Day03 Python基础
Day03 Python基础
课程目标:掌握Python基础中的必备语法知识
- 循环语句
- 字符串格式化
- 运算符(面试题)
1. 循环语句
- while循环
- for循环(后期)
while 条件:
...
...
...
print("123")
while 条件:
...
...
...
print("456")
1.1 循环语句基本使用
示例1:
print("开始")
while True:
print("xxx是傻子")
print("结束")
# 输出
开始
xxx是傻子
xxx是傻子
xxx是傻子
..... # 死循环
实例2:
print("开始")
while 1 > 2:
print("xxx是傻子")
print("结束")
# 输出
开始
结束
实例3:
data = True
print("开始")
while data:
print("xxx是傻子")
print("结束")
# 输出
开始
xxx是傻子
xxx是傻子
xxx是傻子
..... # 死循环
实例4:
print("开始")
flag = True
while flag:
print("xxx是傻子")
flag = False
print("结束")
# 输出
开始
xxx是傻子
结束
实例5:
print("开始")
num = 1
while num < 3:
print("xxx是傻子")
num = 5
print("结束")
# 输出
开始
xxx是傻子
结束
实例6:
print("start")
num = 1
while num < 5:
print("xxx is very stupid")
num = num + 1
print("end")
# 输出
start
xxx is very stupid
xxx is very stupid
xxx is very stupid
xxx is very stupid
end
练习题: 重复3次出现输出我爱我的祖国answer:num = 0while num < 3: print("我爱我的祖国") num = num + 1
1.2 综合小案例
请实现一个用户登陆系统,如果密码错误则反复提示让用户重新输入,直到输入正确才停止
print("开始运行系统")
flag = True
while flag:
name = input("请输入用户名")
passwd = input("请输入密码")
if name == "xiaoming" and passwd == "xiaoming":
print("登陆成功")
flag = False
else:
print("请重新输入")
print("系统结束 ")
1.3 break
用于在循环中中止循环的。
print("start")
while True:
print("1")
break
print("2")
print("end")
# 输出
1
end
1.4 continue
continue,在循环中用于结束本次循环,开始下一次循环
print("start")
while True:
print("1")
continue
print("2")
print("end")
# 输出
start
1
1
...
1
1.5 while else
当循环正常结束时执行,否则不执行(eg:遇到break时退出循环)
num = 1
while num < 5:
print(num)
num = num + 1
else:
print("end")
# 输出:
1
2
3
4
end
while True:
