【Java基础总结】集合框架

集合和数组的区别
集合只存储对象,长度是可变的;
数组既可以存储基本数据类型,又可以存储对象,但长度是固定的。
1. Collection接口
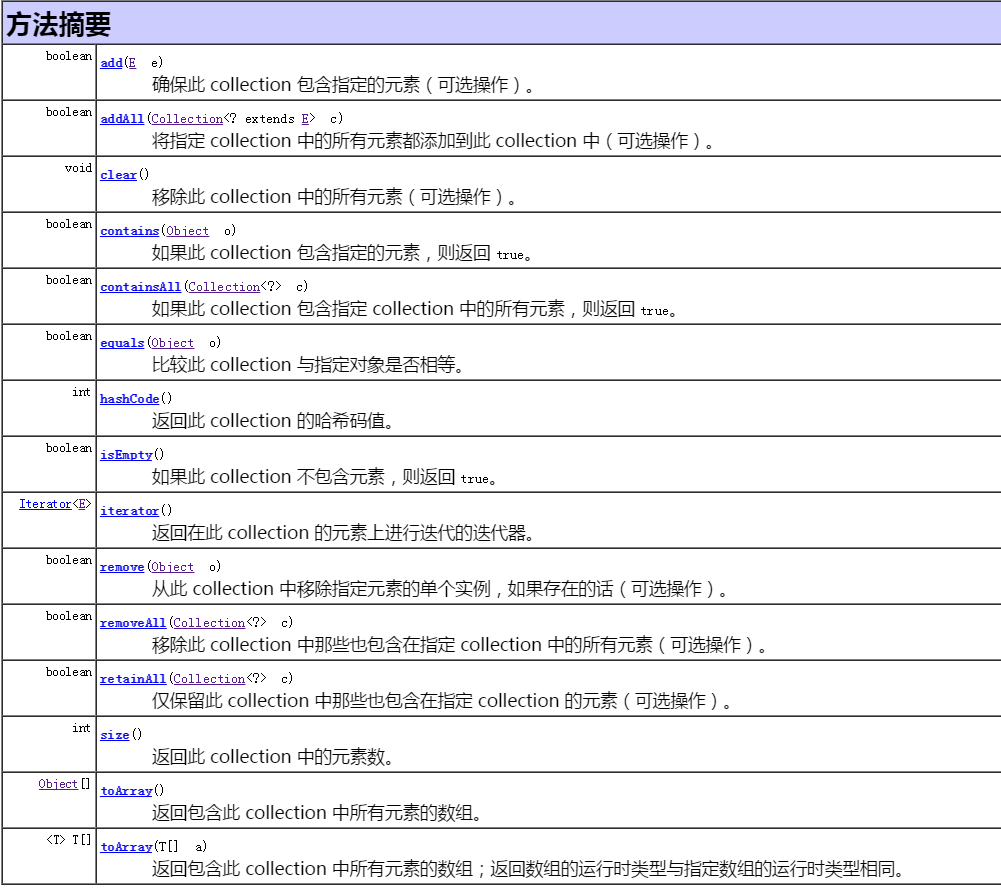
代码演示

