【Java 并发编程系列】【J.U.C】:CountDownLatch&CyclicBarrier&Semaphore
CountDownLatch
CountDownLatch 适用于需要在主线程中开启多个线程去并行执行任务并且主线程需要等待所有子线程执行完后再进行汇总的场景。
使用示例
实例代码如下:
public class JoinCountDownLatch {
// 创建一个CountDownLatch 实例
private static volatile CountDownLatch countDownLunch = new CountDownLatch(2);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
executorService.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
countDownLunch.countDown();
}
System.out.println("child threadOne over!");
}
});
executorService.submit(new Runnable() {@
Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
countDownLunch.countDown();
}
System.out.println("child threadTwo over!");
}
});
System.out.println("wait all child thread over!");
// 等待子线程执行完毕
countDownLunch.await();
System.out.println("all child thread over!");
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
输出如下:
wait all child thread over!
child threadOne over!
child threadTwo over!
all child thread over!
CountDownLatch 与join 方法的区别:
- 调用一个子线程的join() 方法后,该线程会一直被阻塞直到子线程运行完毕,而CountDownLatch 使用计数器来允许子线程运行完毕或者在运行中递减计数,也就是CountDownLatch 可以在子线程运行的任何时候让await 方法返回而不一定必须等到线程结束。
- 使用线程池来管理线程时一般都是直接添加Runable 到线程池,这时候就没有办法再调用线程的join 方法,CountDownLatch 相比join 对线程同步控制更加灵活。
实现原理
UML
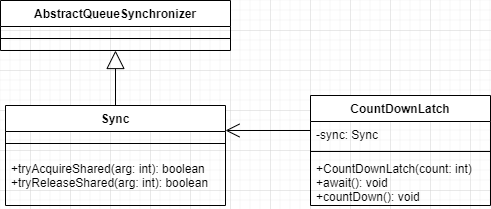
从类图可以看出,CountDownLatch 是使用AQS 实现的。通过下面的构造函数可知,实际上是把计数器的值赋给了AQS 的状态变量state ,也就是使用AQS 状态值来表示计数器值。
public CountDownLatch(int count) {
if (count < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("count < 0");
this.sync = new Sync(count);
}
Sync(int count) {
setState(count);
}
void await 方法
当线程调用CountDownLatch 对象的await 方法后,当前线程会被阻塞,直到下面的情况之一发生才会返回:
- 当所有线程都调用了CountDownLatch 对象的 countDown 方法后,也就是计数器值为0 时
- 其他线程调用了当前线程的interrupt() 方法中断了当前线程,当前线程抛出InterruptedException 异常返回
public void await() throws InterruptedException {
// 调用AQS acquireSharedInterruptibly 方法,其内使用了模板方法,调用tryAcquireShared 实现
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1);
}
// AQS
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
}
// Sync
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
return (getState() == 0) ? 1 : -1; // 计数器是0直接返回,不是0则需要阻塞当前线程
}
boolean await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) 方法
当前线程会被阻塞,直到下面的情况之一发生才会返回:
- 当所有线程都调用了CountDownLatch 对象的 countDown 方法后,也就是计数器值为0 时,返回true
- 设置的timeout 时间到了,超时返回false
- 其他线程调用了当前线程的interrupt() 方法中断了当前线程,当前线程抛出InterruptedException 异常返回
public boolean await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
return sync.tryAcquireSharedNanos(1, unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
void countDown 方法
线程调用该方法后,计数器的值递减,递减后如果计数器值为0,则唤醒所有因调用await 法而被阻塞的线程,否则什么都不做。
public void countDown() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
// AQS
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
// AQS 释放资源
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Sync
protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
// 循环进行CAS,直到当前线程成功完成CAS使计数器值(状态值state )减1 并更新到state
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) // 如果计数器为0直接返回
return false;
int nextc = c-1;
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc)) // CAS让state减1
return nextc == 0;
}
}
long getCount 方法
获取当前计数器的值,也就是AQS state 值,一般在测试时使用该方法。
public long getCount() {
return sync.getCount();
}
回环屏障 CyclicBarrier
由于CountDownLatch 计数器是一次性的,计数器值变为0 后,再调用await 和countDown 方法都会立刻返回。为了满足计数器可以重置的需要,JDK 提供了CyclicBarrier,但CyclicBarrier 类的功能并不限于CountDownLatch 的功能。
从字面意思理解,CyclicBarrier 是回环屏障的意思,CyclicBarrier 可以让一组线程全部达到一个状态后再全部同时执行,之所以叫作回环是因为当所有等待线程执行完毕,并重置CyclicBarrier 的状态后它可以被重用。之所以叫作屏障是因为线程调用await 方法后就会被阻塞,这个阻塞点就称为屏障点,等所有线程都调用了await 方法后,线程们就会冲破屏障,继续向下运行。
使用示例
public class CyclicBarrierTest {
