof [1,2,3]) // object
为此引入了 instanceof
instanceof 操作符用于检测对象是否属于某个 class,同时,检测过程中也会将继承关系考虑在内
class Parent{} let parent = new Parent() console.log(parent instanceof Parent) // true // 也可以是构造函数 function Child(){} let child = new Child() console.log(child instanceof Child) // true
2、instanceof 与 typeof
instanceof 与 typeof 相比,instanceof 方法要求开发者明确地确认对象为某特定类型。即 instanceof 用于判断引用类型属于哪个构造函数的方法。
var arr = [] console.log(arr instanceof Array) // true console.log(typeof arr) // "object" // typeof是无法判断类型是否为数组
3、instanceof 在继承关系中
另外,更为重要的一点是 instanceof 可以在继承关系中用来判断一个实例是否属于它的父类型。
// 判断 f 是否是 Foo 类的实例,并且是否是其父类型的实例 function Aoo(){} function Foo(){} // JavaScript原型继承 Foo.prototype = new Aoo() var foo = new Foo() console.log(foo instanceof Foo) // true console.log(foo instanceof Aoo) // true
f instanceof Foo 的判断逻辑是:
- f 的 __proto__ 一层一层往上,是否对应到 Foo.prototype
- 再往上,看是否对应着 Aoo.prototype
- 在试着判断 f instanceof Object
即 instanceof 可以用于判断多层继承关系
下面看一组复杂例子:
console.log(Object instanceof Object) // true console.log(Function instanceof Function) // true console.log(Number instanceof Number) // false console.log(String instanceof String) // false console.log(Array instanceof Array) // false console.log(Function instanceof Object) // true console.log(Foo instanceof Function) // true console.log(Foo instanceof Foo) //false
在这组数据中,Object、Function 来 instanceof 自己均为 true,其他的 instanceof 自己都为false,这就要从 instanceof 的内部实现机制以及JS原型继承机制讲起了。
二、instanceof的内部实现机制
instanceof 的内部实现机制是:通过判断对象的原型链上是否能找到对象的 prototype,来确定 instanceof 返回值
1、内部实现
解释:prototype 是挂在构造函数(类)下面的显式原型,__proto__ 是挂在实例上的隐式原型
例如:
var arr = [] console.log(arr.__proto__ === Array.prototype) // true
下面是instanceof的内部实现代码:
// instanceof 的内部实现 function instance_of(L, R){ // L为变量,R为类型 // 取R的显式原型 var prototype = R.prototype // 取L的隐式原型 L = L.__proto__ // 判断对象 L 的类型是否严格等于类型 R 的显式原型 while(true){ if(L === null){ return false } // 重点:当 prototype 严格等于 L时,返回true if(prototype === L){ return true } // 赋值之前,L为刚传入时变量 L 的隐式原型 // 赋值之后,L为隐式原型的隐式原型(递归向上查找) L = L.__proto__ } }
instanceof 运算符用来检测 constructor.prototype 是否存在于参数 object 的原型链上
2、你真的了解 instanceof 了吗
看下面一个例子,instanceof 为什么会返回 true ?很显然,child 并不是通过 Child() 创建的
function Child(){} function Parent(){} Child.prototype = Parent.prototype = {} let child = new Child() console.log(child instanceof Parent) // true
这是因为 instanceof 关心的并不是构造函数,而是原型链
console.log(child.__proto__ === Child.prototype) // true console.log(Child.prototype === Parent.prototype) // true // 即 console.log(child.__proto__ === Parent.prototype) // true
即有 child.__proto__ === Parent.prototype 成立,所以 child instanceof Parent 返回了 true
所以,按照 instanceof 的逻辑,真正决定类型的是 prototype,不是构造函数
三、JS原型链继承关系
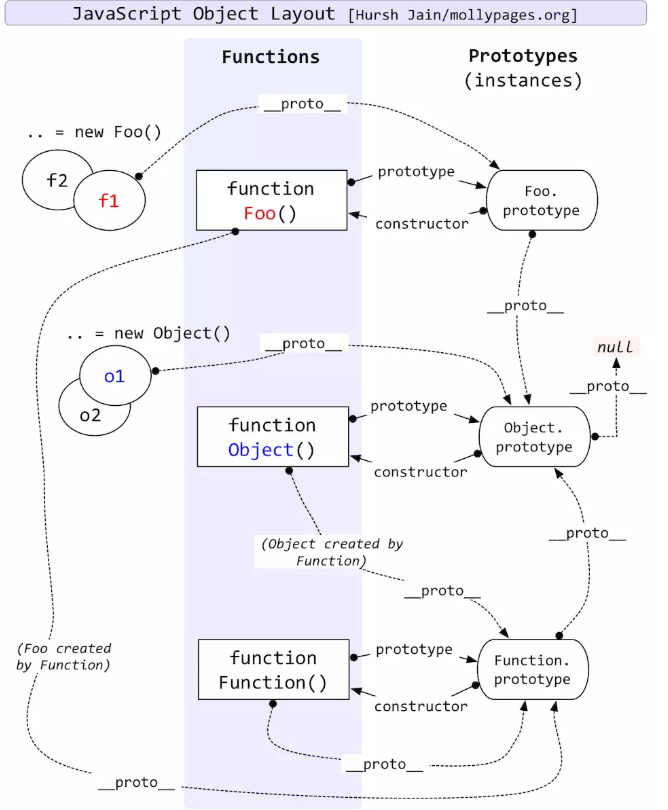
显示原型:prototype
隐式原型:__proto__
在JavaScript原型继承结构里面,规范中用 [Prototype] 表示对象隐式的原型,在JavaScript中用 __proto__ 表示,并且在 Firefox 和 Chrome 浏览器中是可以访问得到这个属性的,但是IE下不行。所有JavaScript对象都有 __proto__ 属性,但只有 Object.prototype.__proto__ 为 null,前提是没有在Firefox或者Chrome下修改过这个属性。这个属性指向它的原型对象。至于显示的原型,在JavaScript里用 prototype 属性表示,这个是JavaScript原型继承的基础知识:https://github.com/sisterAn/blog/issues/5