print("123")
break
else:
print("666")
# 输出
123
2. 字符串格式化
使用更便捷的形式,实现字符串的拼接。
2.1 %
2.1.1 基本格式化操作
name = "xiaoming"
# 占位符
text = "我叫%s,今年18岁" % name
print(text)
# 输出
我叫xiaoming,今年18岁
name = "xiaoming"
age = 18
# %s字符串站位 %d为数字站位
text = "我叫%s,今年%d岁" %(name, age)
print(text)
# 输出
我叫xiaoming,今年18岁
https://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/5484747.html
message = "%(name)s你什么时候过来啊" %{"name":"死鬼"}
print(message)
# 输出
死鬼你什么时候过来啊
2.1.2 百分比的表示
text = "已经完成了90%了"
# %% 解决%问题
text = "%s,已经完成了90%%了" %"老板"
一旦字符串格式化中存在百分比的显示,请一定要加%%以实现输出%。
2.2 format
text = "我叫{0},今年18岁".format("tom")
text = "我叫{0},今年{1}岁".format("tom",18)
text = "我叫{0},今年{1}岁,真实的姓名是{0}。".format("tom",18)
text = "我叫{},今年18岁".format("tom")
text = "我叫{},今年{}岁".format("tom",18) # 不加序号的时候,系统会自动按照顺序加上数字,但是无法进行复用
text = "我叫{name},今年{age}岁".format(name="tom",age=18)
text = "我叫{0},今年{1}"
data = text.format("tom",18)
2.3 f
到python3.6版本以上,更便捷。
name = 'tom'
age = 18
text = f'{name},今年{age}岁'
print(text)
# 输出
tom,今年18岁
name = 'tom'
age = 18
text = f'{name},今年{age+2}岁'
print(text)
# 输出
tom,今年20岁
# python 3.8引入的
name = 'tom'
text = f'{name},今年{18 + 2 = }岁'
print(text)
# 输出
tom,今年18 + 2 = 20岁
v1 = "tom今年{22}岁"
print(v1) # tom今年22岁
v1 = "tom今年{22:#b}岁"
print(v1) # tom今年22(2进制格式显示)岁
v1 = "tom今年{22:#o}岁"
print(v1) # tom今年22(8进制格式显示)岁
v1 = "tom今年{22:#x}岁"
print(v1) # tom今年22(16进制格式显示)岁
# 理解
name = "xiaoming"
text = f"i am {name.upper()}"
print(text)
3. 运算符
提到运算符,我想大家首先想到的就是加、减、乘、除之类, 本节要系统的跟大家来聊一聊,我们写代码时常见的运算符可以分为5种:
-
算数运算符,例如:加减乘除
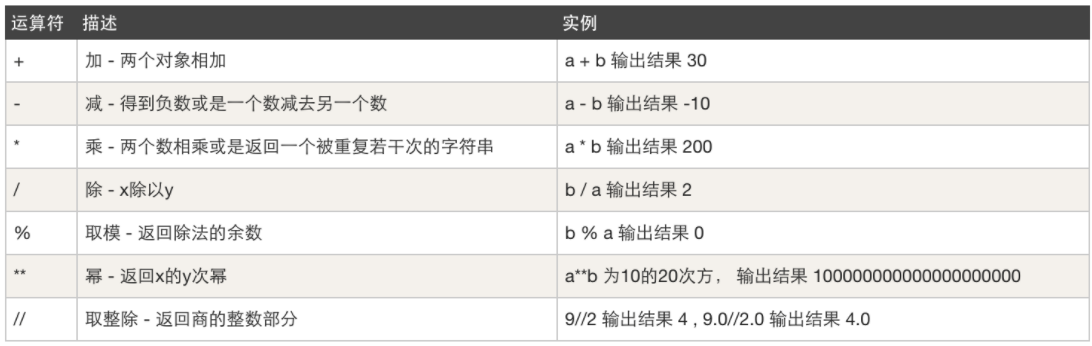
-
比较运算符,例如:大于、小于