1 List<String> c1 = new ArrayList<String>(); 2 //判断集合是否为空 isEmpty() 3 if(c1.isEmpty()){ 4 System.out.println("集合为空"); 5 } 6 7 //添加元素 add(E e) 8 c1.add("北京"); 9 c1.add("河南"); 10 c1.add("山东"); 11 System.out.println(c1); //打印结果:[北京, 河南, 山东] 12 13 //集合大小 size() 14 int size = c1.size(); 15 System.out.println(size); //打印结果:3 16 17 //转为数组,返回结果只能是Object[],无法强转为其他类型数组 toArray() 18 Object[] arr = c1.toArray(); 19 for(Object o : arr){ 20 System.out.print(o); 21 } 22 System.out.println(); 23 24 //转为指定数组 toArray(T[] t) // 25 String[] arr2 = new String[size]; 26 arr2 = c1.toArray(arr2); 27 for(String s : arr2){ 28 System.out.print(s); 29 } 30 System.out.println(); 31 32 List<String> c2 = new ArrayList<String>(); 33 c2.add("香港"); 34 c2.add("澳门"); 35 c2.add("台湾"); 36 37 //向集合中添加指定集合 addAll(Collection<?> c) 38 c1.addAll(c2); 39 System.out.println(c1); //打印结果:[北京, 河南, 山东, 香港, 澳门, 台湾] 40 41 //判断集合中是否包含指定对象 contains(Object o) 42 if(c2.contains("台湾")){ 43 //移除集合中的指定对象 remove(Object o) 44 c2.remove("台湾"); 45 } 46 System.out.println(c2); //打印结果:[香港, 澳门] 47 48 //判断集合是否包含指定集合 containsAll(Collection c) 49 if(c1.containsAll(c2)){ 50 //移除集合中的指定集合 removeAll(Collection c) 51 c1.removeAll(c2); 52 } 53 System.out.println(c1); //打印结果:[北京, 河南, 山东, 台湾] 54 55 c1.addAll(c2); 56 //保留集合中指定的集合元素 retainAll(Collection c) 57 c1.retainAll(c2); 58 System.out.println(c1); //打印结果:[香港, 澳门] 59 60 //遍历的2种方法 61 //第1种 62 Iterator<String> it = c1.iterator(); 63 while(it.hasNext()){ 64 System.out.println(it.next()); 65 } 66 //第2种 67 for(String s : c1){ 68 System.out.println(s); 69 }
2.1 List接口
特点:有序、有索引、可以重复
List接口的独有方法
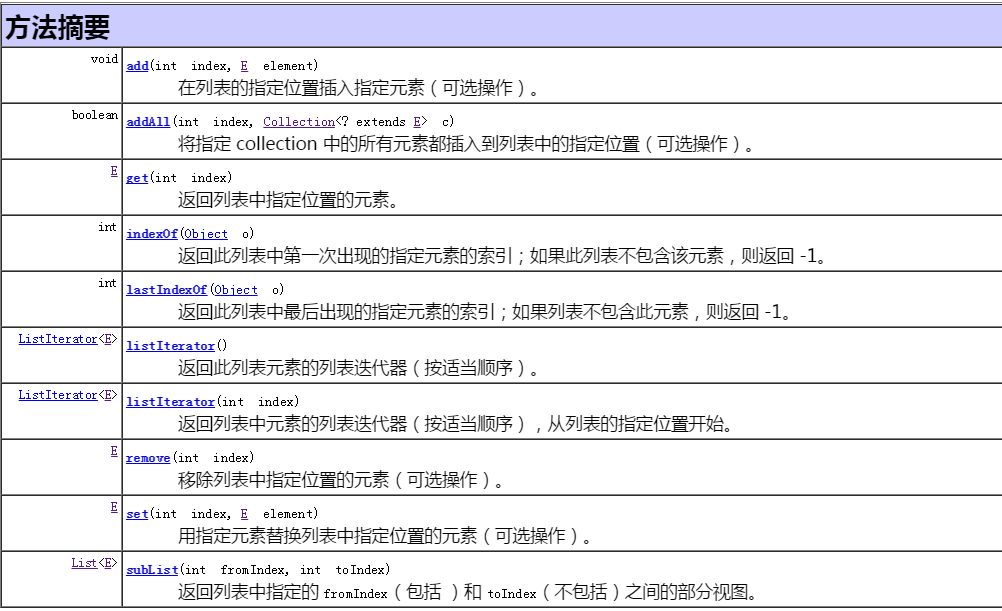
代码演示