下面介绍几个例子及推理过程,加深理解:
1、Object instanceof Object
// 为了方便表述,首先区分左侧表达式和右侧表达式 var ObjectL = Object var ObjectR = Object // 下面根据规范逐步推演(左侧是实例,右侧是类) var L = ObjectL.__proto__ = Function.prototype var R = ObjectR.prototype = Object.prototype // 第一次判断 R != L // 循环查找L是否还有 __proto__ L = Function.prototype.__proto__ = Object.prototype // 第二次判断 R === L // 返回true
个人理解:函数(类)都是显式原型(prototype),实例都是隐式原型(__proto__)
2、Function instanceof Function
// 为了方便表述,首先区分左侧表达式和右侧表达式 var FunctionL = Function var FunctionR = Function // 下面根据规范逐步推演(左侧是实例,右侧是类) var L = FunctionL.__proto__ = Function.prototype var R = FunctionR.prototype = Function.prototype // 判断 console.log(R === L); // 返回true
3、Foo instanceof Foo
// 为了方便表述,首先区分左侧表达式和右侧表达式 var FooL = Foo var FooR = Foo // 下面根据规范逐步推演(左侧是实例,右侧是类) var L = FooL.__proto__ = Function.prototype var R = FooR.prototype = Foo.prototype // 第一次判断 L != R // 循环再次寻找 L 是否还有 __proto__ L = Function.prototype.__proto__ = Object.prototype // 第二次判断 L != R // 再次查找L是否还有 __proto__ L = Object.prototype.__proto__ = null // 第三次判断 L == null // 返回false
四、扩展:Object.prototype.toString 方法
默认情况下(不覆盖 toString 方法的前提下),任何一个对象调用 Object 原生的 toString 方法都会返回 "[object type]",其中 type 是对象的类型
let obj = {} console.log(obj) // {} console.log(obj.toString()) // "[object Object]"
1、[[Class]]
每个实例都有一个 [[Class]] 属性,在属性中就指定了上述字符串中的 type (构造函数名)。[[Class]] 不能直接地被访问,但通常可以间接地通过在这个值上借用默认的 Object.prototype.toString.call(..)方法调用来展示。
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call("abc")); // "[object String]" console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(100)); // "[object Number]" console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(true)); // "[object Boolean]" console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(null)); // "[object Null]" console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(undefined)); // "[object Undefined]" console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call([1,2,3])); // "[object Array]" console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(/\w/)); // "[object RegExp]"
2、使用 Object.prototype.toString.call(..) 检测对象类型
function isFunc(value){ return Object.prototype.toString.call(value) === "[object Function]" } function isDate(value){ return Object.prototype.toString.call(value) === "[object Date]" } function isRegExp(value){ return Object.prototype.toString.call(value) === "[object RegExp]" } isDate(new Date()); // true isRegExp(/\w/); // true isFunction(function(){}); //true
或者可以写成:
function generator(type){ return function(value){ return Object.prototype.toString.call(value) === `[object ${type}]` } } let isFunc = generator("Function") let isArray = generator("Array") let isDate = generator("Date") let isRegExp = generator("RegExp") isArray([]) // true isDate(new Date()) // true isRegExp(/\w/) // true isFunc(function(){}) // true
五、总结

Object.prototype.toString 基本上就是一增强版 typeof
instanceof 在涉及多层类结构的场合中比较实用,这种情况下需要将类的继承关系考虑在内。