private static CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(2, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " task merge result");
}
});
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
executorService.execute(() - > {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " task-1 start");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " task-1 enter in barrier");
try {
cyclicBarrier.await();
} catch(InterruptedException | BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " task-1 enter out barrier");
});
executorService.execute(() - > {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " task-2 start");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " task-2 enter in barrier");
try {
cyclicBarrier.await();
} catch(InterruptedException | BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " task-2 enter out barrier");
});
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
输出结果:
Thread[pool-1-thread-1,5,main] task-1 start
Thread[pool-1-thread-1,5,main] task-1 enter in barrier
Thread[pool-1-thread-2,5,main] task-2 start
Thread[pool-1-thread-2,5,main] task-2 enter in barrier
Thread[pool-1-thread-2,5,main] task merge result
Thread[pool-1-thread-2,5,main] task-2 enter out barrier
Thread[pool-1-thread-1,5,main] task-1 enter out barrier
实现原理
UML
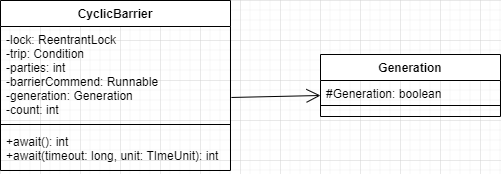
由类图可知,CyclicBarrier 基于独占锁实现,其底层还是基于AQS 的。parties 用来记录线程个数,这里表示多少线程调用await 后,所有线程才会冲破屏障。而count 一开始等于parties ,每当有线程调用await 就减1 ,当count 为0 表示所有线程都到了屏障点。
barrierCommand 任务,这个任务的执行时机是当所有线程都到达屏障点后。
在变量 generation 部有一 变量 broken ,其用来记录当前屏障是否被打破。
int await 方法
当前线程调用CyclicBarrier 该方法后会被阻塞,直到满足下面条件之一才会返回:
- parties 个线程都调用了await 方法,也就是线程都达到了屏障点
- 其他线程调用了当前线程的interrupt 方法中断了当前线程,则当前线程会抛出InterruptedException 异常而返回
- 与当前屏障点关联的Generation 对象的broken 标志被设置true 时,会抛BrokenBarrierException 异常后返回
public int await() throws InterruptedException, BrokenBarrierException {
try {
return dowait(false, 0L);
} catch (TimeoutException toe) {
throw new Error(toe); // cannot happen
}
}
boolean await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) 方法
当前线程调用CyclicBarrier 该方法后会被阻塞,直到满足下面条件之一才会返回:
- parties 个线程都调用了await 方法,也就是线程都达到了屏障点,返回true
- 设置的超时时间到了后返回false
- 其他线程调用了当前线程的interrupt 方法中断了当前线程,则当前线程会抛出InterruptedException 异常而返回
- 与当前屏障点关联的Generation 对象的broken 标志被设置true 时,会抛BrokenBarrierException 异常后返回
public int await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException,
BrokenBarrierException,
TimeoutException {
return dowait(true, unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
int dowait(boolean timed, long nanos) 方法
该方法实现了CyclicBarrer 的核心功能,其代码如下:
private int dowait(boolean timed, long nanos)
throws InterruptedException, BrokenBarrierException,
TimeoutException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
final Generation g = generation;
if (g.broken)
throw new BrokenBarrierException();
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
breakBarrier();
throw new InterruptedException();
}
int index = --count;
if (index == 0) { // index==0说明所有线程都到了屏障点,此时执行初始化时传递的任务
boolean ranAction = false;
try {
final Runnable command = barrierCommand;
if (command != null)
command.run(); // 执行任务
ranAction = true;
nextGeneration(); // 激活其他因调用await方法而阻塞的线程,并重置CyclicBarrier
return 0;
} finally {
if (!ranAction)
breakBarrier();
}
}
// loop until tripped, broken, interrupted, or timed out
// index != 0
for (;;) {
try {
if (!timed) // 没有设置超时时间
trip.await();
else if (nanos > 0L) // 设置了超时时间
nanos = trip.awaitNanos(nanos);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
if (g == generation && ! g.broken) {
breakBarrier();
throw ie;
} else {
// We're about to finish waiting even if we had not
// been interrupted, so this interrupt is deemed to
// "belong" to subsequent execution.
