Spring Boot学习日志------连接数据库三方法之Springboot yml注入
目录
基础调用操作
不同的配置文件的调用
基础调用操作
目录
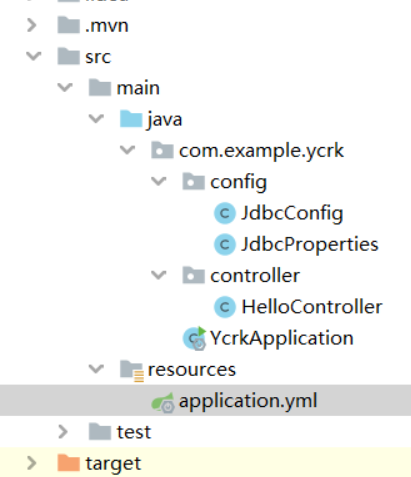
application.yml文件
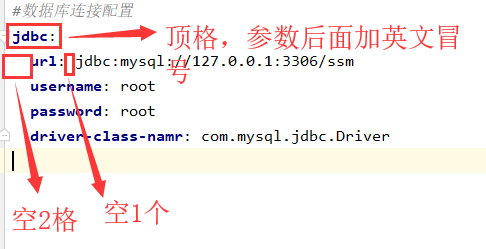
#数据库连接配置 jdbc: url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/ssm username: root password: root driver-class-namr: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
HelloController 文件
package com.example.ycrk.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import javax.sql.DataSource; @RestController public class HelloController { @Autowired private DataSource dataSource; @GetMapping("hello") public String hello(){ System.out.println("dataSource="+dataSource); return "Hello,Spring Boot!"; } }
JdbcProperties文件
package com.example.ycrk.config; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * ConfigurationProperties从application配置文件中读取配置 * prefix配置项前缀 * 配置项前缀的类变量名必须与前缀之后的配置项名称保持 松散绑定 */ @Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix="jdbc") public class JdbcProperties { private String driverClassNamr; private String url; private String username; private String password; public String getDriverClassNamr() { return driverClassNamr; } public void setDriverClassNamr(String driverClassNamr) { this.driverClassNamr = driverClassNamr; } public String getUrl() { return url; } public void setUrl(String url) { this.url = url; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } }
JdbcConfig文件
package com.example.ycrk.config; import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; import javax.sql.DataSource; @Configuration @EnableConfigurationProperties(JdbcProperties.class) public class JdbcConfig { @Bean public DataSource dataSource(JdbcProperties jdbcProperties){ DruidDataSource druidDataSource=new DruidDataSource(); druidDataSource.setDriverClassName(jdbcProperties.getDriverClassNamr()); druidDataSource.setUrl(jdbcProperties.getUrl()); druidDataSource.setUsername(jdbcProperties.getUsername()); druidDataSource.setPassword(jdbcProperties.getPassword()); return druidDataSource; } }
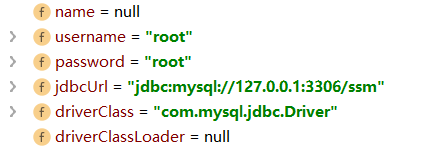
操作结果
不同的配置文件的调用
文件格式:application-XXX.yml
调用在application.yml文件中使用
添加文件application-test.yml
baidu: url: http://www.baidu.com
修改application.yml,在active后面添加参数横线后面的名字
#数据库连接配置 jdbc: url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/ssm username: root password: root driver-class-namr: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver spring: profiles: active: test
输出,修改HelloController.java
package com.example.ycrk.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import javax.sql.DataSource; @RestController public class HelloController { @Autowired private DataSource dataSource; @Value("${baidu.url}") private String baidu; @GetMapping("hello") public String hello(){ System.out.println("baidu="+baidu); System.out.println("dataSource="+dataSource); return "Hello,Spring Boot!"; } }
文件目录