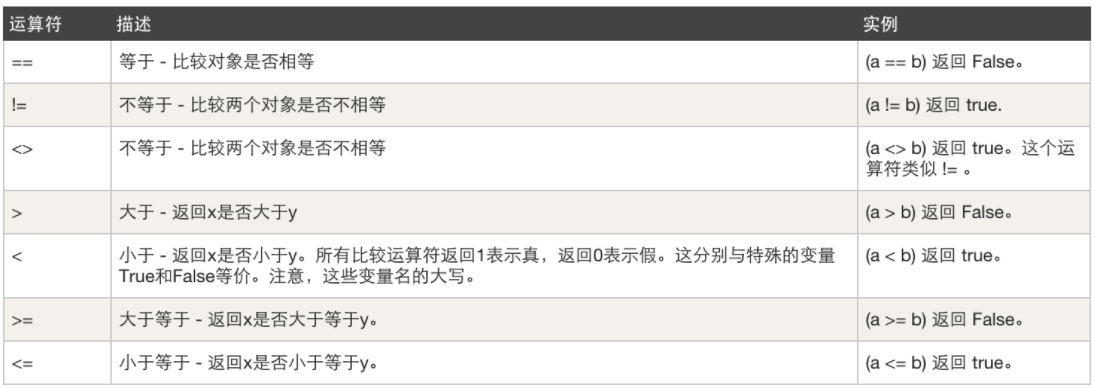
注意:python3中不支持
<> -
赋值运算,例如:变量赋值
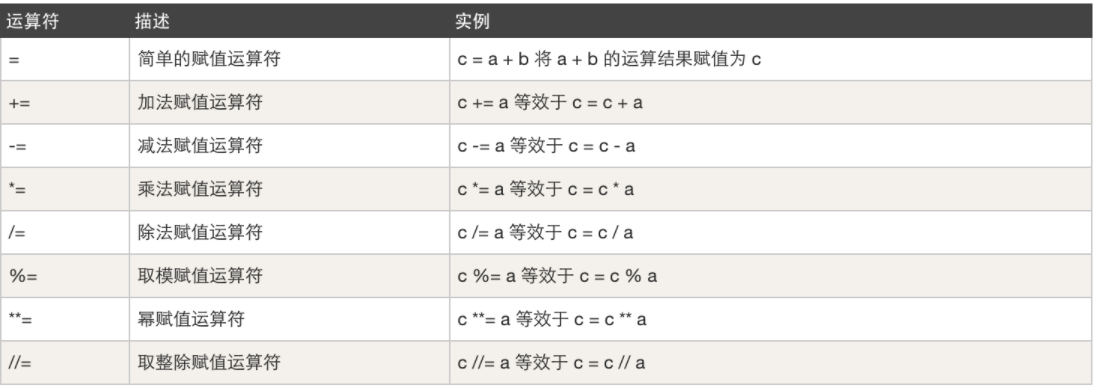
-
成员运算,例如:是否包含
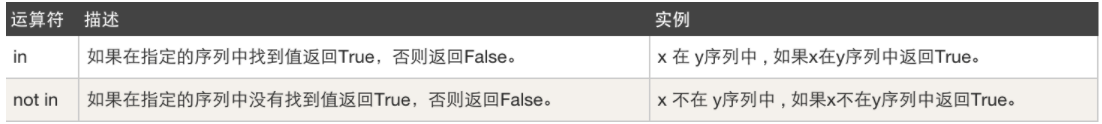
-
逻辑运算,例如:且或非
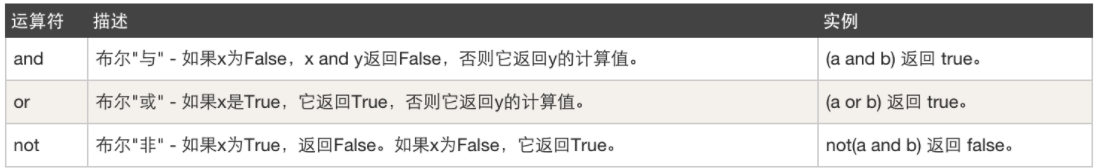
3.1 优先级
运算符的优先级有很多,常见的没几个,推荐你记住3个即可:
-
算数优先级优先级 大于 比较运算符
if 2 + 10 > 11: print("真")else: print("假") -
比较运算符优先级 大于 逻辑运算符
if 1>2 and 2<10: print("成立")else: print("不成立") -
逻辑运算符内部三个优先级 not > and > or
if not 1 and 1>2 or 3 == 8: print("真")else: print("假")
上述这3个优先级从高到低总结:加减乘除 > 比较 > not and or 。绝招:加括号。
3.2 面试题
逻辑运算中:and or
v1 = name == "alex" and pwd == "123"# v1 = True and Falseif name == "alex" and pwd == "123": pass
v2 = "wupeiqi" and "alex"
# 第一步:将and前后的只转换为布尔值 True and True
# 第二步:判断本次操作取决于谁?由于前面的是True,所以本次逻辑判断取决于后面的值。
# 所以,后面的只等于多少最终结果就是多少。
v2 = "alex"v3 = "" and "alex"
# 第一步:将and前后的只转换为布尔值 False and True
# 第二步:判断本次操作取悦于谁?由于前面的是False,所以本次逻辑判断取决于前面的值。
# 所以,前面的只等于多少最终结果就是多少。
v2 = ""v4 = 1 or 8
# 第一步:将and前后的只转换为布尔值 True or True
# 第二步:判断本次操作取悦于谁?由于前面的是True,所以本次逻辑判断取决于前面的值。
# v4 = 1
v5 = 0 or 8
# 第一步:将and前后的只转换为布尔值 False or True
# 第二步:判断本次操作取悦于谁?由于前面的是False,所以本次逻辑判断取决于后面的值。
# v5 = 8
练习题:
v1 = 1 or 2 # 1
v2 = -1 or 3 # -1
v3 = 0 or -1 # -1
v4 = 0 or 100 # 100
v5 = "" or 10 # 10
v6 = "xiaoming" or "" # xiaoming
v7 = 0 or "" # ""
print(v1,v2,v3,v4,v5,v6,v7)
# or,看第一个值,如果第一个值为真,结果就应该是第一个值,否则就结果就是第二个值。
v1 = 4 and 8 # 8
v2 = 0 and 6 # 0
v3 = -1 and 88 # 88
v4 = "" and 7 # ""
v5 = "xiaoming" and "" # ""
v6 = "" and 0 # ""
v7 = 0 and "中国" # ""
print(v1,v2,v3,v4,v5,v6,v7)#
and,看第一个值,如果第一个值真,结果就应该是第二个值,否则结果就是第一个值。
面试题
如果多个and 和or的情况,先计算and再计算or.