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
if (g.broken)
throw new BrokenBarrierException();
if (g != generation)
return index;
if (timed && nanos <= 0L) {
breakBarrier();
throw new TimeoutException();
}
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
private void nextGeneration() {
// signal completion of last generation
trip.signalAll(); // 唤醒条件队列中的阻塞队列
// set up next generation
count = parties; // 重置CyclicBarrier
generation = new Generation();
}
信号量 Semaphore
Semaphore 信号量也是Java 中的一个同步器,与CountDownLatch 和CycleBarrier 不同的是,它内部的计数器是递增的,并且在一开始初始化Semaphore 时可以指定一个初始值,但是并不需要知道需要同步的线程个数,而是在需要同步的地方调用acquire 方法时指定需要同步的线程个数。
使用示例
在主线程中开启两个子线程让它们执行,等所有子线程执行完毕后主线程再继续向下运行。
public class SemaphoreTest {
// 创建信号量示例,参数0 表示当前信号量计数器值为0
private static Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(0);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
executorService.execute(() - > {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " over");
semaphore.release(); // 信号量计数器加1
});
executorService.execute(() - > {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " over");
semaphore.release();
});
// 阻塞直到信号量计数为2
semaphore.acquire(2);
System.out.println("all child thread over");
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
输出结果:
Thread[pool-1-thread-1,5,main] over
Thread[pool-1-thread-2,5,main] over
all child thread over
实现原理
UML
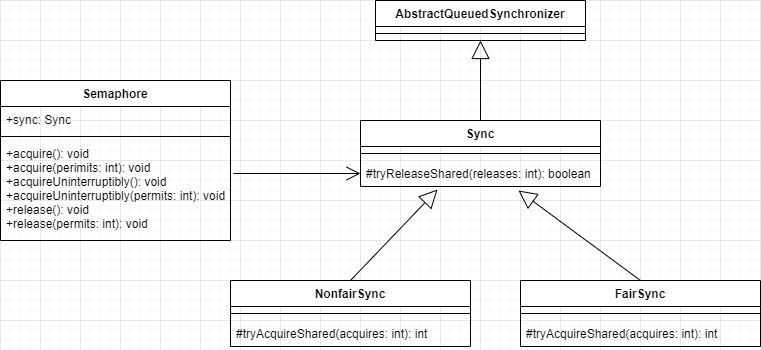
由类图可知,Semaphor 还是使用AQS 实现的。 Sync 只是对AQS 的一个修饰,并且Sync 有两个实现类,用来指定获取信号量时是否采用公平策略。例如,下面的代码在创建Semaphore 时会使用一个变量指定是否使用非公平策略。
public Semaphore(int permits) {
sync = new NonfairSync(permits);
}
public Semaphore(int permits, boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync(permits) : new NonfairSync(permits);
}
Sync(int permits) {
setState(permits);
}
在如上代码中Semaphore 默认采用非公平策略,如果需要使用公平策略则可以使用带两个参数的构造函数来构造Semaphore 对象。另外,如CountDownLatch 构造函数传递的初始化信号量permits 被赋给了AQS state 状态变量一样,这里AQS state 表示当前持有的信号量个数。
void acquire 方法
当前线程调用该方法的目的是希望获取一个信号量资源。 如果当前信号量个数大于0,则信号量的个数会减1,然后该方法直接返回。否则如果当前信号量个数等于0 ,则当前线程会被放入AQS 的阻塞队列。当其他线程调用了当前线程interrupt 方法中断了当前线程时,则当前线程会抛出InterruptedEception 异常返回。
public void acquire() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1); // AQS 内部调用tryAcquireShared
}
// 非公平策略 NonfairSync
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquireShared(acquires);
}
final int nonfairTryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
for (;;) {
int available = getState(); // 当前信号量值
int remaining = available - acquires; // 剩余值
if (remaining < 0 ||
compareAndSetState(available, remaining)) // 如果当前剩余值小于0或者CAS设置成功则返回
return remaining;
}
}
// 公平策略 FairSync
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
for (;;) {
if (hasQueuedPredecessors()) // 公平策略,看当前线程节点的前驱节点是否也在等待获取此资源,如果是则当前线程会被放到AQS阻塞队列,否则直接获取
return -1;
int available = getState();
int remaining = available - acquires;
if (remaining < 0 ||
compareAndSetState(available, remaining))
return remaining;
}
}
void acquire(int permits) 方法
该方法与acquire方法不同,后者只需要获取一个信号量值,而前者则获取permits 个。
public void acquire(int permits) throws InterruptedException {
if (permits < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(permits);
}
void acquireUninterruptibly() 方法
该方法与acquire 方法相似,不同之处在于该方法对中断不响应。
public void acquireUninterruptibly() {
sync.acquireShared(1);
}
void acquireUninterruptibly(int permits) 方法
该方法与acquire(int permits) 方法的不同之处在于该方法对中断不响应。
public void acquireUninterruptibly(int permits) {
if (permits < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
sync.acquireShared(permits);
}
void release() 方法
该方法的作用是把当前Semaphore 信号量值增加1 ,如果当前有线程因为调用aquire 方法被阻塞而被放入了AQS 阻塞队列,则会根据公平策略选择一个信号量个数能被满足的线程进行激活,激活的线程会尝试获取刚增加的信号。
public void release() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) { // 尝试释放资源
doReleaseShared(); // 资源释放后调用park方法唤醒AQS队列中最先挂起的线程
return true;
}
return false;
}
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
for (;;) {
int current = getState(); // 当前信号量值
int next = current + releases; // 当前信号量+1
if (next < current) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum permit count exceeded");
if (compareAndSetState(current, next)) // CAS修改信号量值
return true;
}
}
void release(int permits) 方法
该方法与不带参数的release 方法的不同之处在于,前者每次调用会在原信号量值的基础上增加 permit ,而后者每次增加1 。
public void release(int permits) {
if (permits < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
sync.releaseShared(permits);
}