1 List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); 2 //add(index, E element) 3 list.add(0, "太阳"); 4 list.add(1, "月亮"); 5 list.add(2, "地球"); 6 7 List<String> list2 = new ArrayList<String>(); 8 list2.add(0, "土星"); 9 list2.add(1, "木星"); 10 //addAll(index, Collection c) 在index位置添加集合 11 list.addAll(2, list2); 12 13 14 //listIterator()遍历 15 ListIterator<String> lit = list.listIterator(); 16 //正向遍历 17 while(lit.hasNext()){ 18 System.out.println(lit.nextIndex() + "." +lit.next()); 19 } 20 //倒序遍历 21 while(lit.hasPrevious()){ 22 System.out.println(lit.previousIndex() + "." +lit.previous()); 23 } 24 25 //listIterator(int index) 部分遍历 26 ListIterator<String> lit2 = list.listIterator(1); 27 while(lit2.hasNext()){ 28 System.out.println(lit2.nextIndex() + "," +lit2.next()); 29 } 30 31 //indexOf(Object o) 查询元素在集合中的首次出现的位置 32 int index = list.indexOf("月亮"); 33 //remove(index) 删除指定位置的元素 34 if(index>=0) list.remove(index); 35 //lastIndexOf(Object o) 查询元素在集合中的最后出现的位置 36 int lastIndex = list.lastIndexOf("月亮"); 37 System.out.println(list); 38 39 //set(index, E e) 修改指定位置的集合元素 40 list.set(2, "火星"); 41 42 int size = list.size(); 43 for(int i=0; i<size; i++){ 44 //get(index) 获取index位置的集合元素 45 System.out.println( i + ":" + list.get(i)); 46 } 47 //subList(fromIndex, endIndex) 获取指定范围的集合元素 48 List<String> listCopy = list.subList(0, size); 49 System.out.println(listCopy);
ArrayList和LinkedList:ArrayList查询快,添加删除慢;LinkedList查询慢,添加删除快
2.2 Set接口
特点:无序,不重复
Set保证元素不重复的方法: e1.hashCode().equals(e2.hashCode()) && e1.equals(e2)
代码演示

1 Set<String> set = new HashSet<String>(); 2 set.add("刘德华"); 3 set.add("周杰伦"); 4 set.add("王菲"); 5 //集合元素无序 6 Iterator<String> it = set.iterator(); 7 while(it.hasNext()){ 8 System.out.println(it.next()); 9 } 10 11 System.out.println(set); 12 set.add("周杰伦"); 13 //集合元素不重复 14 System.out.println(set);
Set接口有2个实现类,HashSet和TreeSet。
其中TreeSet能够对元素进行排序,自定义排序的两种方法:
1. 集合元素继承Comparable接口,使自身具有比较性
2. 继承Comparator接口,创建一个比较器