v1 = 0 or 4 and 3 or 7 or 9 and 6
0 or 3 or 7 or 9 and 6
0 or 3 or 7 or 6
3 or 7 or 6
3 or 6
3
v2 = 8 or 3 and 4 or 2 and 0 or 9 and 7
8 or 4 or 0 or 7
8 or 0 or 7
8 or 7
8
v3 = 0 or 2 and 3 and 4 or 6 and 0 or 3
0 or 3 and 4 or 6 and 0 or 3
0 or 4 or 0 or 3
4 or 0 or 3
4 or 3
4
先计算not,在计算and,最后计算or
v4 = not 8 or 3 and 4 or 2 4
总结
- while循环语句
- break和continue关键字的作用
- 三种字符串格式化的方式
- 基本运算符(逻辑运算符涉及的相关面试题)
今日练习题
-
判断下列逻辑语句的True,False
1 > 1 or 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 and 9 > 8 or 7 < 6 # Truenot 2 > 1 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 and 9 > 8 or 7 < 6 # False -
求出下列逻辑语句的值。
8 or 3 and 4 or 2 and 0 or 9 and 7 # 80 or 2 and 3 and 4 or 6 and 0 or 3 # 4 -
下列结果是什么?
6 or 2 > 1 # 6 3 or 2 > 1 # 3 0 or 5 < 4 # False 5 < 4 or 3 # 3 2 > 1 or 6 # True 3 and 2 > 1 # True 0 and 3 > 1 # 0 2 > 1 and 3 # 3 3 > 1 and 0 # 0 3 > 1 and 2 or 2 < 3 and 3 and 4 or 3 > 2 # 2 -
实现用户登录系统,并且要支持连续三次输错之后直接退出,并且在每次输错误时显示剩余错误次数(提示:使⽤字符串格式化)。
count = 3 correct_username = "zhouhaining" correct_passwd = "123456" while True: if count == 0: break username = input("请输入用户名") passwd = input("请输入密码") if username == correct_username and correct_passwd == passwd: print("登陆成功") break else: count = count - 1 if count != 0: print(f'还剩{count}次') else: print("您的机会已用完") -
猜年龄游戏
要求:允许用户最多尝试3次,3次都没猜对的话,就直接退出,如果猜对了,打印恭喜信息并退出。count = 3 correct_number = 66 while True: number = int(input("请输入您猜的数字:")) if number == correct_number: print("恭喜您猜中了") break else: count = count - 1 if count != 0: print(f'您还有{count}次机会') else: print("您的机会已用完") break -
猜年龄游戏升级版
要求:允许用户最多尝试3次,每尝试3次后,如果还没猜对,就问用户是否还想继续玩,如果回答Y,就继续让其猜3次,以此往复,如果回答N,就退出程序,如何猜对了,就直接退出。count = 3 correct_number = 66 while True: number = int(input("请输入您猜的数字:")) if number == correct_number: print("恭喜您猜中了") break else: count = count - 1 if count != 0: print(f'您还有{count}次机会') else: print("您的机会已用完") choice = input("您是是否想继续玩,是请回复Y,退出请回复N:") if choice == "Y": count = 3 else: break



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号