1 public class CollectionDemo4{ 2 public static void main(String[] args){ 3 Set<Student> set = new TreeSet<Student>(); 4 set.add(new Student("小明", 20)); 5 set.add(new Student("小强", 21)); 6 set.add(new Student("小红", 19)); 7 8 System.out.println(set); 9 10 11 //2. 创建一个比较器 12 Set<Student2> treeSet = new TreeSet<Student2>( 13 new Comparator<Student2>(){ 14 public int compare(Student2 s1, Student2 s2){ 15 return s1.getAge()-s2.getAge(); 16 } 17 } 18 ); 19 treeSet.add(new Student2("xiaoming", 20)); 20 treeSet.add(new Student2("xiaoqiang", 21)); 21 treeSet.add(new Student2("xiaohong", 19)); 22 System.out.println(treeSet); 23 } 24 } 25 //1. 集合元素继承comparable,使自身具有比较性 26 class Student implements Comparable<Student>{ 27 private String name; 28 private int age; 29 Student(String name, int age){ 30 this.name = name; 31 this.age = age; 32 } 33 //该方法在TreeSet底层被调用,用来比较对象的大小从而进行排序。 34 @Override 35 public int compareTo(Student s){ 36 return this.age-s.age; //按age升序排序 37 } 38 39 @Override 40 public String toString(){ 41 return this.name + "-" + this.age; 42 } 43 } 44 45 class Student2 { 46 private String name; 47 private int age; 48 Student2(String name, int age){ 49 this.name = name; 50 this.age = age; 51 } 52 public int getAge(){ 53 return this.age; 54 } 55 @Override 56 public String toString(){ 57 return this.name + "-" + this.age; 58 } 59 }
2. Map接口
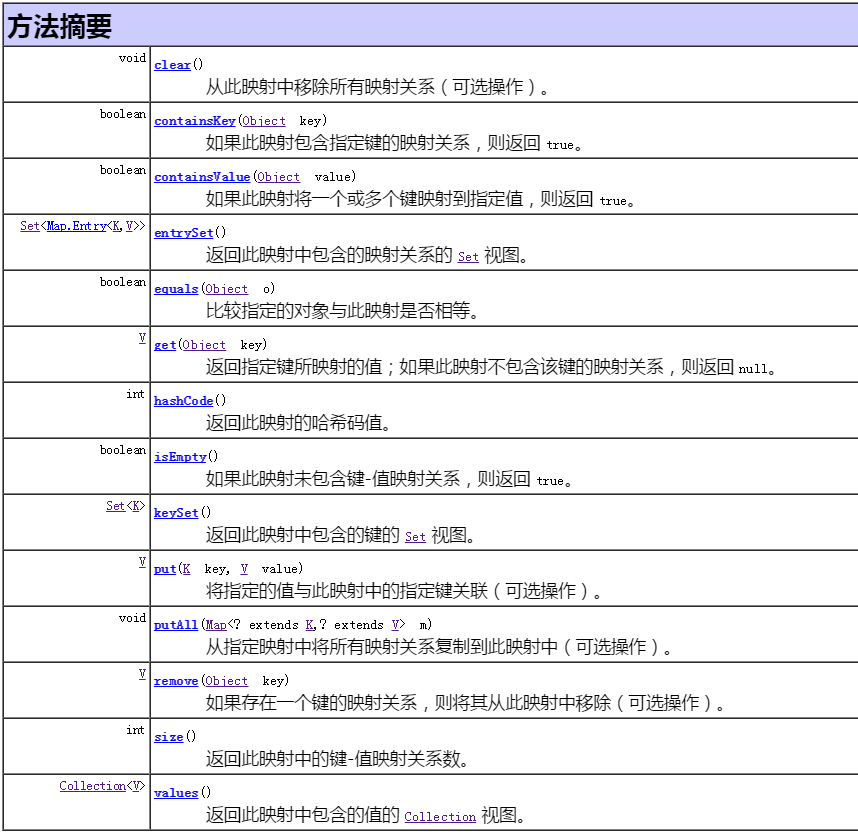
代码演示

1 Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(); 2 //判断是否为空 isEmpty() 3 if(map.isEmpty()){ 4 System.out.println("集合为空!"); 5 } 6 7 //添加键值对 put(k, v) 8 map.put("百度", "www.baidu.com"); 9 10 //获取map的长度 size() 11 int size = map.size(); 12 13 Map<String, String> map2 = new HashMap<String, String>(); 14 map2.put("腾讯", "www.qq.com"); 15 map2.put("阿里巴巴", "www.taobao.com"); 16 //添加map putAll(map) 17 map.putAll(map2); 18 System.out.println(map); 19 20 //判断是否包含key值 containsKey(key) 21 if(map.containsKey("百度")){ 22 System.out.println("百度exist"); 23 } 24 //判断是否包含value值 containsValue(value) 25 if(map.containsValue("www.qq.com")){ 26 System.out.println("www.qq.com exist"); 27 } 28 29 //获取map的全部key值 keySet() 30 Set<String> keySet = map.keySet(); 31 System.out.println(keySet); 32 //获取map的全部value值 values() 33 Collection<String> c = map.values(); 34 System.out.println(c); 35 36 //根据key值获取value值 get(k) 37 String baiduSite = map.get("百度"); 38 System.out.println(baiduSite); 39 40 //遍历1 41 Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entrySet = map.entrySet(); 42 Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> it = entrySet.iterator(); 43 while(it.hasNext()){ 44 Map.Entry<String, String> me = it.next(); 45 String key = me.getKey(); 46 String value = me.getValue(); 47 System.out.println(key + ":" + value); 48 } 49 50 //遍历2 51 for(String k : keySet){ 52 String value = map.get(k); 53 System.out.println(k + "=" + value); 54 }
8. HashMap和TreeMap




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律